Specviz Simple Demo#
Use case: This notebook demonstrates how to inspect spectra in Specviz, export spectra from the GUI in the notebook, select regions in the GUI and in the notebook, and measure the redshift of a source in the GUI.
Data: NIRISS 1D spectra from the NGDEEP survey. The dataset is directly obtain from MAST after the default JWST pipeline processing.
Tools: specutils, jdaviz.
Cross-intrument: all instruments.
Documentation: This notebook is part of a STScI’s larger post-pipeline Data Analysis Tools Ecosystem.
Updated on: 2023/10/11
# To use 100% of the browser window
from IPython.display import display, HTML
display(HTML("<style>.container { width:100% !important; }</style>"))
Imports:
matplotlib for plotting data
astropy for handling of fits files, units, and tables
specutils for interactions with Specviz and region definition/extraction
jdaviz for the visualization tool Specviz
# Plotting and tabling
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Import astropy
import astropy
import astropy.units as u
from astropy.io import fits
from astropy.nddata import StdDevUncertainty
from astropy.table import QTable
# Import specutils
import specutils
from specutils import Spectrum1D, SpectralRegion
from specutils.manipulation import extract_region
# Import viztools
import jdaviz
from jdaviz import Specviz
# Customization of matplotlib style
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (10, 5)
params = {'legend.fontsize': '18', 'axes.labelsize': '18',
'axes.titlesize': '18', 'xtick.labelsize': '18',
'ytick.labelsize': '18', 'lines.linewidth': 2,
'axes.linewidth': 2, 'animation.html': 'html5',
'figure.figsize': (8, 6)}
plt.rcParams.update(params)
plt.rcParams.update({'figure.max_open_warning': 0})
Check versions
print('astropy:', astropy.__version__)
print('specutils:', specutils.__version__)
print('jdaviz:', jdaviz.__version__)
astropy: 6.0.0
specutils: 1.12.0
jdaviz: 3.8.0
1. Load NIRISS pipeline output#
The JWST/NIRISS data are stored on box. We work with the x1d file which contains all extracted 1D spectra.
filelink = 'https://data.science.stsci.edu/redirect/JWST/jwst-data_analysis_tools/specviz_notebook_gui_interaction/jw02079004002_11101_00001_nis_x1d.fits'
hdu = fits.open(filelink)
hdu.info()
Filename: /home/runner/.astropy/cache/download/url/cb25b167f5e051a9e693b45b4a9d0bba/contents
No. Name Ver Type Cards Dimensions Format
0 PRIMARY 1 PrimaryHDU 350 ()
1 EXTRACT1D 1 BinTableHDU 76 180R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
2 EXTRACT1D 2 BinTableHDU 76 200R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
3 EXTRACT1D 3 BinTableHDU 76 160R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
4 EXTRACT1D 4 BinTableHDU 76 182R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
5 EXTRACT1D 5 BinTableHDU 76 180R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
6 EXTRACT1D 6 BinTableHDU 76 185R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
7 EXTRACT1D 7 BinTableHDU 76 151R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
8 EXTRACT1D 8 BinTableHDU 76 175R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
9 EXTRACT1D 9 BinTableHDU 76 132R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
10 EXTRACT1D 10 BinTableHDU 76 135R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
11 EXTRACT1D 11 BinTableHDU 76 123R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
12 EXTRACT1D 12 BinTableHDU 76 135R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
13 EXTRACT1D 13 BinTableHDU 76 145R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
14 EXTRACT1D 14 BinTableHDU 76 16R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
15 EXTRACT1D 15 BinTableHDU 76 152R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
16 EXTRACT1D 16 BinTableHDU 76 44R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
17 EXTRACT1D 17 BinTableHDU 76 157R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
18 EXTRACT1D 18 BinTableHDU 76 138R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
19 EXTRACT1D 19 BinTableHDU 76 150R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
20 EXTRACT1D 20 BinTableHDU 76 137R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
21 EXTRACT1D 21 BinTableHDU 76 149R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
22 EXTRACT1D 22 BinTableHDU 76 134R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
23 EXTRACT1D 23 BinTableHDU 76 124R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
24 EXTRACT1D 24 BinTableHDU 76 129R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
25 EXTRACT1D 25 BinTableHDU 76 137R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
26 EXTRACT1D 26 BinTableHDU 76 130R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
27 EXTRACT1D 27 BinTableHDU 76 155R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
28 EXTRACT1D 28 BinTableHDU 76 150R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
29 EXTRACT1D 29 BinTableHDU 76 121R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
30 EXTRACT1D 30 BinTableHDU 76 131R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
31 EXTRACT1D 31 BinTableHDU 76 134R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
32 EXTRACT1D 32 BinTableHDU 76 137R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
33 EXTRACT1D 33 BinTableHDU 76 128R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
34 EXTRACT1D 34 BinTableHDU 76 127R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
35 EXTRACT1D 35 BinTableHDU 76 115R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
36 EXTRACT1D 36 BinTableHDU 76 133R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
37 EXTRACT1D 37 BinTableHDU 76 123R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
38 EXTRACT1D 38 BinTableHDU 76 126R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
39 EXTRACT1D 39 BinTableHDU 76 125R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
40 EXTRACT1D 40 BinTableHDU 76 126R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
41 EXTRACT1D 41 BinTableHDU 76 129R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
42 EXTRACT1D 42 BinTableHDU 76 128R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
43 EXTRACT1D 43 BinTableHDU 76 134R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
44 EXTRACT1D 44 BinTableHDU 76 118R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
45 EXTRACT1D 45 BinTableHDU 76 149R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
46 EXTRACT1D 46 BinTableHDU 76 118R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
47 EXTRACT1D 47 BinTableHDU 76 117R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
48 EXTRACT1D 48 BinTableHDU 76 125R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
49 EXTRACT1D 49 BinTableHDU 76 129R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
50 EXTRACT1D 50 BinTableHDU 76 145R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
51 EXTRACT1D 51 BinTableHDU 76 126R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
52 EXTRACT1D 52 BinTableHDU 76 109R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
53 EXTRACT1D 53 BinTableHDU 76 127R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
54 EXTRACT1D 54 BinTableHDU 76 119R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
55 EXTRACT1D 55 BinTableHDU 76 129R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
56 EXTRACT1D 56 BinTableHDU 76 117R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
57 EXTRACT1D 57 BinTableHDU 76 106R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
58 EXTRACT1D 58 BinTableHDU 76 118R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
59 EXTRACT1D 59 BinTableHDU 76 128R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
60 EXTRACT1D 60 BinTableHDU 76 117R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
61 EXTRACT1D 61 BinTableHDU 76 120R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
62 EXTRACT1D 62 BinTableHDU 76 121R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
63 EXTRACT1D 63 BinTableHDU 76 111R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
64 EXTRACT1D 64 BinTableHDU 76 126R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
65 EXTRACT1D 65 BinTableHDU 76 114R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
66 EXTRACT1D 66 BinTableHDU 76 133R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
67 EXTRACT1D 67 BinTableHDU 76 133R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
68 EXTRACT1D 68 BinTableHDU 76 112R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
69 EXTRACT1D 69 BinTableHDU 76 118R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
70 EXTRACT1D 70 BinTableHDU 76 112R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
71 EXTRACT1D 71 BinTableHDU 76 112R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
72 EXTRACT1D 72 BinTableHDU 76 113R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
73 EXTRACT1D 73 BinTableHDU 76 118R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
74 EXTRACT1D 74 BinTableHDU 76 123R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
75 EXTRACT1D 75 BinTableHDU 76 113R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
76 EXTRACT1D 76 BinTableHDU 76 108R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
77 EXTRACT1D 77 BinTableHDU 76 106R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
78 EXTRACT1D 78 BinTableHDU 76 7R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
79 EXTRACT1D 79 BinTableHDU 76 108R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
80 EXTRACT1D 80 BinTableHDU 76 105R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
81 EXTRACT1D 81 BinTableHDU 76 108R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
82 EXTRACT1D 82 BinTableHDU 76 110R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
83 EXTRACT1D 83 BinTableHDU 76 113R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
84 EXTRACT1D 84 BinTableHDU 76 108R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
85 EXTRACT1D 85 BinTableHDU 76 121R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
86 EXTRACT1D 86 BinTableHDU 76 112R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
87 EXTRACT1D 87 BinTableHDU 76 110R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
88 EXTRACT1D 88 BinTableHDU 76 108R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
89 EXTRACT1D 89 BinTableHDU 76 121R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
90 EXTRACT1D 90 BinTableHDU 76 107R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
91 EXTRACT1D 91 BinTableHDU 76 116R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
92 EXTRACT1D 92 BinTableHDU 76 109R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
93 EXTRACT1D 93 BinTableHDU 76 104R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
94 EXTRACT1D 94 BinTableHDU 76 120R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
95 EXTRACT1D 95 BinTableHDU 76 93R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
96 EXTRACT1D 96 BinTableHDU 76 115R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
97 EXTRACT1D 97 BinTableHDU 76 120R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
98 EXTRACT1D 98 BinTableHDU 76 105R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
99 EXTRACT1D 99 BinTableHDU 76 110R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
100 EXTRACT1D 100 BinTableHDU 76 113R x 18C [D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, D, J, D, D, D, D, D, D]
101 ASDF 1 BinTableHDU 11 1R x 1C [677775B]
2. Open Specviz and load the 1D spectra we are interested in#
viz = Specviz()
viz.show()

The following cell opens one extension of the x1d file (75), creates a Spectrum1D object, and loads it into Specviz. A mask is set to only keep the part of the spectra with good sensitivity (1.34 to 1.66 micron) in the F150W filter.
for i in range(74, 75):
spec_load = hdu[i+1].data
wave = spec_load['WAVELENGTH']
flux = spec_load['FLUX']
error = spec_load['FLUX_ERROR']
# mask the parts where the sensitivity in the bandpass is poor
mask = ((wave > 1.34) & (wave < 1.66))
spec1d = Spectrum1D(spectral_axis=wave[mask]*u.um,
flux=flux[mask]*u.Jy,
uncertainty=StdDevUncertainty(error[mask]*u.Jy)) #
viz.load_data(spec1d, "NIRISS 1D {}".format(str(i+1)))
3. Select the emission lines using the GUI and in the notebook#
I select the region spanning the emission lines from roughly 1.58 to 1.63 microns.
Instructions: https://jdaviz.readthedocs.io/en/latest/specviz/displaying.html#defining-spectral-regions
See what data is used in this specviz istance#
dataout = viz.get_spectra(apply_slider_redshift=False)
spec1d_line = dataout["NIRISS 1D 75"]
print(spec1d_line)
Spectrum1D (length=69)
flux: [ 1.6163e-06 Jy, ..., 2.6548e-06 Jy ], mean=3.4997e-06 Jy
spectral axis: [ 1.6593 um, ..., 1.3403 um ], mean=1.4998 um
uncertainty: [ StdDevUncertainty(1.28849383e-07), ..., StdDevUncertainty(9.87921686e-08) ]
See the subsets defined in the GUI#
I include a try-except in case the notebook is run without human interaction.
try:
region = viz.get_spectral_regions()
print(region['Subset 1'])
except KeyError:
print("No region defined in the GUI")
No region defined in the GUI
Select the same region programmatically#
I can define my own region (cont_region) between arbitrary bounds. I choose 1.598um and 1.621um. I can then extract the spectrum in that region.
cont_region = SpectralRegion(1.598*u.um, 1.621*u.um)
spec1d_el_code = extract_region(spec1d_line, cont_region)
print(spec1d_el_code)
Spectrum1D (length=5)
flux: [ 5.2924e-06 Jy, ..., 5.8119e-06 Jy ], mean=8.3154e-06 Jy
spectral axis: [ 1.6171 um, ..., 1.5983 um ], mean=1.6077 um
uncertainty: [ StdDevUncertainty(1.16859251e-07), ..., StdDevUncertainty(1.15005193e-07) ]
Or I can extract the spectrum in the region I defined in the GUI (region[‘Subset 1’]).
try:
spec1d_el_viz = extract_region(spec1d_line, region['Subset 1'])
print(spec1d_el_viz)
except KeyError:
print("Region was not defined in the GUI")
# Define spec1d_el_viz as spec1d_el_code
spec1d_el_viz = spec1d_el_code
Region was not defined in the GUI
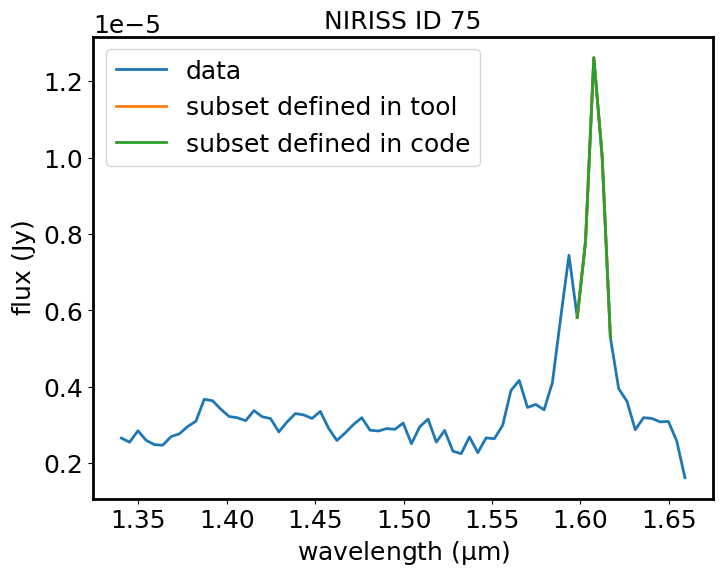
Plot the spectrum and the subset with matplotlib#
plt.plot(spec1d_line.spectral_axis, spec1d_line.flux, label='data')
plt.plot(spec1d_el_viz.spectral_axis, spec1d_el_viz.flux, label='subset defined in tool')
plt.plot(spec1d_el_code.spectral_axis, spec1d_el_code.flux, label='subset defined in code')
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("wavelength ({:latex})".format(spec1d_line.spectral_axis.unit))
plt.ylabel("flux ({:latex})".format(spec1d_line.flux.unit))
plt.title("NIRISS ID 75")
plt.show()
4. Use the redshift slider in Specviz to find the redshift#
I start by opening a new instance of Specviz so that I do not have to scroll up and down too much.
viz2 = Specviz()
viz2.show()

I load just the interesting spectrum (spec1d_line).
viz2.load_data(spec1d_line, "NIRISS 1D lines")
I can use an available line lists or define my own lines (I know I need Hb4861.3 and the [OIII]4958.9,5006.8 doublet) and play with the redshift slider to match the lines in the line list with the lines in the spectrum. The line list plugin can be found clicking the plugin icon on the upper right of the viewer. To input just the three lines, I can use the “Custom” menu.
Here is the documentation where line lists are explained: https://jdaviz.readthedocs.io/en/latest/specviz/plugins.html#line-lists
I can also define the lines of interest programmatically, as shown in the following cell.
lt = QTable()
lt['linename'] = ['Hb', '[OIII]1', '[OIII]2']
lt['rest'] = [4861.3, 4958.9, 5006.8]*u.AA
viz2.load_line_list(lt)
The lines are not showing now because their rest value is outside the range plotted here. I can move the lines using the redshift slider in the line list plugin. It is best to first set the redshift to 2 in the box with the number and then move the slider to bring the lines on top of the observed emission lines.
Get the redshift out in the Spectrum1D object#
spec1d_redshift = viz2.get_spectra(apply_slider_redshift=True)["NIRISS 1D lines"]
print(spec1d_redshift)
print()
if spec1d_redshift.redshift != 0.0:
print("NIRISS 1D lines redshift=", spec1d_redshift.redshift)
else:
print("Redshift was not defined in GUI. Defining it here.")
spec1d_redshift.set_redshift_to(2.2138)
print("NIRISS 1D lines redshift=", spec1d_redshift.redshift)
Spectrum1D (length=69)
flux: [ 1.6163e-06 Jy, ..., 2.6548e-06 Jy ], mean=3.4997e-06 Jy
spectral axis: [ 1.6593 um, ..., 1.3403 um ], mean=1.4998 um
uncertainty: [ StdDevUncertainty(1.28849383e-07), ..., StdDevUncertainty(9.87921686e-08) ]
Redshift was not defined in GUI. Defining it here.
NIRISS 1D lines redshift= 2.2138000000000004
5. Model the continuum of the spectrum#
I open another instance of Specviz and load the same specrum used before.
viz3 = Specviz()
viz3.show()

viz3.load_data(spec1d_line, "NIRISS 1D lines")
I can use the GUI to select the region where I see the continuum. Challenge: select a discontinuous subset that covers two intervals (1.35-1.55um and 1.63-1.65um). Hint: select “Add” at the top near the Subset dropdown.
I can then use the Model Fitting plugin under the plugin icon to fit a linear model to the selected region. Instructions can be found here: https://jdaviz.readthedocs.io/en/latest/specviz/plugins.html#model-fitting. The individual steps to complete this task are:
Select Subset 1 under Data
Select Linear1D under Model
Click Add model
Enter a name for the model under Model Label (I choose “continuum”)
Click Fit
I can extract the model and its parameters from the datasets in use.
try:
dataout3 = viz3.get_spectra()
spectrum = dataout3["NIRISS 1D lines"] # This is exactly the same as the spec1d_lines loaded a few cells above
continuum = dataout3["continuum"]
model_param = viz3.get_model_parameters()
print(continuum)
print(model_param['continuum'])
except KeyError:
print("Continuum has not been created. Setting it to 0")
continuum = Spectrum1D(spectral_axis=spectrum.spectral_axis, flux=0.*spectrum.flux)
Continuum has not been created. Setting it to 0
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.11.6/x64/lib/python3.11/site-packages/jdaviz/configs/specviz/helper.py:131: UserWarning: Applying the value from the redshift slider to the output spectra. To avoid seeing this warning, explicitly set the apply_slider_redshift keyword option to True or False.
warnings.warn("Applying the value from the redshift "
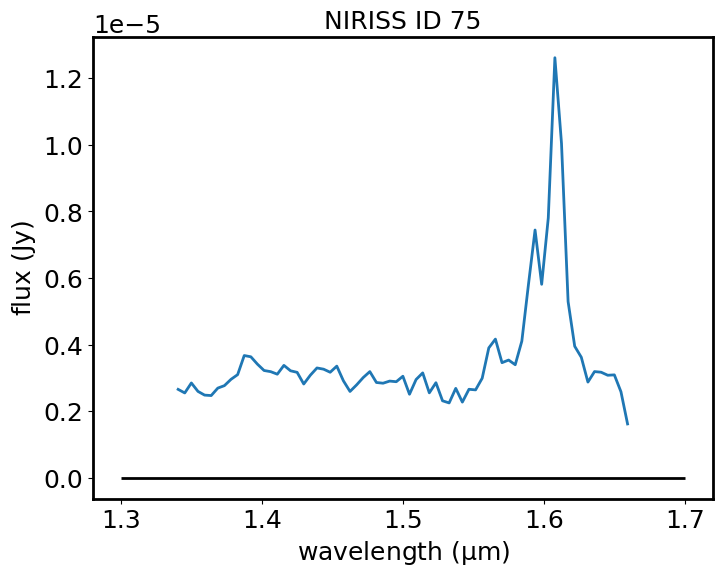
I can do a continuum subtraction and plot the result with matplotlib. If the continuum has not been defined in the GUI, this operation returns the original spectrum unchanged.
spectrum_sub = spectrum - continuum
plt.plot(spectrum_sub.spectral_axis, spectrum_sub.flux)
plt.hlines(0, 1.3, 1.7, color='black')
plt.xlabel("wavelength ({:latex})".format(spectrum_sub.spectral_axis.unit))
plt.ylabel("flux ({:latex})".format(spectrum_sub.flux.unit))
plt.title("NIRISS ID 75")
plt.show()