Simulating WFI Imaging Data with Roman I-Sim#
Nexus Server Information#
IMPORTANT: Running the parallelized examples in the advanced use cases section will require a “Medium” or larger server.
Kernel Information and Read-Only Status#
To run this notebook, please select the “Roman Calibration” kernel at the top right of your window.
This notebook is read-only. You can run cells and make edits, but you must save changes to a different location. We recommend saving the notebook within your home directory, or to a new folder within your home (e.g. file > save notebook as > my-nbs/nb.ipynb). Note that a directory must exist before you attempt to add a notebook to it.
Reference Data#
The cell below will check to ensure ancillary reference files for the stpsf package are installed. If not, it will download the ancillary reference files and install them under your home directory (i.e., ${HOME}/refdata/).
Local Run Settings#
If you want to run the notebook in your local machine, refer to the information in the local installation instructions before proceeding with the notebook. The instructions provide inportant information about setting up your environment, installing dependnecies, and adding to your working directory scripts to help with the reference data installation.
Depending on which (if any) reference data are missing, this cell may take several minutes to execute.
On the Roman Research Nexus#
If you are working on the Nexus, then the ancillary reference data are pre-installed and this cell will execute instantly.
import os
import sys
import importlib.util
import notebook_data_dependencies as ndd
# Download reference data (if necessary)
result = ndd.install_files(packages=['stpsf'])
ndd.setup_env(result)
Found stpsf path /home/runner/refdata/stpsf-data
Reference data paths set to:
STPSF_PATH = /home/runner/refdata/stpsf-data
Imports#
Libraries used
argparse for formatting input options in romanisim
asdf for opening Roman WFI ASDF files
astroquery.gaia for querying the Gaia catalog
astropy.coordinates for storing celestial coordinates as Python objects
astropy.time for storing time information as Python objects
astropy.table for working with Astropy Table objects
astropy.units for handling and combining units
astropy.visualization for image normalization
copy for making copies of Python objects
galsim for image simulations
importlib for reloading Python modules
matplotlib for displaying images
numpy for array operations
os for file operations
romanisim for image simulations
roman_datamodels for opening Roman WFI ASDF files
s3fs for accessing files in an S3 bucket
In the Advanced Use Cases section further below, we include some additional imports:
pysiaf for determining dither positions
dataclasses for creating a class
typing for doing type checking on inputs
dask for parallelization
Note: dask is not installed in the Roman Calibration kernel by default. In the Advanced Use Cases - Parallelized Simulations section, the code cells have been commented out and there is a cell at the beginning of the section that will use pip to install the required packages.
import argparse
import asdf
from astroquery.gaia import Gaia
from astropy.coordinates import SkyCoord
from astropy.time import Time
from astropy.table import Table, vstack
from astropy import units as u
from astropy.visualization import simple_norm
import copy
import galsim
import importlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import os
import roman_datamodels as rdm
from romanisim import gaia, bandpass, catalog, log, wcs, persistence, parameters, ris_make_utils as ris
from romanisim.image import inject_sources_into_l2
import s3fs
Introduction#
The purpose of this notebook is to show how to generate simulated Level 1 (L1; uncalibrated ramp cubes) and Level 2 (L2; calibrated rate images) Roman Wide Field Instrument (WFI) Advanced Scientific Data Format (ASDF) files with Roman I-Sim (package name romanisim). Details about the Roman data levels can be found in the Data Levels and Products article in the Roman Documentation System (RDox). Briefly, a L1 file contains a single uncalibrated ramp exposure in units of Data Numbers (DN). L1 files are three-dimensional data cubes, one dimension for time and two dimensions for image coordinates, that are shaped as arrays with (N resultants, 4096 image rows, 4096 image columns). A resultant is a sample up-the-ramp, and represents either a single read of the WFI detectors or multiple reads that have been combined. The L2 WFI data are calibrated images in instrumental units of DN / second. They are two-dimensional arrays shaped as (4088 image rows, 4088 image columns).
Tutorial Data#
In this tutorial, we will create necessary data in memory or retrieve it from a catalog service. A catalog file is also available in the RRN S3 bucket, and can be streamed into memory using astropy.table.Table and the s3fs package instructions in the Data Discovery and Access tutorial. Also see the RRN documentation for more information on the catalog available in the S3 bucket.
Source Catalog Generation#
The romanisim package offers two options for generating source catalogs:
Retrieve the source catalog from Gaia; or
Parametrically generate a catalog of stars and/or galaxies.
First, let’s explore how to create a romanisim-compatible source catalog using Gaia. We will use a combination of astroquery and romanisim to query the Gaia catalog and then write the file in a format compatible with romanisim.
In the example below, we query the Gaia DR3 catalog for sources centered at (RA, Dec) = (270.94, -0.2) degrees within a radius of 1 degree.
Note: The Gaia query may take several minutes to complete.
ra = 270.94 # Right ascension in degrees
dec = -0.2 # Declination in degrees
radius = 1 # Search radius in degrees
query = f'SELECT * FROM gaiadr3.gaia_source WHERE distance({ra}, {dec}, ra, dec) < {radius}'
job = Gaia.launch_job_async(query)
print(job)
result = job.get_results()
2025-12-11 19:47:39 INFO Query finished.
INFO: Query finished. [astroquery.utils.tap.core]
<Table length=389468>
name dtype unit description n_bad
------------------------------- ------- ------------- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------
solution_id int64 Solution Identifier 0
designation object Unique source designation (unique across all Data Releases) 0
source_id int64 Unique source identifier (unique within a particular Data Release) 0
random_index int64 Random index for use when selecting subsets 0
ref_epoch float64 yr Reference epoch 0
ra float64 deg Right ascension 0
ra_error float32 mas Standard error of right ascension 0
dec float64 deg Declination 0
dec_error float32 mas Standard error of declination 0
parallax float64 mas Parallax 53139
parallax_error float32 mas Standard error of parallax 53139
parallax_over_error float32 Parallax divided by its standard error 53139
pm float32 mas / yr Total proper motion 53139
pmra float64 mas / yr Proper motion in right ascension direction 53139
pmra_error float32 mas / yr Standard error of proper motion in right ascension direction 53139
pmdec float64 mas / yr Proper motion in declination direction 53139
pmdec_error float32 mas / yr Standard error of proper motion in declination direction 53139
ra_dec_corr float32 Correlation between right ascension and declination 0
ra_parallax_corr float32 Correlation between right ascension and parallax 53139
ra_pmra_corr float32 Correlation between right ascension and proper motion in right ascension 53139
ra_pmdec_corr float32 Correlation between right ascension and proper motion in declination 53139
dec_parallax_corr float32 Correlation between declination and parallax 53139
dec_pmra_corr float32 Correlation between declination and proper motion in right ascension 53139
dec_pmdec_corr float32 Correlation between declination and proper motion in declination 53139
parallax_pmra_corr float32 Correlation between parallax and proper motion in right ascension 53139
parallax_pmdec_corr float32 Correlation between parallax and proper motion in declination 53139
pmra_pmdec_corr float32 Correlation between proper motion in right ascension and proper motion in declination 53139
astrometric_n_obs_al int16 Total number of observations in the along-scan (AL) direction 0
astrometric_n_obs_ac int16 Total number of observations in the across-scan (AC) direction 0
astrometric_n_good_obs_al int16 Number of good observations in the along-scan (AL) direction 0
astrometric_n_bad_obs_al int16 Number of bad observations in the along-scan (AL) direction 0
astrometric_gof_al float32 Goodness of fit statistic of model wrt along-scan observations 0
astrometric_chi2_al float32 AL chi-square value 0
astrometric_excess_noise float32 mas Excess noise of the source 0
astrometric_excess_noise_sig float32 Significance of excess noise 0
astrometric_params_solved int16 Which parameters have been solved for? 0
astrometric_primary_flag bool Primary or seconday 0
nu_eff_used_in_astrometry float32 1 / um Effective wavenumber of the source used in the astrometric solution 237998
pseudocolour float32 1 / um Astrometrically estimated pseudocolour of the source 204609
pseudocolour_error float32 1 / um Standard error of the pseudocolour of the source 204609
ra_pseudocolour_corr float32 Correlation between right ascension and pseudocolour 204609
dec_pseudocolour_corr float32 Correlation between declination and pseudocolour 204609
parallax_pseudocolour_corr float32 Correlation between parallax and pseudocolour 204609
pmra_pseudocolour_corr float32 Correlation between proper motion in right asension and pseudocolour 204609
pmdec_pseudocolour_corr float32 Correlation between proper motion in declination and pseudocolour 204609
astrometric_matched_transits int16 Matched FOV transits used in the AGIS solution 0
visibility_periods_used int16 Number of visibility periods used in Astrometric solution 0
astrometric_sigma5d_max float32 mas The longest semi-major axis of the 5-d error ellipsoid 0
matched_transits int16 The number of transits matched to this source 0
new_matched_transits int16 The number of transits newly incorporated into an existing source in the current cycle 0
matched_transits_removed int16 The number of transits removed from an existing source in the current cycle 0
ipd_gof_harmonic_amplitude float32 Amplitude of the IPD GoF versus position angle of scan 0
ipd_gof_harmonic_phase float32 deg Phase of the IPD GoF versus position angle of scan 0
ipd_frac_multi_peak int16 Percent of successful-IPD windows with more than one peak 0
ipd_frac_odd_win int16 Percent of transits with truncated windows or multiple gate 0
ruwe float32 Renormalised unit weight error 53139
scan_direction_strength_k1 float32 Degree of concentration of scan directions across the source 5602
scan_direction_strength_k2 float32 Degree of concentration of scan directions across the source 5602
scan_direction_strength_k3 float32 Degree of concentration of scan directions across the source 5602
scan_direction_strength_k4 float32 Degree of concentration of scan directions across the source 5602
scan_direction_mean_k1 float32 deg Mean position angle of scan directions across the source 5602
scan_direction_mean_k2 float32 deg Mean position angle of scan directions across the source 5602
scan_direction_mean_k3 float32 deg Mean position angle of scan directions across the source 5602
scan_direction_mean_k4 float32 deg Mean position angle of scan directions across the source 5602
duplicated_source bool Source with multiple source identifiers 0
phot_g_n_obs int16 Number of observations contributing to G photometry 0
phot_g_mean_flux float64 electron / s G-band mean flux 630
phot_g_mean_flux_error float32 electron / s Error on G-band mean flux 630
phot_g_mean_flux_over_error float32 G-band mean flux divided by its error 630
phot_g_mean_mag float32 mag G-band mean magnitude 630
phot_bp_n_obs int16 Number of observations contributing to BP photometry 0
phot_bp_mean_flux float64 electron / s Integrated BP mean flux 24166
phot_bp_mean_flux_error float32 electron / s Error on the integrated BP mean flux 24166
phot_bp_mean_flux_over_error float32 Integrated BP mean flux divided by its error 24166
phot_bp_mean_mag float32 mag Integrated BP mean magnitude 24166
phot_rp_n_obs int16 Number of observations contributing to RP photometry 0
phot_rp_mean_flux float64 electron / s Integrated RP mean flux 22318
phot_rp_mean_flux_error float32 electron / s Error on the integrated RP mean flux 22318
phot_rp_mean_flux_over_error float32 Integrated RP mean flux divided by its error 22318
phot_rp_mean_mag float32 mag Integrated RP mean magnitude 22318
phot_bp_rp_excess_factor float32 BP/RP excess factor 24285
phot_bp_n_contaminated_transits int16 Number of BP contaminated transits 24166
phot_bp_n_blended_transits int16 Number of BP blended transits 24166
phot_rp_n_contaminated_transits int16 Number of RP contaminated transits 22318
phot_rp_n_blended_transits int16 Number of RP blended transits 22318
phot_proc_mode int16 Photometry processing mode 153
bp_rp float32 mag BP - RP colour 24285
bp_g float32 mag BP - G colour 24167
g_rp float32 mag G - RP colour 22794
radial_velocity float32 km / s Radial velocity 383852
radial_velocity_error float32 km / s Radial velocity error 383852
rv_method_used int16 Method used to obtain the radial velocity 383852
rv_nb_transits int16 Number of transits used to compute the radial velocity 383852
rv_nb_deblended_transits int16 Number of valid transits that have undergone deblending 383852
rv_visibility_periods_used int16 Number of visibility periods used to estimate the radial velocity 383852
rv_expected_sig_to_noise float32 Expected signal to noise ratio in the combination of the spectra used to obtain the radial velocity 383852
rv_renormalised_gof float32 Radial velocity renormalised goodness of fit 388325
rv_chisq_pvalue float32 P-value for constancy based on a chi-squared criterion 388324
rv_time_duration float32 d Time coverage of the radial velocity time series 383852
rv_amplitude_robust float32 km / s Total amplitude in the radial velocity time series after outlier removal 388324
rv_template_teff float32 K Teff of the template used to compute the radial velocity 383852
rv_template_logg float32 log(cm.s**-2) Logg of the template used to compute the radial velocity 383852
rv_template_fe_h float32 dex [Fe/H] of the template used to compute the radial velocityy 383852
rv_atm_param_origin int16 Origin of the atmospheric parameters associated to the template 383852
vbroad float32 km / s Spectral line broadening parameter 388785
vbroad_error float32 km / s Uncertainty on the spectral line broadening 388785
vbroad_nb_transits int16 Number of transits used to compute vbroad 388785
grvs_mag float32 mag Integrated Grvs magnitude 383964
grvs_mag_error float32 mag Grvs magnitude uncertainty 383964
grvs_mag_nb_transits int16 Number of transits used to compute Grvs 383964
rvs_spec_sig_to_noise float32 Signal to noise ratio in the mean RVS spectrum 389417
phot_variable_flag object Photometric variability flag 0
l float64 deg Galactic longitude 0
b float64 deg Galactic latitude 0
ecl_lon float64 deg Ecliptic longitude 0
ecl_lat float64 deg Ecliptic latitude 0
in_qso_candidates bool Flag indicating the availability of additional information in the QSO candidates table 0
in_galaxy_candidates bool Flag indicating the availability of additional information in the galaxy candidates table 0
non_single_star int16 Flag indicating the availability of additional information in the various Non-Single Star tables 0
has_xp_continuous bool Flag indicating the availability of mean BP/RP spectrum in continuous representation for this source 0
has_xp_sampled bool Flag indicating the availability of mean BP/RP spectrum in sampled form for this source 0
has_rvs bool Flag indicating the availability of mean RVS spectrum for this source 0
has_epoch_photometry bool Flag indicating the availability of epoch photometry for this source 0
has_epoch_rv bool Flag indicating the availability of epoch radial velocity for this source 0
has_mcmc_gspphot bool Flag indicating the availability of GSP-Phot MCMC samples for this source 0
has_mcmc_msc bool Flag indicating the availability of MSC MCMC samples for this source 0
in_andromeda_survey bool Flag indicating that the source is present in the Gaia Andromeda Photometric Survey (GAPS) 0
classprob_dsc_combmod_quasar float32 Probability from DSC-Combmod of being a quasar (data used: BP/RP spectrum, photometry, astrometry) 18878
classprob_dsc_combmod_galaxy float32 Probability from DSC-Combmod of being a galaxy (data used: BP/RP spectrum, photometry, astrometry) 18878
classprob_dsc_combmod_star float32 Probability from DSC-Combmod of being a single star (but not a white dwarf) (data used: BP/RP spectrum, photometry, astrometry) 18878
teff_gspphot float32 K Effective temperature from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
teff_gspphot_lower float32 K Lower confidence level (16%) of effective temperature from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
teff_gspphot_upper float32 K Upper confidence level (84%) of effective temperature from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
logg_gspphot float32 log(cm.s**-2) Surface gravity from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
logg_gspphot_lower float32 log(cm.s**-2) Lower confidence level (16%) of surface gravity from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
logg_gspphot_upper float32 log(cm.s**-2) Upper confidence level (84%) of surface gravity from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
mh_gspphot float32 dex Iron abundance from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
mh_gspphot_lower float32 dex Lower confidence level (16%) of iron abundance from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
mh_gspphot_upper float32 dex Upper confidence level (84%) of iron abundance from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
distance_gspphot float32 pc Distance from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
distance_gspphot_lower float32 pc Lower confidence level (16%) of distance from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
distance_gspphot_upper float32 pc Upper confidence level (84%) of distance from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
azero_gspphot float32 mag Monochromatic extinction $A_0$ at 547.7nm from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
azero_gspphot_lower float32 mag Lower confidence level (16%) of monochromatic extinction $A_0$ at 547.7nm from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
azero_gspphot_upper float32 mag Upper confidence level (84%) of monochromatic extinction $A_0$ at 547.7nm from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
ag_gspphot float32 mag Extinction in G band from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
ag_gspphot_lower float32 mag Lower confidence level (16%) of extinction in G band from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
ag_gspphot_upper float32 mag Upper confidence level (84%) of extinction in G band from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
ebpminrp_gspphot float32 mag Reddening $E(G_{\rm BP} - G_{\rm RP})$ from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
ebpminrp_gspphot_lower float32 mag Lower confidence level (16%) of reddening $E(G_{\rm BP} - G_{\rm RP})$ from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
ebpminrp_gspphot_upper float32 mag Upper confidence level (84%) of reddening $E(G_{\rm BP} - G_{\rm RP})$ from GSP-Phot Aeneas best library using BP/RP spectra 288418
libname_gspphot object Name of library that achieves the highest mean log-posterior in MCMC samples and was used to derive GSP-Phot parameters in this table 0
Jobid: 82c0ac99-d6c9-11f0-9f4e-bc97e148b76b-O
Phase: COMPLETED
Owner: None
Output file: async_20251211194222.vot
Results: None
Once we have the result from the Gaia query, we can transform it into a format compatible with Roman I-Sim:
# Filter the Gaia results for stars and exclude bright stars
result = result[result['classprob_dsc_combmod_star'] >= 0.7]
result = result[result['phot_g_mean_mag'] > 16.5]
# Set the observation time
obs_time = '2026-10-31T00:00:00'
# Make the Roman I-Sim formatted catalog
gaia_catalog = gaia.gaia2romanisimcat(result, Time(obs_time), fluxfields=set(bandpass.galsim2roman_bandpass.values()))
We have excluded very bright stars (Gaia g-band > 16.5 mag in this example) because Roman I-Sim uses a maximum size of the simulated point spread function (PSF) in pixels that can result in the appearance of box-shaped boundaries around bright sources. This will be fixed in a future update.
When using a real catalog like Gaia, it is essential to remove any entries with missing information. This can be achieved with the code in the cell below:
# Reject anything with missing fluxes or positions
names = [f for f in gaia_catalog.dtype.names if f[0] == 'F']
names += ['ra', 'dec']
bad = np.zeros(len(gaia_catalog), dtype='bool')
for b in names:
bad = ~np.isfinite(gaia_catalog[b])
if hasattr(gaia_catalog[b], 'mask'):
bad |= gaia_catalog[b].mask
gaia_catalog = gaia_catalog[~bad]
Now that we have a catalog, let’s take a look at it. The catalog in memory is an astropy.table.Table object with over 1e5 rows:
gaia_catalog
| ra | dec | type | n | half_light_radius | pa | ba | F087 | F158 | F146 | F129 | F213 | F184 | F106 | F062 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| float64 | float64 | str3 | int64 | int64 | int64 | int64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 |
| 271.19129613484586 | -1.1677613835078477 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 7.6987404386869e-09 | 7.6987404386869e-09 | 7.6987404386869e-09 | 7.6987404386869e-09 | 7.6987404386869e-09 | 7.6987404386869e-09 | 7.6987404386869e-09 | 7.6987404386869e-09 |
| 271.09450738004523 | -1.185891080497458 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 8.720800176983999e-09 | 8.720800176983999e-09 | 8.720800176983999e-09 | 8.720800176983999e-09 | 8.720800176983999e-09 | 8.720800176983999e-09 | 8.720800176983999e-09 | 8.720800176983999e-09 |
| 271.1067045607792 | -1.1705607386426884 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 3.9809668017158344e-08 | 3.9809668017158344e-08 | 3.9809668017158344e-08 | 3.9809668017158344e-08 | 3.9809668017158344e-08 | 3.9809668017158344e-08 | 3.9809668017158344e-08 | 3.9809668017158344e-08 |
| 271.0875037421011 | -1.1810658578077189 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 8.414217479850343e-09 | 8.414217479850343e-09 | 8.414217479850343e-09 | 8.414217479850343e-09 | 8.414217479850343e-09 | 8.414217479850343e-09 | 8.414217479850343e-09 | 8.414217479850343e-09 |
| 271.0952940937574 | -1.1764766665382813 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 2.951290105766723e-08 | 2.951290105766723e-08 | 2.951290105766723e-08 | 2.951290105766723e-08 | 2.951290105766723e-08 | 2.951290105766723e-08 | 2.951290105766723e-08 | 2.951290105766723e-08 |
| 271.0958091400958 | -1.17217366554771 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 3.644473751435503e-08 | 3.644473751435503e-08 | 3.644473751435503e-08 | 3.644473751435503e-08 | 3.644473751435503e-08 | 3.644473751435503e-08 | 3.644473751435503e-08 | 3.644473751435503e-08 |
| 271.0929744751323 | -1.1685017594340839 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 5.529973924709251e-08 | 5.529973924709251e-08 | 5.529973924709251e-08 | 5.529973924709251e-08 | 5.529973924709251e-08 | 5.529973924709251e-08 | 5.529973924709251e-08 | 5.529973924709251e-08 |
| 271.0983758256309 | -1.161585594182199 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1.2025314283427287e-08 | 1.2025314283427287e-08 | 1.2025314283427287e-08 | 1.2025314283427287e-08 | 1.2025314283427287e-08 | 1.2025314283427287e-08 | 1.2025314283427287e-08 | 1.2025314283427287e-08 |
| 271.1471396728475 | -1.1617762687469662 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 8.546476629428577e-09 | 8.546476629428577e-09 | 8.546476629428577e-09 | 8.546476629428577e-09 | 8.546476629428577e-09 | 8.546476629428577e-09 | 8.546476629428577e-09 | 8.546476629428577e-09 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 270.85769202755245 | 0.773636140913735 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 |
| 270.8678714354956 | 0.7813771659605562 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 |
| 270.8810884457293 | 0.7918143514923536 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 |
| 270.92454702622655 | 0.7993537136787594 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 |
| 270.83084247667165 | 0.788319808618689 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 |
| 270.8567519994558 | 0.7790670197665834 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 |
| 270.8586204015057 | 0.7708144043522202 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 |
| 270.8727696686416 | 0.7881045599926982 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 |
| 270.85350681512693 | 0.789461511245047 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 |
| 270.9061584399961 | 0.7992513585093951 | PSF | -1 | -1 | -1 | -1 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 |
Alternatively, we can generate a completely synthetic catalog of stars and galaxies using tools in Roman I-Sim (see parameters in the cell below). In this tutorial, we will simulate a galaxy catalog and merge it with the Gaia star catalog. This approach addresses the limitation of Gaia’s catalog, which includes only relatively bright sources, by adding galaxies. At the same time, real Gaia point sources are necessary for the Roman calibration pipeline to match images to Gaia astrometry.
Note that we can additionally simulate a star catalog if desired. This may be useful for including stars fainter than the Gaia magnitude limit, or when the Gaia astrometric step in RomanCal is not required.
Note that in the cell below, we have commented out the last line, which would save the catalog to disk as an Enhanced Character-Separated Values (ECSV) file. We do not need the catalog to be saved on disk for this tutorial, but you may optionally uncomment the line to save the file if you wish. The same file is available in the S3 bucket for any other tutorials that may need it. Having a saved version of the catalog removes the need to re-run the Gaia query above if you need to start over, but you will need to add code to read the catalog file below.
# Galaxy catalog parameters
ra = 270.94 # Right ascension of the catalog center in degrees
dec = -0.2 # Declination of the catalog center in degrees
radius = 1.0 # Radius of the catalog in degrees
n_gal = 30_000 # Number of galaxies
faint_mag = 22 # Faint magnitude limit of simulated sources
hlight_radius = 0.3 # Half-light radius at the faint magnitude limit in units of arcseconds
optical_element = 'F062 F087 F106 F129 F146 F158 F184 F213'.split() # List of optical elements to simulate
seed = 4642 # Random number seed for reproducibility
# Create galaxy catalog
galaxy_cat = catalog.make_galaxies(SkyCoord(ra, dec, unit='deg'), n_gal, radius=radius, index=0.4, faintmag=faint_mag,
hlr_at_faintmag=hlight_radius, bandpasses=optical_element, rng=None, seed=seed)
# Merge the galaxy and Gaia catalogs
full_catalog = vstack([galaxy_cat, gaia_catalog])
#full_catalog.write('full_catalog.ecsv', format='ascii.ecsv', overwrite=True)
The following cell is commented out, but if uncommented will create a simulated star catalog.
#n_star = 30_000 # Number of stars
#star_cat = catalog.make_stars(SkyCoord(ra, dec, unit='deg'), n_star, radius=radius, index=5/3., faintmag=faint_mag,
# truncation_radius=None, bandpasses=optical_element, rng=None, seed=seed)
As before, we have commented out the line that will write this to disk, and instead have kept it in memory. Below, let’s print out the catalog and take a look:
full_catalog
| ra | dec | type | n | half_light_radius | pa | ba | F062 | F087 | F106 | F129 | F146 | F158 | F184 | F213 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| float64 | float64 | str3 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 |
| 271.6295510520961 | -0.03965028067096237 | SER | 3.516215236599453 | 0.8056893348693848 | 252.7303924560547 | 0.7235707640647888 | 3.6905281053378758e-09 | 1.1479291295302119e-08 | 1.2472877841673835e-08 | 6.86679868522333e-09 | 1.4913801305027619e-09 | 1.0117606308313043e-08 | 4.943988773931096e-09 | 2.402744225804554e-09 |
| 270.7539155586658 | -1.175434326974954 | SER | 1.0399398592419549 | 0.946480393409729 | 336.08306884765625 | 0.4800519347190857 | 3.1115434673267828e-09 | 5.331648900153141e-09 | 9.049362148516593e-09 | 6.6658691899590394e-09 | 2.0099595321454444e-09 | 1.5802696040623232e-08 | 1.0280717610555712e-08 | 1.096286439405958e-08 |
| 270.8648924331985 | 0.5861049874846664 | SER | 2.8206730415136585 | 1.3277175426483154 | 73.26484680175781 | 0.6938181519508362 | 1.3153379718744418e-08 | 6.075517422488019e-09 | 3.1850986292880634e-09 | 7.20732051817663e-09 | 6.512435035688213e-09 | 6.66888944067523e-09 | 4.776757656088648e-09 | 6.596417634341378e-09 |
| 270.70544440611565 | -0.1905627389524337 | SER | 1.2080757918109357 | 0.573934018611908 | 273.72601318359375 | 0.5772462487220764 | 3.2391787030405794e-09 | 1.9316861443741118e-09 | 3.5669256437387276e-09 | 1.699146068290247e-08 | 9.461913919039944e-09 | 7.503919152718197e-10 | 4.7414845383286774e-09 | 5.4636619672976394e-09 |
| 271.0763272819082 | 0.28776831750222365 | SER | 2.7301807784747587 | 5.05323600769043 | 236.8221435546875 | 0.907397985458374 | 7.582467986821939e-08 | 7.082852704343168e-08 | 3.547680762494565e-07 | 2.0032227610045084e-07 | 2.793574651605013e-07 | 2.3345998556578706e-07 | 3.1447200399270514e-07 | 1.8613071972595208e-07 |
| 271.1748280956513 | 0.707003102302135 | SER | 3.1848109641065934 | 0.10060989856719971 | 126.41947937011719 | 0.7899426817893982 | 1.5315970713913885e-09 | 8.170578102983939e-10 | 1.1321914517026244e-09 | 5.698110872032203e-09 | 3.009007709664502e-09 | 2.8135679897012267e-10 | 2.320242442621634e-09 | 2.7085311771202214e-09 |
| 270.2732744737068 | -0.5242855117710061 | SER | 2.170910622844513 | 0.7404346466064453 | 333.9393005371094 | 0.5321943163871765 | 4.550629206789836e-09 | 6.8587584500789944e-09 | 3.520021607528179e-08 | 6.720015477412744e-08 | 1.7618161507471086e-07 | 5.838797179080757e-08 | 3.523029690200019e-08 | 2.141273469646876e-08 |
| 271.4612060810417 | 0.48981218301356017 | SER | 3.9307805517506704 | 0.30752477049827576 | 114.4226303100586 | 0.26505595445632935 | 6.278863207143104e-09 | 6.867115764919163e-10 | 1.5396568464609572e-09 | 1.934612026133209e-09 | 4.098307027078363e-09 | 1.5311047985022697e-09 | 4.907185768843192e-09 | 1.902641377782288e-09 |
| 270.5213999343187 | 0.3768383558530194 | SER | 1.1385050100070848 | 0.8638880848884583 | 180.25221252441406 | 0.6406149864196777 | 2.1948302730834257e-07 | 1.7533350771259393e-08 | 2.676470600704306e-08 | 6.562089538419968e-08 | 2.8127658424637048e-08 | 1.7247877792669897e-08 | 1.6523750900887535e-07 | 2.2672709931725876e-08 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 270.85769202755245 | 0.773636140913735 | PSF | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 | 8.986796115574053e-08 |
| 270.8678714354956 | 0.7813771659605562 | PSF | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 | 2.9739923273900245e-08 |
| 270.8810884457293 | 0.7918143514923536 | PSF | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 | 1.0099146401647886e-08 |
| 270.92454702622655 | 0.7993537136787594 | PSF | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 | 6.088817097858871e-08 |
| 270.83084247667165 | 0.788319808618689 | PSF | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 | 2.9773849683440578e-08 |
| 270.8567519994558 | 0.7790670197665834 | PSF | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 | 1.2046944861879528e-08 |
| 270.8586204015057 | 0.7708144043522202 | PSF | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 | 6.308154822102114e-09 |
| 270.8727696686416 | 0.7881045599926982 | PSF | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 | 7.121531420844011e-09 |
| 270.85350681512693 | 0.789461511245047 | PSF | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 | 3.9139177455632116e-08 |
| 270.9061584399961 | 0.7992513585093951 | PSF | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -1.0 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 | 1.1693905898571949e-07 |
We can see galaxies at the top of the stacked catalog (notice type == “SER” for Sersic and values of n (the Sersic index) are not -1, while stars have type == PSF).
Image Simulation#
Here we show how to run the actual simulation using Roman I-Sim. The method for running the simulation for both L1 and L2 data is the same, so we will show an example for L2, and give instructions of how to modify this for L1.
In our example, we are simulating only a single image, so we have set the persistance to the default. Future updates may include how to simulate persistance from multiple exposures.
Notes:
Roman I-Sim allows the user to either use reference files from CRDS or to use no reference files. The latter is not recommended.
Each detector is simulated separately. Below, in the Advanced Use Cases - Parallelized Simulations section, we include instructions on how to parallelize the simulations using Dask.
Currently, the simulator does not include the effect of 1/f noise.
Multi-accumulation (MA) tables control the total exposure time and sampling up-the-ramp. For more information, see the MA table article in the Roman APT Users Guide.
In this case, we will create an observation using the detector WFI01 and the F106 optical element. The observation is simulated to occur at UTC time 2026-10-31T00:00:00 and an exposure time of approximately 60 seconds.
Note: It will take several minutes to download the appropriate calibration reference files the first time this cell is run. Any changes to the settings below may require downloading additional files, which could increase the run time.
obs_date = '2026-10-31T00:00:00' # Datetime of the simulated exposure
sca = 1 # Change this number to simulate different WFI detectors 1 - 18
optical_element = 'F106' # Optical element to simulate
ma_table_number = 3 # Multi-accumulation (MA) table number (see RDox for more information)
seed = 7 # Galsim random number generator seed for reproducibility
level = 2 # WFI data level to simulate...1 or 2
cal_level = 'cal' if level == 2 else 'uncal' # File name extension for data calibration level
filename = f'r0003201001001001004_0001_wfi{sca:02d}_{optical_element.lower()}_{cal_level}.asdf' # Output file name on disk. Only change the first part up to _WFI to change the rootname of the file.
# Set other arguments for use in Roman I-Sim. The code expects a specific format for these, so this is a little complicated looking.
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.set_defaults(usecrds=True, stpsf=True, level=level, filename=filename, drop_extra_dq=True, sca=sca,
bandpass=optical_element, pretend_spectral=None)
args = parser.parse_args([])
# Set reference files to None for CRDS
for k in parameters.reference_data:
parameters.reference_data[k] = None
# Set Galsim RNG object
rng = galsim.UniformDeviate(seed)
# Set default persistance information
persist = persistence.Persistence()
# Set metadata
metadata = ris.set_metadata(date=obs_date, bandpass=optical_element, sca=sca, ma_table_number=ma_table_number, usecrds=True)
# Update the WCS info
wcs.fill_in_parameters(metadata, SkyCoord(ra, dec, unit='deg', frame='icrs'), boresight=False, pa_aper=0.0)
# Run the simulation
ris.simulate_image_file(args, metadata, full_catalog, rng, persist)
2025-12-11 19:47:44 INFO Simulating filter F106...
2025-12-11 19:47:44 INFO NumExpr defaulting to 4 threads.
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Using pupil mask 'F062' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Using pupil mask 'F062' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Using pupil mask 'F106' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO No source spectrum supplied, therefore defaulting to 5700 K blackbody
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Computing wavelength weights using synthetic photometry for F106...
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Using pupil mask 'F106' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO PSF calc using fov_arcsec = 5.000000, oversample = 4, number of wavelengths = 10
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Creating optical system model:
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Initialized OpticalSystem: Roman+WFI
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Roman Entrance Pupil: Loaded amplitude transmission from /home/runner/refdata/stpsf-data/WFI/pupils/RST_WIM_Filter_F106_WFI01.fits.gz
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Roman Entrance Pupil: Loaded OPD from /home/runner/refdata/stpsf-data/upscaled_HST_OPD.fits
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Added pupil plane: Roman Entrance Pupil
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Added coordinate inversion plane: OTE exit pupil
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Added pupil plane: Field Dependent Aberration (WFI01)
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Added detector with pixelscale=0.1078577405 and oversampling=4: WFI detector
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Calculating PSF with 10 wavelengths
2025-12-11 19:47:49 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.4555e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:47:56 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.7265e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:47:57 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.9975e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:47:57 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.02685e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:47:58 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.05395e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:47:58 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.08105e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:47:59 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.10815e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:47:59 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.13525e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:00 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.16235e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:00 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.18945e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Calculation completed in 11.315 s
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO PSF Calculation completed.
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Calculating jitter using gaussian
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Jitter: Convolving with Gaussian with sigma=0.012 arcsec
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO resulting image peak drops to 0.946 of its previous value
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Detector charge diffusion not applied because charge_diffusion_sigma option is 0
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Adding extension with image downsampled to detector pixel scale.
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Downsampling to detector pixel scale, by 4
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Downsampling to detector pixel scale, by 4
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Using pupil mask 'F062' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Using pupil mask 'F062' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Using pupil mask 'F106' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO No source spectrum supplied, therefore defaulting to 5700 K blackbody
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Computing wavelength weights using synthetic photometry for F106...
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Using pupil mask 'F106' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO PSF calc using fov_arcsec = 5.000000, oversample = 4, number of wavelengths = 10
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Creating optical system model:
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Initialized OpticalSystem: Roman+WFI
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Roman Entrance Pupil: Loaded amplitude transmission from /home/runner/refdata/stpsf-data/WFI/pupils/RST_WIM_Filter_F106_WFI01.fits.gz
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Roman Entrance Pupil: Loaded OPD from /home/runner/refdata/stpsf-data/upscaled_HST_OPD.fits
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Added pupil plane: Roman Entrance Pupil
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Added coordinate inversion plane: OTE exit pupil
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Added pupil plane: Field Dependent Aberration (WFI01)
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Added detector with pixelscale=0.1078577405 and oversampling=4: WFI detector
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Calculating PSF with 10 wavelengths
2025-12-11 19:48:01 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.4555e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:48:02 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.7265e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:48:02 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.9975e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:48:03 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.02685e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:03 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.05395e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:04 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.08105e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:04 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.10815e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:05 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.13525e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:05 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.16235e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:06 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.18945e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:06 INFO Calculation completed in 5.162 s
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO PSF Calculation completed.
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Calculating jitter using gaussian
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Jitter: Convolving with Gaussian with sigma=0.012 arcsec
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO resulting image peak drops to 0.946 of its previous value
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Detector charge diffusion not applied because charge_diffusion_sigma option is 0
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Adding extension with image downsampled to detector pixel scale.
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Downsampling to detector pixel scale, by 4
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Downsampling to detector pixel scale, by 4
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Using pupil mask 'F062' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Using pupil mask 'F062' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Using pupil mask 'F106' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO No source spectrum supplied, therefore defaulting to 5700 K blackbody
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Computing wavelength weights using synthetic photometry for F106...
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Using pupil mask 'F106' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO PSF calc using fov_arcsec = 5.000000, oversample = 4, number of wavelengths = 10
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Creating optical system model:
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Initialized OpticalSystem: Roman+WFI
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Roman Entrance Pupil: Loaded amplitude transmission from /home/runner/refdata/stpsf-data/WFI/pupils/RST_WIM_Filter_F106_WFI01.fits.gz
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Roman Entrance Pupil: Loaded OPD from /home/runner/refdata/stpsf-data/upscaled_HST_OPD.fits
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Added pupil plane: Roman Entrance Pupil
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Added coordinate inversion plane: OTE exit pupil
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Added pupil plane: Field Dependent Aberration (WFI01)
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Added detector with pixelscale=0.1078577405 and oversampling=4: WFI detector
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Calculating PSF with 10 wavelengths
2025-12-11 19:48:07 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.4555e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:48:08 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.7265e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:48:08 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.9975e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:48:09 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.02685e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:09 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.05395e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:10 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.08105e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:10 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.10815e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:11 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.13525e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:11 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.16235e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:12 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.18945e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:12 INFO Calculation completed in 5.201 s
2025-12-11 19:48:12 INFO PSF Calculation completed.
2025-12-11 19:48:12 INFO Calculating jitter using gaussian
2025-12-11 19:48:12 INFO Jitter: Convolving with Gaussian with sigma=0.012 arcsec
2025-12-11 19:48:12 INFO resulting image peak drops to 0.946 of its previous value
2025-12-11 19:48:12 INFO Detector charge diffusion not applied because charge_diffusion_sigma option is 0
2025-12-11 19:48:12 INFO Adding extension with image downsampled to detector pixel scale.
2025-12-11 19:48:12 INFO Downsampling to detector pixel scale, by 4
2025-12-11 19:48:12 INFO Downsampling to detector pixel scale, by 4
2025-12-11 19:48:12 INFO Using pupil mask 'F062' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:48:12 INFO Using pupil mask 'F062' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Using pupil mask 'F106' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO No source spectrum supplied, therefore defaulting to 5700 K blackbody
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Computing wavelength weights using synthetic photometry for F106...
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Using pupil mask 'F106' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO PSF calc using fov_arcsec = 5.000000, oversample = 4, number of wavelengths = 10
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Creating optical system model:
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Initialized OpticalSystem: Roman+WFI
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Roman Entrance Pupil: Loaded amplitude transmission from /home/runner/refdata/stpsf-data/WFI/pupils/RST_WIM_Filter_F106_WFI01.fits.gz
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Roman Entrance Pupil: Loaded OPD from /home/runner/refdata/stpsf-data/upscaled_HST_OPD.fits
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Added pupil plane: Roman Entrance Pupil
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Added coordinate inversion plane: OTE exit pupil
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Added pupil plane: Field Dependent Aberration (WFI01)
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Added detector with pixelscale=0.1078577405 and oversampling=4: WFI detector
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Calculating PSF with 10 wavelengths
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.4555e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:48:13 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.7265e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:48:14 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.9975e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:48:15 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.02685e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:15 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.05395e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:16 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.08105e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:16 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.10815e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:17 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.13525e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:17 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.16235e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:18 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.18945e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:48:18 INFO Calculation completed in 5.114 s
2025-12-11 19:48:18 INFO PSF Calculation completed.
2025-12-11 19:48:18 INFO Calculating jitter using gaussian
2025-12-11 19:48:18 INFO Jitter: Convolving with Gaussian with sigma=0.012 arcsec
2025-12-11 19:48:18 INFO resulting image peak drops to 0.946 of its previous value
2025-12-11 19:48:18 INFO Detector charge diffusion not applied because charge_diffusion_sigma option is 0
2025-12-11 19:48:18 INFO Adding extension with image downsampled to detector pixel scale.
2025-12-11 19:48:18 INFO Downsampling to detector pixel scale, by 4
2025-12-11 19:48:18 INFO Downsampling to detector pixel scale, by 4
2025-12-11 19:48:23 WARNING max(flat) > 1.1; this seems weird?!
2025-12-11 19:48:23 INFO Adding 1745 sources to image...
2025-12-11 19:49:48 INFO Rendered 1745 sources...
2025-12-11 19:49:51 INFO Apportioning electrons to resultants...
2025-12-11 19:50:21 INFO Adding IPC...
2025-12-11 19:50:22 INFO Adding read noise...
2025-12-11 19:50:26 INFO Fitting ramps.
2025-12-11 19:50:32 INFO Simulation complete.
If we want to simulate an L1 ramp cube, then we can change the level variable above to 1, which will also change the output file name to *_uncal.asdf. The rest of the information stays the same.
Advanced Use Cases#
Dithered Observations#
Dithering is the process of shifting the telescope position slightly such that astronomical sources fall on different pixel positions in consecutive observations. Dithers comes in two flavors:
Large dithers: Used to fill the gaps between detectors and to reject pixels affected by undesirable effects
Sub-pixel dithers: Used for sampling the point spread function (PSF)
If we want to create a set of dithered observations, we need to determine the new pointing of the WFI. Here we introduce a Python class that can take an initial right ascension, declination, and position angle of the WFI and then apply offsets to update those parameters for a new pointing. First, let’s import some new packages and modules that will help, specifically:
pysiaf for WFI coordinate transformations
dataclasses for simplifying the definition of a class
typing for type hinting of inputs and outputs
In this section, we show you how to determine the pointing positions necessary for dithering with the Roman WFI. In the Advanced Use Cases - Simulating Dithered Observations in Parallel section, we combine the dithering information and parallelization with Dask to show how to put this information to use.
import pysiaf
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Union
Next, we create a Python class called PointWFI that takes three inputs: ra, dec, and roll_angle. Defining a class may be a little complicated for those who are new to Python, so don’t worry too much about the details for now. Just know that this class takes your input position, creates an attitude matrix for the spacecraft using PySIAF, applies the offsets, and updates the pointing information.
@dataclass(init=True, repr=True)
class PointWFI:
"""
Inputs
------
ra (float): Right ascension of the target placed at the geometric
center of the Wide Field Instrument (WFI) focal plane
array. This has units of degrees.
dec (float): Declination of the target placed at the geometric
center of the WFI focal plane array. This has units
of degrees.
position_angle (float): Position angle of the WFI relative to the V3 axis
measured from North to East. A value of 0.0 degrees
would place the WFI in the "smiley face" orientation
(U-shaped) on the celestial sphere. To place WFI
such that the position angle of the V3 axis is
zero degrees, use a WFI position angle of -60 degrees.
Description
-----------
To use this class, insantiate it with your initial pointing like so:
>>> point = PointWFI(ra=30, dec=-45, position_angle=10)
and then dither using the dither method:
>>> point.dither(x_offset=10, y_offset=140)
This would shift the WFI 10 arcseconds along the X-axis of the WFI
and 140 arcseconds along the Y-axis of the WFI. These axes are in the ideal
coordinate system of the WFI, i.e, with the WFI oriented in a U-shape with
+x to the right and +y up. You can pull the new pointing info out of the object
either as attributes or by just printing the object:
>>> print(point.ra, point.dec)
>>> 29.95536280064078 -44.977122003232786
or
>>> point
>>> PointWFI(ra=29.95536280064078, dec=-44.977122003232786, position_angle=10)
"""
# Set default pointing parameters
ra: float = 0.0
dec: float = 0.0
position_angle: float = -60.0
# Post init method sets some other defaults and initializes
# the attitude matrix using PySIAF.
def __post_init__(self) -> None:
self.siaf_aperture = pysiaf.Siaf('Roman')['WFI_CEN']
self.v2_ref = self.siaf_aperture.V2Ref
self.v3_ref = self.siaf_aperture.V3Ref
self.attitude_matrix = pysiaf.utils.rotations.attitude(self.v2_ref, self.v3_ref, self.ra,
self.dec, self.position_angle)
self.siaf_aperture.set_attitude_matrix(self.attitude_matrix)
# Compute the V3 position angle
self.tel_roll = pysiaf.utils.rotations.posangle(self.attitude_matrix, 0, 0)
# Save initial pointing
self.att0 = self.attitude_matrix.copy()
# Save a copy of the input RA and Dec in case someone needs it
self.ra0 = copy.copy(self.ra)
self.dec0 = copy.copy(self.dec)
def dither(self, x_offset: Union[int, float],
y_offset: Union[int, float]) -> None:
"""
Purpose
-------
Take in an ideal X and Y offset in arcseconds and shift the telescope
pointing to that position.
Inputs
------
x_offset (float): The offset in arcseconds in the ideal X direction.
y_offset (float): The offset in arcseconds in the ideal Y direction.
"""
self.ra, self.dec = self.siaf_aperture.idl_to_sky(x_offset, y_offset)
Now let’s dither the WFI. We will use the BOXGAP4 dither pattern for our example. See the RDox article on WFI Dithering for more information. Note that the dither offsets are represented in the ideal X and Y directions (this means that +X is to the right and +Y is up when the WFI is in the U-shaped orientation with WFI07 and WFI16 in the upper-right and upper-left corners, respectively). The offsets are in units of arcseconds, and each offset represents the offset from the initial starting position. Here is the pattern:
Dither Step |
Offset X (arcsec) |
Offset Y (arcsec) |
|---|---|---|
0 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
1 |
-205.20 |
0.88 |
2 |
-204.32 |
206.08 |
3 |
0.88 |
205.20 |
Now let’s instantiate the PointWFI object with our initial pointing and move to the first dither position:
pointing = PointWFI(ra=270.7, dec=-0.2, position_angle=0.0)
pointing.dither(x_offset=-205.20, y_offset=0.88)
print(pointing)
PointWFI(ra=np.float64(270.7282882327223), dec=np.float64(-0.15051433561208868), position_angle=0.0)
We can see that the WFI shifted slightly in both right ascension and declination, but not by -205.20 and +0.88 arcseconds. Remember that the WFI dither offsets are specified in a coordinate system local to the WFI, so the offsets on the sky will be different (hence the need for the class we created above). To make it easier to script our simulations, we can pull the variables out of the pointing object, such as below where we show how to retrieve the .ra attribute:
pointing.ra
np.float64(270.7282882327223)
Parallelized Simulations#
Often, we will want to run a simulation using multiple detectors rather than just one at a time. Looping over the above in a serial fashion can take quite a long time, so we want to parallelize the work. In the example below, we will show how to parallelize the procedure with Dask. These cells are commented out by default, so to run them you need to uncomment all of the lines. Comments in code cells are marked with two # symbols (e.g., ## Comment), so be sure to remove only the leading single # symbol.
!pip install dask[complete]
Requirement already satisfied: dask[complete] in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (2025.11.0)
Requirement already satisfied: click>=8.1 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (8.3.1)
Requirement already satisfied: cloudpickle>=3.0.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (3.1.2)
Requirement already satisfied: fsspec>=2021.09.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (2025.12.0)
Requirement already satisfied: packaging>=20.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (25.0)
Requirement already satisfied: partd>=1.4.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (1.4.2)
Requirement already satisfied: pyyaml>=5.3.1 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (6.0.3)
Requirement already satisfied: toolz>=0.10.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (1.1.0)
Requirement already satisfied: pyarrow>=14.0.1 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (22.0.0)
Requirement already satisfied: lz4>=4.3.2 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (4.4.5)
Requirement already satisfied: locket in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from partd>=1.4.0->dask[complete]) (1.0.0)
Requirement already satisfied: numpy>=1.24 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (2.3.5)
Requirement already satisfied: pandas>=2.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (2.3.3)
Requirement already satisfied: distributed==2025.11.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (2025.11.0)
Requirement already satisfied: bokeh>=3.1.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (3.8.1)
Requirement already satisfied: jinja2>=2.10.3 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from dask[complete]) (3.1.6)
Requirement already satisfied: msgpack>=1.0.2 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from distributed==2025.11.0->dask[complete]) (1.1.2)
Requirement already satisfied: psutil>=5.8.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from distributed==2025.11.0->dask[complete]) (7.1.3)
Requirement already satisfied: sortedcontainers>=2.0.5 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from distributed==2025.11.0->dask[complete]) (2.4.0)
Requirement already satisfied: tblib>=1.6.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from distributed==2025.11.0->dask[complete]) (3.2.2)
Requirement already satisfied: tornado>=6.2.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from distributed==2025.11.0->dask[complete]) (6.5.3)
Requirement already satisfied: urllib3>=1.26.5 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from distributed==2025.11.0->dask[complete]) (2.6.1)
Requirement already satisfied: zict>=3.0.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from distributed==2025.11.0->dask[complete]) (3.0.0)
Requirement already satisfied: contourpy>=1.2 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from bokeh>=3.1.0->dask[complete]) (1.3.3)
Requirement already satisfied: narwhals>=1.13 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from bokeh>=3.1.0->dask[complete]) (2.13.0)
Requirement already satisfied: pillow>=7.1.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from bokeh>=3.1.0->dask[complete]) (12.0.0)
Requirement already satisfied: xyzservices>=2021.09.1 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from bokeh>=3.1.0->dask[complete]) (2025.11.0)
Requirement already satisfied: MarkupSafe>=2.0 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from jinja2>=2.10.3->dask[complete]) (3.0.3)
Requirement already satisfied: python-dateutil>=2.8.2 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from pandas>=2.0->dask[complete]) (2.9.0.post0)
Requirement already satisfied: pytz>=2020.1 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from pandas>=2.0->dask[complete]) (2025.2)
Requirement already satisfied: tzdata>=2022.7 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from pandas>=2.0->dask[complete]) (2025.2)
Requirement already satisfied: six>=1.5 in /home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages (from python-dateutil>=2.8.2->pandas>=2.0->dask[complete]) (1.17.0)
from dask.distributed import Client
At this point, it’s helpful to redefine our simulation call above as a single function:
def run_romanisim(catalog, ra=80.0, dec=30.0, obs_date = '2026-10-31T00:00:00', sca=1, expnum=1, optical_element='F106',
ma_table_number=3, level=2, filename=f'r0003201001001001004', seed=5346):
cal_level = 'cal' if level == 2 else 'uncal'
filename = f'{filename}_{expnum:04d}_wfi{sca:02d}_{optical_element.lower()}_{cal_level}.asdf'
# Set other arguments for use in Roman I-Sim. The code expects a specific format for these, so this is a little complicated looking.
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.set_defaults(usecrds=True, stpsf=True, level=level, filename=filename, drop_extra_dq=True, sca=sca,
bandpass=optical_element, pretend_spectral=None)
args = parser.parse_args([])
# Set reference files to None for CRDS
for k in parameters.reference_data:
parameters.reference_data[k] = None
# Set Galsim RNG object
rng = galsim.UniformDeviate(seed)
# Set default persistance information
persist = persistence.Persistence()
# Set metadata
metadata = ris.set_metadata(date=obs_date, bandpass=optical_element, sca=sca, ma_table_number=ma_table_number, usecrds=True)
# Update the WCS info
wcs.fill_in_parameters(metadata, SkyCoord(ra, dec, unit='deg', frame='icrs'), boresight=False, pa_aper=0.0)
# Run the simulation
sim_result = ris.simulate_image_file(args, metadata, catalog, rng, persist)
# Clean up the memory
del sim_result
Now we initialize the Dask Client() and pass our simulation jobs to it. Dask will take care of scheduling the jobs and allocating resources. That said, we do have to be careful to not overload the Client. Set the number of WFI detectors to be simulated in the for loop appropriately to n_detectors = 3 for a large RRN server.
The variable offset adds an offset to the numbering of the WFI detector names. If you want to simulate, e.g., detectors WFI01, WFI02, and WFI03, then set n_detectors = 3 and offset = 0. If instead you want to simulate, e.g., detectors WFI04, WFI05, and WFI06, then set n_detectors = 3 and offset = 3. The expnum variable lets you change the exposure number in the file name (this is useful if you are simulated a series of dithered observations).
WARNING: Please be cautious when parallelizing tasks such as Roman I-Sim as it can easily consume all of your RRN resources if handled incorrectly!
We have commented out the lines below. If you want to run the parallelized simulation, uncomment all of the lines in the following code cell.
Note: This cell may take several minutes to run. In addition, logging messages from romanisim and its dependencies will appear cluttered as they are executing simultaneously.
## Number of detectors to simulate. Change offset to select
## higher detector IDs (e.g., n_detectors = 3 and offset = 3
## will simulate detectors WFI04, WFI05, and WFI06.
#n_detectors = 3
#offset = 0
#
## Change this to increment the exposure number in the simulation output filename
#expnum = 1
## Set up Dask client
## Give each simulation call its own worker so that no one worker exceeds
## the allocated memory.
#dask_client = Client(n_workers=n_detectors)
#
## Create simulation runs to send to the client
#tasks = []
#for i in range(n_detectors):
#
# # Create simulations with the full_catalog defined above and for 3
# # WFI detectors. Otherwise, use the default parameters.
# tasks.append(dask_client.submit(run_romanisim, full_catalog, **{'ra': pointing.ra, 'dec': pointing.dec, 'sca': i+1+offset, 'expnum': expnum}))
#
## Wait for all tasks to complete
#results = dask_client.gather(tasks)
#
## Don't forget to close the Dask client!
#dask_client.close()
Simulating Dithered Observations in Parallel#
Now that we have demonstrated how to determine the WFI pointing positions necessary for any dither pattern, and how to parallelize Roman I-Sim simulations to simulate multiple detectors simultaneously, let’s combine that information to simulate a series of dithered observations. As in the Advanced Use Cases - Parallelized Simulations section, we have commented out all of the code cells below.
Note: If you have not reviewed the Advanced Use Cases - Parallelized Simulations section, please review the information in that part of the tutorial before proceeding. At a minimum, you will need to install Dask and define the Roman I-Sim wrapper function before running the cells below.
We will use the four-point box gap-filling dither pattern described in Advanced Use Cases - Dithered Observations. We will also re-use the Roman I-Sim wrapper function that we defined for Dask. As you can see in the cell below, we are simulating three WFI detectors at a time at each dither position before proceeding to the next dither position. At each dither position, we incrementally update the exposure number. The resulting file names are: r0003201001001001004_XXXX_wfiNN_f106_uncal.asdf, where XXXX is the zero-padded exposure number (e.g., 0001) and NN is the WFI detector ID (e.g., WFI01). Note that these are L1 files rather than the L2 file that was simulated previously.
## Initial pointing
#pointing = PointWFI(ra=270.94, dec=-0.2, position_angle=0.0)
#
## Number of detectors to simulate. Change offset to select
## higher detector IDs (e.g., n_detectors = 3 and offset = 3
## will simulate detectors WFI04, WFI05, and WFI06.
#n_detectors = 3
#offset = 0
#
## Change this to increment the exposure number in the simulation output filename
#expnum = 1
#
## Set up Dask client
## Give each simulation call its own worker so that no one worker exceeds
## the allocated memory.
#dask_client = Client(n_workers=n_detectors)
#
## Create simulation runs to send to the client
#tasks = []
#for i in range(n_detectors):
#
# # Create simulations with the full_catalog defined above and for 3
# # WFI detectors. Otherwise, use the default parameters.
# tasks.append(dask_client.submit(run_romanisim, full_catalog, **{'ra': pointing.ra, 'dec': pointing.dec, 'sca': i+1+offset, 'expnum': expnum, 'level': 1}))
#
## Wait for all tasks to complete
#results = dask_client.gather(tasks)
#
## Exposure 2
## Dither -205.20 +0.88
#pointing.dither(x_offset=-205.20, y_offset=0.88)
#expnum=2
#tasks = []
#for i in range(n_detectors):
# tasks.append(dask_client.submit(run_romanisim, full_catalog, **{'ra': pointing.ra, 'dec': pointing.dec, 'sca': i+1+offset, 'expnum': expnum, 'level': 1}))
#
## Wait for all tasks to complete
#results = dask_client.gather(tasks)
#
## Exposure 3
## Dither -204.32 +206.08
#pointing.dither(x_offset=-204.32, y_offset=206.08)
#expnum=3
#tasks = []
#for i in range(n_detectors):
# tasks.append(dask_client.submit(run_romanisim, full_catalog, **{'ra': pointing.ra, 'dec': pointing.dec, 'sca': i+1+offset, 'expnum': expnum, 'level': 1}))
#
## Wait for all tasks to complete
#results = dask_client.gather(tasks)
#
## Exposure 4
## Dither +0.88 +205.20
#pointing.dither(x_offset=0.88, y_offset=205.20)
#expnum=4
#tasks = []
#for i in range(n_detectors):
# tasks.append(dask_client.submit(run_romanisim, full_catalog, **{'ra': pointing.ra, 'dec': pointing.dec, 'sca': i+1+offset, 'expnum': expnum, 'level': 1}))
#
## Wait for all tasks to complete
#results = dask_client.gather(tasks)
#
## Don't forget to close the Dask client!
#dask_client.close()
Injecting Sources into L2 Images#
Another advanced use case is injecting sources into L2 images. This may be useful, for example, to assess completeness and to test systematics in our data (simulated or otherwise). We can also use this for creating time-variable sources in a series of simulations. Right now, Roman I-Sim only supports injection at L2, though work is underway to add this capability for L1 images in the future.
To inject sources into a L2 image, we need to create a Roman I-Sim input catalog. However, the catalog will be a shortened version containing just the sources that we want to inject. Also recall that the catalog brightnesses are specified in units of maggies, which are defined such that one maggie is equal to the reference AB magnitude flux (3,631 Jy), i.e., maggies $\equiv 10^{-0.4m_{\mathrm{AB}}}$.
First, let’s read in a L2 file and display it. We will use one of the images we just simulated, but after it has been run through the Exposure Pipeline to generate the L2 file. You can either visit the Exposure Pipeline tutorial for more information to do this yourself, or use one of the files in the Nexus S3 bucket.
#Stream the files from the S3 bucket if they are not in local storage
if os.path.exists('r0003201001001001004_0001_wfi01_f106_cal.asdf'):
dm = rdm.open('r0003201001001001004_0001_wfi01_f106_cal.asdf')
else:
fs = s3fs.S3FileSystem(anon=True)
asdf_dir_uri = 's3://stpubdata/roman/nexus/soc_simulations/tutorial_data/'
asdf_file_uri = asdf_dir_uri + 'r0003201001001001004_0001_wfi01_f106_cal.asdf'
with fs.open(asdf_file_uri, 'rb') as f:
af = asdf.open(f)
dm = rdm.open(af).copy()
Now let’s take a look at our image around some area we would like to inject a new source. For this, let’s choose pixel (X, Y) = (1000, 1000) to be the position of our new source, so we will display the area around that pixel. For more information on how to visualize your data, see the Data Visualization tutorial.
norm = simple_norm(dm.data, 'asinh', percent=99.7)
plt.imshow(dm.data[900:1100, 900:1100], norm=norm, cmap='afmhot', origin='lower',
extent=[900, 1100, 900, 1100]);
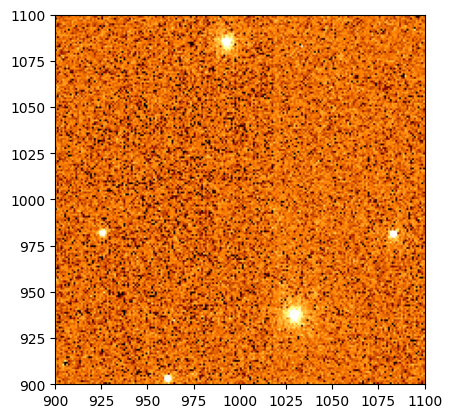
Next, let’s create our catalog. Let’s choose a brightness of 2 x 10-8 maggies (~19.25 AB magnitudes) for our source. Note that if you are injecting galaxies, then you will also need to supply the other parameters Roman I-Sim needs for galaxy sources (e.g., Sérsic index and half-light radius).
In the next cell, we make a function for creating and saving our injection catalog:
# Define a function to create the catalog for sources
# that we want to inject into our L2 image.
def make_cat(ra, dec, fluxes, filename='injection_cat.ecsv'):
filtlist = 'F062 F087 F106 F129 F146 F158 F184 F213'.split()
tab = Table([ra, dec], names = ('ra', 'dec'))
src_types = np.array(['PSF' for i in ra])
tab['type'] = src_types
for k, v in fluxes.items():
if k.upper() in filtlist:
tab[k.upper()] = v
else:
raise ValueError(f'Incorrect filter name {k}!')
tab.write(filename, overwrite=True)
And now run the function with our inputs:
# Get the RA and Dec from the WCS
ra, dec = dm.meta.wcs(1000, 1000)
# Make the injection catalog
make_cat([ra], [dec], {'F106': [2e-8]})
Let’s take a look at the catalog we just created and make sure it looks correct:
tab = Table.read('injection_cat.ecsv')
tab
| ra | dec | type | F106 |
|---|---|---|---|
| float64 | float64 | str3 | float64 |
| 270.904026679121 | -0.19579469786176076 | PSF | 2e-08 |
Previously in this tutorial, we wrote a function to run Roman I-Sim. In that function, we overrode all of the default parameters and set them to None to force Roman I-Sim to use calibration reference files from CRDS rather than the Roman I-Sim default scalar values. These default scalar values are intended to allow Roman I-Sim to in an offline mode when you may not have access to a CRDS cache or the CRDS server. However, the current version of the inject_sources_into_l2() function does not use CRDS reference files and must use the Roman I-Sim defaults. Because the injection needs the default parameter values, we need to restore them here. We accomplish that using Python’s importlib.reload() function to reload the installed version of romanisim.parameters into memory:
importlib.reload(parameters)
<module 'romanisim.parameters' from '/home/runner/micromamba/envs/ci-env/lib/python3.13/site-packages/romanisim/parameters.py'>
Now we run the source injection function inject_sources_into_l2() with our image (datamodel), the injection catalog (the variable tab), and we set stpsf=True to use STPSF-generated point spread functions (PSFs) for the simulation. Notice that we make a copy of the image using the .copy() method so that we inject the source into a copy of the image rather than the original. This lets us compare the original and the updated version after we inject the source.
As a reminder, this will use the default Roman I-Sim parameter values for the injected source; however, perhaps the most critical parameter (the gain) can be modified in the function call. The gain is important in the simulation as the WFI zeropoints in the L2 metadata are intended to transform from DN/s to MJy/sr, and therefore contain a factor of the gain. If needed, the gain value used in the zeropoint can be found in the photom reference file. In the cell below, we will set the gain to the default value (2 e–/DN) to demonstrate the proper way to modify the value.
result = inject_sources_into_l2(dm.copy(), tab, stpsf=True, gain=2 * (u.electron / u.DN))
2025-12-11 19:50:35 INFO Using pupil mask 'F062' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:50:35 INFO Using pupil mask 'F062' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:50:35 INFO Using pupil mask 'F106' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO No source spectrum supplied, therefore defaulting to 5700 K blackbody
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO Computing wavelength weights using synthetic photometry for F106...
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO Using pupil mask 'F106' and detector 'WFI01'.
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO PSF calc using fov_arcsec = 5.000000, oversample = 4, number of wavelengths = 10
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO Creating optical system model:
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO Initialized OpticalSystem: Roman+WFI
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO Roman Entrance Pupil: Loaded amplitude transmission from /home/runner/refdata/stpsf-data/WFI/pupils/RST_WIM_Filter_F106_WFI01.fits.gz
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO Roman Entrance Pupil: Loaded OPD from /home/runner/refdata/stpsf-data/upscaled_HST_OPD.fits
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO Added pupil plane: Roman Entrance Pupil
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO Added coordinate inversion plane: OTE exit pupil
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO Added pupil plane: Field Dependent Aberration (WFI01)
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO Added detector with pixelscale=0.1078577405 and oversampling=4: WFI detector
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO Calculating PSF with 10 wavelengths
2025-12-11 19:50:36 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.4555e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:50:37 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.7265e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:50:37 INFO Propagating wavelength = 9.9975e-07 m
2025-12-11 19:50:38 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.02685e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:50:38 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.05395e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:50:39 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.08105e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:50:39 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.10815e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:50:40 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.13525e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:50:40 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.16235e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:50:41 INFO Propagating wavelength = 1.18945e-06 m
2025-12-11 19:50:41 INFO Calculation completed in 5.180 s
2025-12-11 19:50:41 INFO PSF Calculation completed.
2025-12-11 19:50:41 INFO Calculating jitter using gaussian
2025-12-11 19:50:41 INFO Jitter: Convolving with Gaussian with sigma=0.012 arcsec
2025-12-11 19:50:41 INFO resulting image peak drops to 0.946 of its previous value
2025-12-11 19:50:41 INFO Detector charge diffusion not applied because charge_diffusion_sigma option is 0
2025-12-11 19:50:41 INFO Adding extension with image downsampled to detector pixel scale.
2025-12-11 19:50:41 INFO Downsampling to detector pixel scale, by 4
2025-12-11 19:50:41 INFO Downsampling to detector pixel scale, by 4
2025-12-11 19:50:42 INFO Adding 1 sources to image...
2025-12-11 19:50:42 INFO Rendered 1 sources...
2025-12-11 19:50:42 INFO Fitting ramps.
Finally, let’s re-plot the same region as before to show the injected source:
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2)
axs[0].imshow(dm.data[900:1100, 900:1100], norm=norm,
cmap='afmhot', origin='lower',
extent=[900, 1100, 900, 1100])
axs[0].set_title('Original')
axs[1].imshow(result.data[900:1100, 900:1100], norm=norm,
cmap='afmhot', origin='lower',
extent=[900, 1100, 900, 1100])
axs[1].set_title('Injected')
plt.tight_layout();
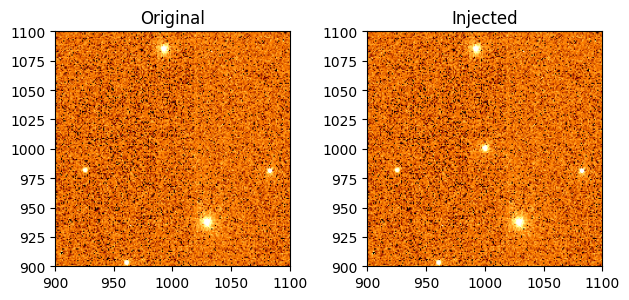
Additional Resources#
About this Notebook#
Author: Sanjib Sharma, Tyler Desjardins
Updated On: 2025-12-04
| ↑ Top of page |

|

|
