JWST PSFs: Using Wavefronts Measured On Orbit#
STPSF, formerly knows as WebbPSF, includes code for using the results of in-flight wavefront sensing measurements, by retrieving Optical Path Difference (OPD) files. These can be used to create simulated PSFs appropriate for a given instrument, detector, and time.
This notebook serves as a reference for how to use STPSF to search for and retrieve an OPD file, and explains the contents of this file. It also shows how to load multiple OPD files and plot changes in the wavefront properties over time. It also contains an example case of using an OPD file to create and subtract a simulated PSF from an in-flight image.
Details on the use of STPSF’s in-flight OPDs are given here: https://stpsf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/jwst_measured_opds.html
Author: Marcio Melendez Hernandez
Last Updated: 13 Feb 2025
Index#
For other STPSF examples: https://stpsf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/more_examples.html
Imports and Setup#
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
import poppy
import numpy as np
import os
import datetime
import tarfile
from urllib.parse import urlparse
import requests
import stpsf
import astropy
from astropy.nddata import Cutout2D
from astropy.visualization import simple_norm
from astropy.io import fits
from astropy.stats import SigmaClip
from astropy.visualization.mpl_normalize import ImageNormalize
from astropy.visualization import LogStretch
from astropy.modeling import models, fitting
import photutils
from photutils.background import Background2D, MedianBackground
from photutils.detection import IRAFStarFinder
from photutils.psf import PSFPhotometry
**WARNING**: LOCAL JWST PRD VERSION PRDOPSSOC-068 DOESN'T MATCH THE CURRENT ONLINE VERSION PRDOPSSOC-071
Please consider updating pysiaf, e.g. pip install --upgrade pysiaf or conda update pysiaf
# Files containing such information as the JWST pupil shape, instrument throughputs, and aperture positions are distributed separately from STPSF.
# To run STPSF, you must download these files and tell STPSF where to find them using the STPSF_PATH environment variable.
# Set environmental variables
os.environ["STPSF_PATH"] = "./data/stpsf-data"
# STPSF Data
stpsf_url = 'https://stsci.box.com/shared/static/kqfolg2bfzqc4mjkgmujo06d3iaymahv.gz'
stpsf_file = './stpsf-data-LATEST.tar.gz'
stpsf_folder = "./data"
def download_file(url, dest_path, timeout=60):
parsed_url = urlparse(url)
if parsed_url.scheme not in ["http", "https"]:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported URL scheme: {parsed_url.scheme}")
response = requests.get(url, stream=True, timeout=timeout)
response.raise_for_status()
with open(dest_path, "wb") as f:
for chunk in response.iter_content(chunk_size=8192):
f.write(chunk)
# Gather stpsf files
stpsfExist = os.path.exists(stpsf_folder)
if not stpsfExist:
os.makedirs(stpsf_folder)
download_file(stpsf_url, stpsf_file)
gzf = tarfile.open(stpsf_file)
gzf.extractall(stpsf_folder, filter='data')
Finding the measured wavefront near a given date#
nrc = stpsf.NIRCam()
nrc.filter = 'F200W'
nrc.detector = 'NRCB2'
nrc.detector_position = (1024, 1024)
The interpixel capacitance effect is now included for oversampled outputs as well as for the detector-sampled outputs (in the geometric distortion extension). Remember that, in general, the last (“DET_DIST”) FITS extension of the output PSF FITS file are the output data product that most represents the PSF as actually observed on a detector.
In any case, there are way to disable any detector effects or to adjust the empirical approximation of charge difussion. For example:
nrc.options['charge_diffusion_sigma'] = 0
nrc.options['add_ipc'] = False
output_path = os.getcwd()
nrc.load_wss_opd_by_date('2022-07-01T00:00:00', plot=True, output_path=output_path)
# choice : string . Default 'closest'
# Method to choose which OPD file to use, e.g. 'before', 'after'
MAST OPD query around UTC: 2022-07-01T00:00:00.000
MJD: 59761.0
OPD immediately preceding the given datetime:
URI: mast:JWST/product/R2022063002-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits
Date (MJD): 59759.6628
Delta time: -1.3372 days
OPD immediately following the given datetime:
URI: mast:JWST/product/R2022070403-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits
Date (MJD): 59761.5484
Delta time: 0.5484 days
User requested choosing OPD time closest in time to 2022-07-01T00:00:00.000, which is R2022070403-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits, delta time 0.548 days
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022070403-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to /home/runner/work/jdat_notebooks/jdat_notebooks/notebooks/cross_instrument/stpsf_examples/R2022070403-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Importing and format-converting OPD from /home/runner/work/jdat_notebooks/jdat_notebooks/notebooks/cross_instrument/stpsf_examples/R2022070403-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits
Backing out SI WFE and OTE field dependence at the WF sensing field point (NRCA3_FP1)
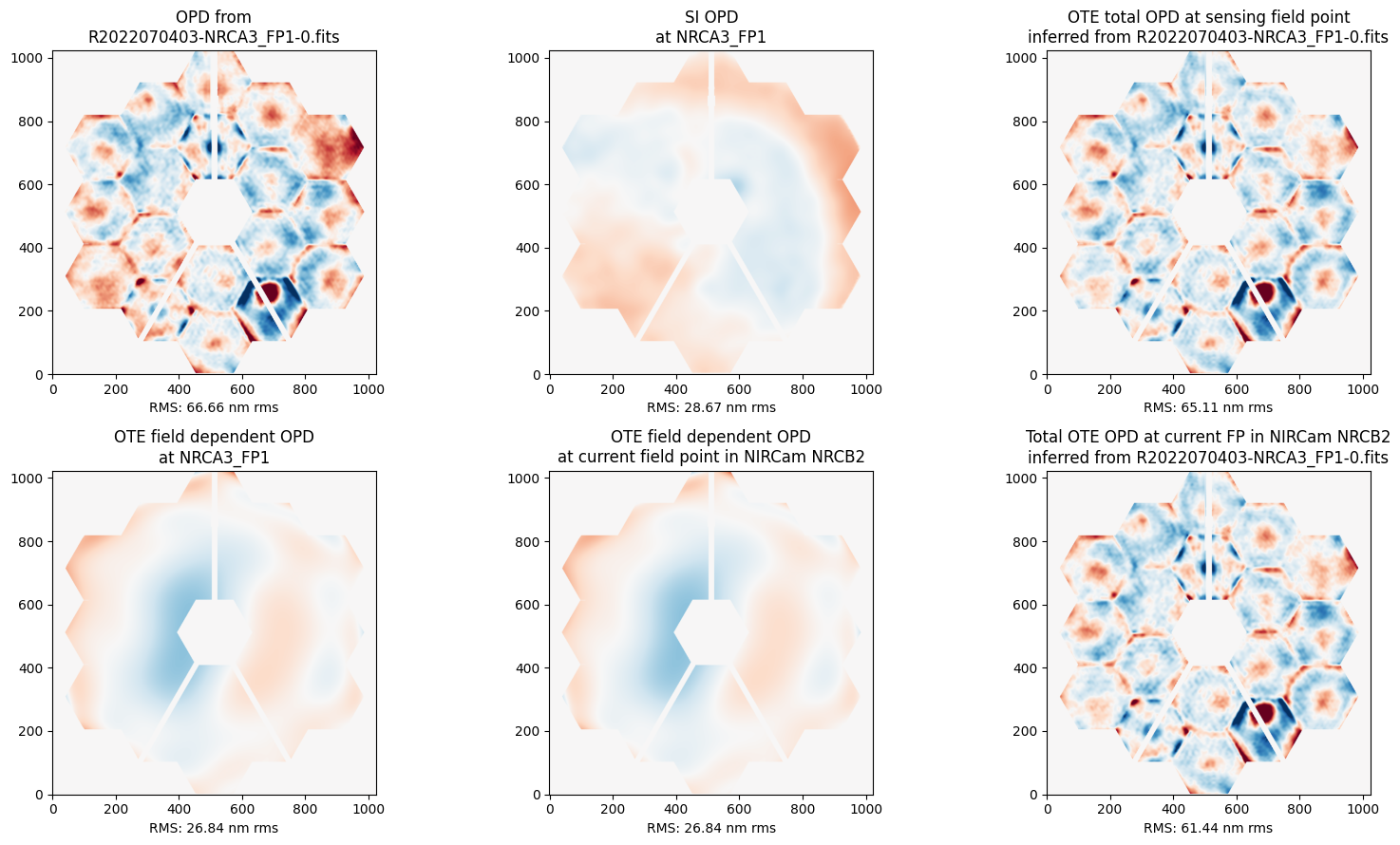
Upper Left: This is the measured OPD as sensed in NIRCam at “field point 1” which is in the upper left corner of NRCA3, relatively close to the center of the NIRCam module. This observatory total OPD measurement includes both the telescope and NIRCam contributions to the WFE.
Upper Middle: This is the wavefront map for the NIRCam portion of the WFE at that field point. This is known from ground calibration test data, not measured in flight.
Upper Right: That NIRCam WFE contribution is subtracted from the total observatory WFE to yield this estimate of the OTE-only portion of the WFE.
Lower Left and Middle: These are models for the field dependence of the OTE OPD between the sensing field point in NRCA3 and the requested field ooint, in this case in NRCB2. This field dependence arises mostly from the figure of the tertiary mirror. These are used to transform the estimated OTE OPD from one field position to another.
Lower Right: This is the resulting estimate for the OTE OPD at the requested field point, in this case in NRCB2.
# What's inside an OPD?
opd_fn = 'R2022070403-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits'
opd = fits.open(os.path.join(output_path, opd_fn))
opd.info()
norm = ImageNormalize(stretch=LogStretch(), vmin=1e-10, vmax=1e-6)
plt.figure(figsize=[10, 18])
for i in range(1, len(opd)):
plt.subplot(5, 3, i)
if i == 2:
plt.imshow(opd[i].data, norm=norm, origin='lower')
else:
plt.imshow(opd[i].data, origin='lower')
Filename: /home/runner/work/jdat_notebooks/jdat_notebooks/notebooks/cross_instrument/stpsf_examples/R2022070403-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits
No. Name Ver Type Cards Dimensions Format
0 PRIMARY 1 PrimaryHDU 23 ()
1 RESULT_PHASE 1 ImageHDU 184 (256, 256) float32
2 RESULT_PSF 1 ImageHDU 11 (545, 545) float32
3 EXPECTED 1 ImageHDU 13 (256, 256) float32
4 PUPIL_MASK 1 ImageHDU 11 (256, 256) int16
5 RAW_PSF 1 ImageHDU 14 (256, 256) float32
6 CALC_PSF 1 ImageHDU 12 (546, 546) float32
7 CALC_AMP 1 ImageHDU 12 (256, 256) float32
8 HO_PHASE 1 ImageHDU 12 (256, 256) float32
9 LO_PHASE 1 ImageHDU 12 (256, 256) float32
10 RAW_PSF 1 ImageHDU 14 (256, 256) float32
11 CALC_PSF 1 ImageHDU 12 (546, 546) float32
12 CALC_AMP 1 ImageHDU 12 (256, 256) float32
13 HO_PHASE 1 ImageHDU 12 (256, 256) float32
14 LO_PHASE 1 ImageHDU 12 (256, 256) float32
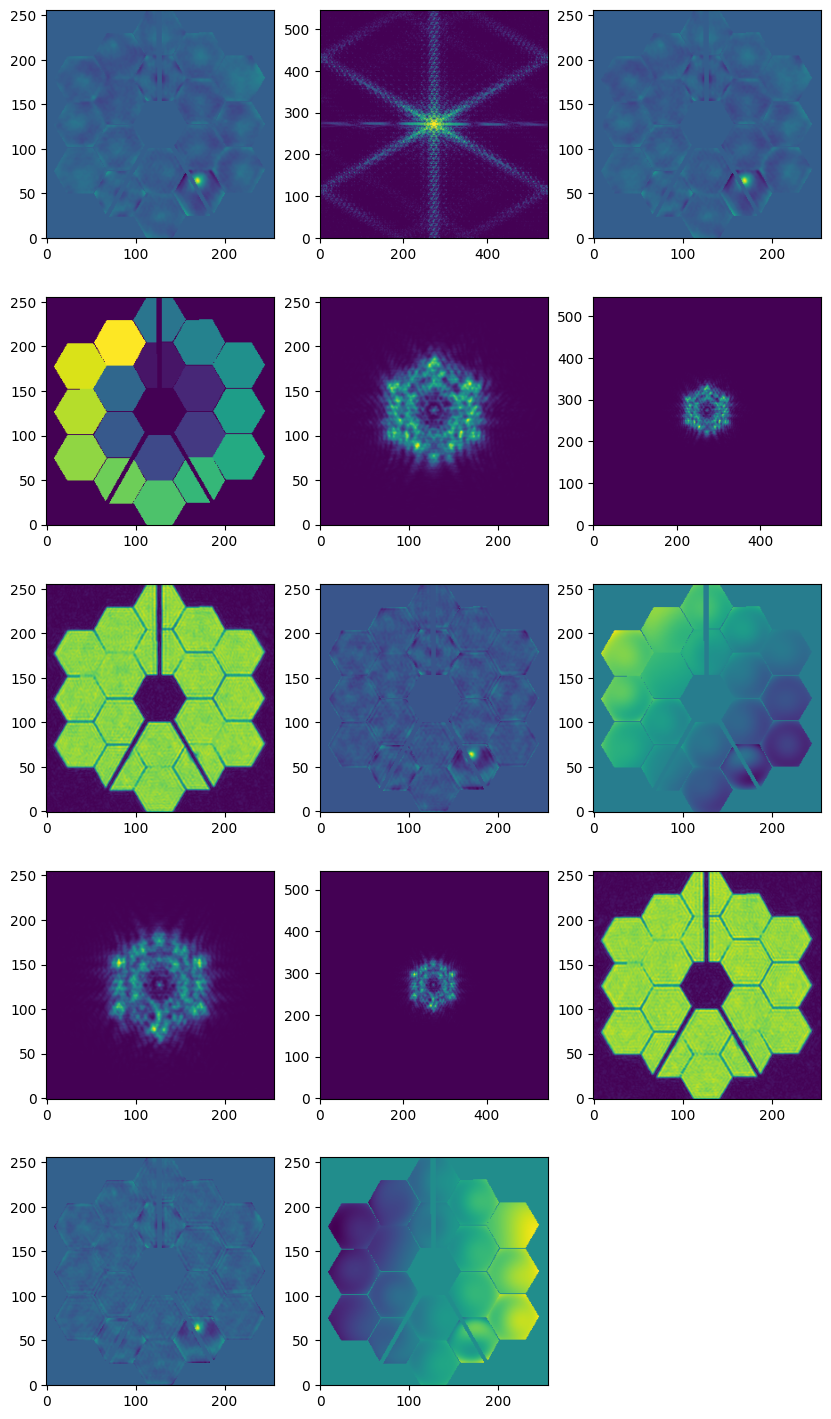
OPD File description#
RESULT_PHASE Image Extension. The FITS file contains a ‘RESULT’ image extension, which is the average of the optical path difference results from all images analyzed together in the phase retrieval
RESULT_PSF Image Extension The FITS file contains a ‘RESULT_PSF’ image extension, which is the PSF computed from the resultant phase by the WAS
EXPECTED Image Extension The FITS file contains an ‘EXPECTED’ image extension, which is the expected optical path difference if the WAS-recommended correction is applied
PUPIL_MASK Image Extension The FITS file contains a ‘PUPIL_MASK’ image extension, which is the pupil mask used to compute the PSF from the resultant phase
The FITS file contains five image extensions for each analyzed input image. In the case of the sensing program, there are 2 images +/-8WL
RAW_PSF Image Extensions For each input image, the Raw PSF extension will contain the raw extracted subimage taken from the calibrated science data
CALC_PSF Image Extensions For each input image, the Calculated PSF extension will contain an image which represents the estimated PSF as calculated by the phase retrieval process
CALC_AMP Image Extension For each input image, the Calculated Amplitude extension will contain an image which represents the estimated pupil amplitude as calculated by the phase retrieval process
HO_PHASE Image Extension For each input image, the High-Order Phase extension will contain an image which represents the retrieved phase information minus the Low-Order (controllable) phase as calculated by the phase retrieval process.
LO_PHASE Image Extension For each input image, the Low-Order Phase extension will contain an image which represents the retrieved controllable phase information as calculated by the phase retrieval process
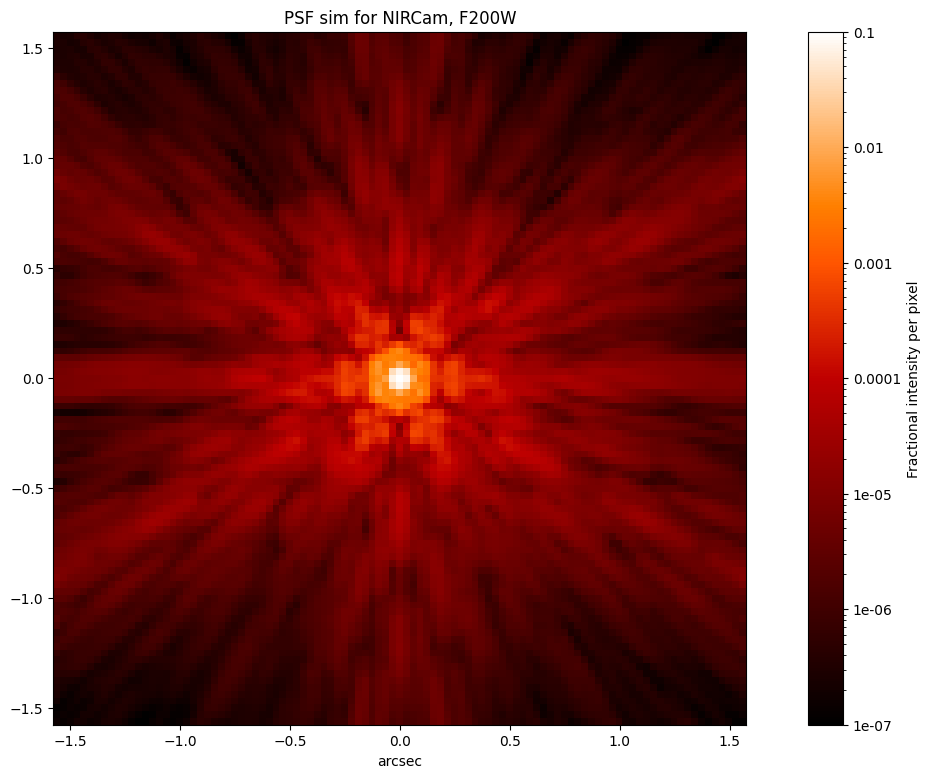
# Let's simulate Webb's PSF from the OPD above
# The PSF below is calculated using the actual
# as-measured-at-L2 state of the telescope WFE near
# the requested date, in this case 2022 July 1.
psf = nrc.calc_psf(fov_pixels=101)
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 9))
stpsf.display_psf(psf, ext=1)
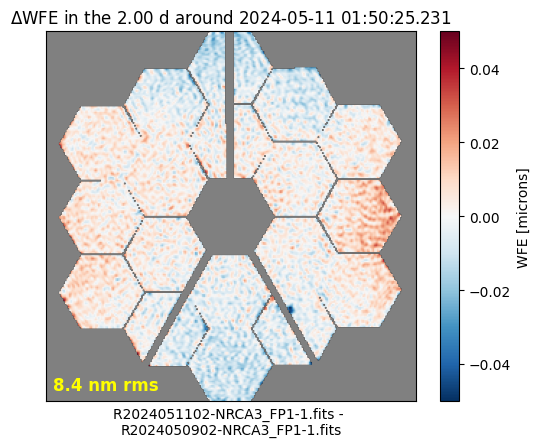
Delta Wavefront Error Around Time of Observation#
stpsf.trending.delta_wfe_around_time('2024-05-11 01:50:25.231')
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024050902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024050902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024051102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024051102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
array([[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
...,
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.]], shape=(256, 256), dtype=float32)
Setup a PSF simulation using a particular observation#
def mast_retrieve_files(filename, output_path=None, verbose=False, redownload=False, token=None):
"""Download files from MAST.
If file is already present locally, the download is skipped and the cached file is used.
"""
import os
from requests.exceptions import HTTPError
from astroquery.mast import Mast
if token:
Mast.login(token=token)
if output_path is None:
output_path = '.'
else:
output_path = output_path
output_filename = os.path.join(output_path, filename)
if not os.path.exists(output_path):
os.mkdir(output_path)
if os.path.exists(output_filename) and not redownload:
if verbose:
print(f"Found file previously downloaded: {filename}")
return output_filename
data_uri = f'mast:JWST/product/{filename}'
# Download the file
url_path = Mast._portal_api_connection.MAST_DOWNLOAD_URL
try:
Mast._download_file(url_path + "?uri=" + data_uri, output_filename)
except HTTPError as err:
print(err)
return output_filename
file = 'jw04500-o056_t012_nircam_f212n-wlm8-nrca3_wfscmb-04.fits'
mast_retrieve_files(file)
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/jw04500-o056_t012_nircam_f212n-wlm8-nrca3_wfscmb-04.fits to ./jw04500-o056_t012_nircam_f212n-wlm8-nrca3_wfscmb-04.fits ...
[Done]
'./jw04500-o056_t012_nircam_f212n-wlm8-nrca3_wfscmb-04.fits'
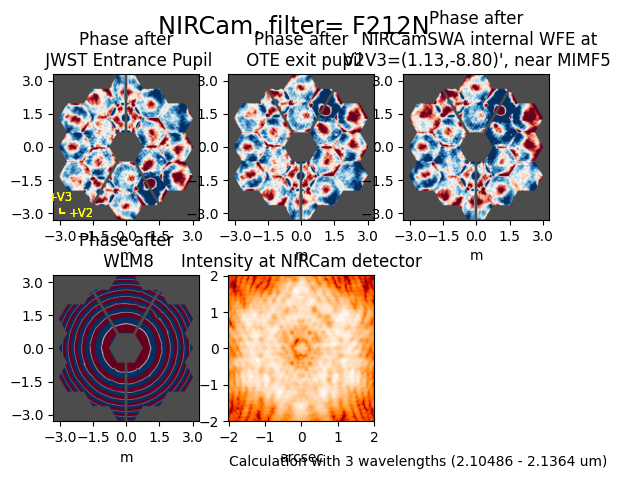
inst = stpsf.setup_sim_to_match_file(file)
position = (512, 1024) # source position
size_pixels = 128 # size in pixels
inst.detector_position = position
single_stpsf_nrc = inst.calc_psf(fov_pixels=size_pixels, display=True)
Setting up sim to match jw04500-o056_t012_nircam_f212n-wlm8-nrca3_wfscmb-04.fits
iterating query, tdelta=3.0
MAST OPD query around UTC: 2024-07-07T13:31:51.488
MJD: 60498.56379037037
OPD immediately preceding the given datetime:
URI: mast:JWST/product/O2024070701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Date (MJD): 60498.5637
Delta time: -0.0001 days
OPD immediately following the given datetime:
URI: mast:JWST/product/O2024070901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Date (MJD): 60500.6226
Delta time: 2.0588 days
User requested choosing OPD time closest in time to 2024-07-07T13:31:51.488, which is O2024070701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits, delta time -0.000 days
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024070701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024070701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Importing and format-converting OPD from data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024070701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Backing out SI WFE and OTE field dependence at the WF sensing field point (NRCA3_FP1)
Configured simulation instrument for:
Instrument: NIRCam
Filter: F212N
Detector: NRCA3
Apername: NRCA3_FULL
Det. Pos.: (1024, 1024)
Image plane mask: None
Pupil plane mask: WLM8
Trending Wavefront Changes over Time#
trend_table = stpsf.trending.monthly_trending_plot(2024, 6, verbose=False)
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024053002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024053002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024060102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024060102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024060302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024060302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024060501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024060501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024060602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024060602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024060801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024060801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024061001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024061001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024061301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024061301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024061501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024061501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024061701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024061701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024061801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024061801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024062101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024062101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024062301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024062301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024062401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024062401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024062601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024062601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024062801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024062801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024062901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024062901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]

trend_table
| Date | Filename | WFS Type | RMS WFE (OTE+SI) | RMS WFE (OTE only) | EE(2.5 pix) | EE(10pix) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nm | nm | |||||
| str23 | str29 | str7 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 |
| 2024-05-29T20:28:16.000 | R2024053002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 67.3914750239438 | 63.37095480426078 | 0.6719226329668622 | 0.8764040777120373 |
| 2024-06-01T07:23:31.400 | R2024060102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 67.58286840572374 | 63.77091225744318 | 0.671716224637393 | 0.8763351547370711 |
| 2024-06-03T03:45:45.700 | R2024060302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 67.85527338663354 | 63.5824560042632 | 0.6717277183894746 | 0.8763239348265368 |
| 2024-06-05T02:32:29.000 | O2024060501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 67.89438388454889 | 63.6531276812743 | 0.6717958424990571 | 0.8764245973149776 |
| 2024-06-06T18:40:02.000 | O2024060602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 68.10348101293754 | 63.930358874980925 | 0.6715480464724863 | 0.8765101726668102 |
| 2024-06-08T10:33:16.100 | O2024060801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 68.35284319652993 | 64.30054670481503 | 0.6712569300298153 | 0.8764032913784519 |
| 2024-06-10T00:25:49.700 | O2024061001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 68.12892606755149 | 64.23481177221457 | 0.6712435376220324 | 0.8764395816200582 |
| 2024-06-12T17:17:56.200 | O2024061301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 68.13602214356894 | 64.29193242420946 | 0.6711962144562941 | 0.8764299998890757 |
| 2024-06-15T02:37:35.900 | O2024061501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 68.65781083419657 | 64.51686307694685 | 0.6710741573631243 | 0.8764018632655044 |
| 2024-06-16T20:16:29.500 | O2024061701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 67.77755625455714 | 63.6214409814475 | 0.6716471649887765 | 0.8770141611678653 |
| 2024-06-18T08:42:51.200 | O2024061801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 68.22087337229252 | 64.30479742513361 | 0.6710999994898569 | 0.876457100479267 |
| 2024-06-20T18:43:56.200 | O2024062101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 68.390468368524 | 64.45326019746298 | 0.6711954538707969 | 0.8764130078787915 |
| 2024-06-23T07:34:47.400 | O2024062301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 68.01667326098666 | 64.34161990641942 | 0.6712244606699806 | 0.8764568399289001 |
| 2024-06-24T12:30:24.200 | O2024062401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 68.11333031194276 | 64.2542535052067 | 0.671209854304376 | 0.8765185680175227 |
| 2024-06-26T05:34:54.000 | O2024062601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 68.29756935101497 | 64.86571635421303 | 0.670749729019986 | 0.8764423226596338 |
| 2024-06-27T19:33:03.300 | O2024062801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 68.01260105823671 | 64.90436149662719 | 0.6707506032794925 | 0.8763846063022834 |
| 2024-06-29T11:11:11.900 | O2024062901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | Sensing | 68.61955754982067 | 65.40644711461796 | 0.670565698344554 | 0.8763606492879847 |
Wavefront time series and histogram plots#
Table of all OPDs#
Retrieve a table of all available OPDs and plot the measurements over time
opdtable = stpsf.mast_wss.retrieve_mast_opd_table()
opdtable = stpsf.mast_wss.deduplicate_opd_table(opdtable)
opdtable
| date | date_obs_mjd | visitId | activity | apername | corr_id | fileName | dataURI | wfs_measurement_type | is_post_correction | is_pre_correction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str23 | float64 | str12 | str5 | str9 | str11 | str29 | str47 | str10 | bool | bool |
| 2022-03-11T19:37:04.200 | 59649.81740972222 | V01160001001 | 02109 | NRCA3_FP1 | R2022031401 | R2022031401-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2022031401-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits | post | True | False |
| 2022-03-12T13:56:12.900 | 59650.58070486111 | V01162001001 | 02101 | NRCA3_FP1 | O2022031301 | O2022031301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/O2022031301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2022-03-12T19:42:19.800 | 59650.8210625 | V01162006001 | 02101 | NRCA3_FP1 | R2022031401 | R2022031401-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2022031401-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2022-03-13T02:02:19.300 | 59651.084945601855 | V01162012001 | 02101 | NRCA3_FP1 | R2022031401 | R2022031401-NRCA3_FP1-12.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2022031401-NRCA3_FP1-12.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2022-03-14T15:44:07.500 | 59652.65564236111 | V01163006001 | 02107 | NRCA3_FP1 | R2022031405 | R2022031405-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2022031405-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | post | True | False |
| 2022-03-17T06:50:00.300 | 59655.284725694444 | V01163001001 | 02101 | NRCA3_FP1 | R2022032002 | R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2022-03-17T15:50:41.300 | 59655.66020023148 | V01163003001 | 02101 | NRCA3_FP1 | R2022031703 | R2022031703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2022031703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2022-03-17T22:54:02.800 | 59655.954199074076 | V01163004001 | 02107 | NRCA3_FP1 | R2022031801 | R2022031801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2022031801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | post | True | False |
| 2022-03-18T05:18:33.700 | 59656.22122337963 | V01163005001 | 02107 | NRCA3_FP1 | R2022032004 | R2022032004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2022032004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits | post | True | False |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2025-09-21T12:42:05.100 | 60939.529225694445 | V07344166001 | 03104 | NRCA1_FP6 | O2025092302 | O2025092302-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/O2025092302-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2025-09-25T22:49:21.900 | 60943.950947916666 | V07344113001 | 03104 | NRCA1_FP6 | O2025092601 | O2025092601-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/O2025092601-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2025-09-30T12:05:32.500 | 60948.50384837963 | V04430019001 | 03104 | NRCA1_FP6 | R2025093002 | R2025093002-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2025093002-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2025-10-05T07:19:49.000 | 60953.30542824074 | V07344139001 | 03104 | NRCA1_FP6 | O2025100501 | O2025100501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/O2025100501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2025-10-08T10:07:21.500 | 60956.42177662037 | V07052046001 | 03104 | NRCA1_FP6 | R2025100902 | R2025100902-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2025100902-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2025-10-11T14:03:29.300 | 60959.58575578704 | V07464004001 | 03104 | NRCA1_FP6 | R2025101202 | R2025101202-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2025101202-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2025-10-15T10:58:14.700 | 60963.45711458333 | V04430166001 | 03104 | NRCA1_FP6 | R2025101602 | R2025101602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2025101602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2025-10-18T22:55:25.400 | 60966.95515509259 | V07052106001 | 03104 | NRCA1_FP6 | R2025101902 | R2025101902-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2025101902-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2025-10-23T01:56:10.500 | 60971.08067708334 | V07344116001 | 03104 | NRCA1_FP6 | R2025102302 | R2025102302-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2025102302-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | pre | False | False |
| 2025-10-26T08:31:56.900 | 60974.355519675926 | V07464115001 | 03104 | NRCA1_FP6 | R2025102602 | R2025102602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | mast:JWST/product/R2025102602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits | pre | False | False |
Download all the OPDs from the opdtable object. Note that some functions need to have all the OPDs available.
stpsf.mast_wss.download_all_opds(opdtable)
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022031401-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022031401-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022031301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022031301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022031401-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022031401-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022031401-NRCA3_FP1-12.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022031401-NRCA3_FP1-12.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022031405-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022031405-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022031703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022031703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022031801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022031801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022031902-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022031902-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022031902-NRCA3_FP1-3.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022031902-NRCA3_FP1-3.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022031902-NRCA3_FP1-4.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022031902-NRCA3_FP1-4.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022031902-NRCA3_FP1-5.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022031902-NRCA3_FP1-5.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022031902-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022031902-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022031902-NRCA3_FP1-7.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022031902-NRCA3_FP1-7.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-3.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-3.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-4.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-4.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-5.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-5.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-7.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032002-NRCA3_FP1-7.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032005-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032005-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022032401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022032401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022032501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022032501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022032601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022032601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022032601-NRCA3_FP1-3.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022032601-NRCA3_FP1-3.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032603-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032603-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032603-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032603-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032701-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032701-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032801-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032801-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022032901-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022032901-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022033101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022033101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022033101-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022033101-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040101-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040101-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040201-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040201-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040301-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040301-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040401-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040401-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040501-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040501-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040602-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040602-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040702-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040702-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040802-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040802-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022040902-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022040902-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041101-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041101-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041201-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041201-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041301-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041301-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041402-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041402-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022041404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022041404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022041501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022041501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041506-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041506-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041506-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041506-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022041601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022041601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022041701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022041701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041906-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041906-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-3.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-3.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-4.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-4.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-5.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-5.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-7.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-7.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-8.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041801-NRCA3_FP1-8.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-3.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-3.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-4.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-4.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-5.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-5.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-7.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-7.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-8.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041902-NRCA3_FP1-8.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022041905-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022041905-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022042302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022042302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022042302-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022042302-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022042601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022042601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022042601-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022042601-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022042801-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022042801-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022043002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022043002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022050302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022050302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022050504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022050504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022050504-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022050504-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022050802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022050802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022050802-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022050802-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022050902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022050902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022051102-NRCA3_FP1-21.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022051102-NRCA3_FP1-21.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022051102-NRCA3_FP1-22.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022051102-NRCA3_FP1-22.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022051102-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022051102-NRCA3_FP1-6.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022051309-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022051309-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022052001-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022052001-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022052301-NRCA3_FP1-56.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022052301-NRCA3_FP1-56.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022052301-NRCA3_FP1-57.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022052301-NRCA3_FP1-57.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022052501-NRCA3_FP1-59.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022052501-NRCA3_FP1-59.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022052701-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022052701-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022052701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022052701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022060101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022060101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022060101-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022060101-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022060103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022060103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022060402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022060402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022060602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022060602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022060802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022060802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022060802-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022060802-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022061001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022061001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022061001-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022061001-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022061302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022061302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022061403-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022061403-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022061602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022061602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022072501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022072501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022061904-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022061904-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022062004-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022062004-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022062004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022062004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022062701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022062701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022062102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022062102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022062704-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022062704-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022063002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022063002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022063002-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022063002-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022070403-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022070403-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022070405-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022070405-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022070601-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022070601-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023050803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023050803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023050804-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023050804-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022071001-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022071001-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022071306-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022071306-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023040601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023040601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023040602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023040602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022071702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022071702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022071902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022071902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022072201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022072201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022072401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022072401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022072601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022072601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022072902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022072902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022073001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022073001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022080204-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022080204-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023050801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023050801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023050802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023050802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022081102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022081102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022081401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022081401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022081601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022081601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022081602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022081602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022082003-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022082003-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022082202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022082202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022090101-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022090101-NRCA3_FP1-2.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022082702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022082702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022082903-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022082903-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022083108-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022083108-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022083109-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022083109-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022090201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022090201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022090302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022090302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022090506-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022090506-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022090903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022090903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022090902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022090902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022090905-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022090905-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022091301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022091301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022091601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022091601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022091801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022091801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022091802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022091802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022092301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022092301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022092102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022092102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022092302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022092302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022092601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022092601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022092801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022092801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022100201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022100201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022100401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022100401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022100803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022100803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022100805-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022100805-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022101103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022101103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022101302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022101302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022101701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022101701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022101904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022101904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022102003-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022102003-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022102005-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022102005-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022102201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022102201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022102401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022102401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022102603-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022102603-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022102703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022102703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022102704-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022102704-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022102903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022102903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022110103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022110103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022110304-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022110304-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022110504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022110504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022110703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022110703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022110904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022110904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022111307-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022111307-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022111308-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022111308-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022111504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022111504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022111703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022111703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022111903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022111903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022112103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022112103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022112503-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022112503-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R202211250C-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R202211250C-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022112901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022112901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022112704-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022112704-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022112904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022112904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022120204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022120204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022120404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022120404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022120601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022120601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022120904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022120904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022121103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022121103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022121303-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022121303-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022121504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022121504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022121703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022121703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022122004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022122004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2022122301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2022122301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022122504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022122504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022122704-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022122704-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022122904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022122904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022123104-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022123104-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023010204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023010204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023010601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023010601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023010704-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023010704-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023011004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023011004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023011203-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023011203-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023011204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023011204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023011403-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023011403-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023011501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023011501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023011802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023011802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023011903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023011903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023012203-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023012203-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023012304-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023012304-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023012604-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023012604-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023012803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023012803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023012904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023012904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023020103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023020103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023020303-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023020303-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023020503-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023020503-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023020604-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023020604-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023020804-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023020804-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023021004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023021004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023021204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023021204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023021504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023021504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023021704-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023021704-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023021904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023021904-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023022103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023022103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023022303-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023022303-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023022503-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023022503-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023022703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023022703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023022803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023022803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023030303-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023030303-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023030503-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023030503-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023030804-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023030804-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023031302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023031302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023031303-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023031303-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023031604-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023031604-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023031703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023031703-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023031902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023031902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023032204-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023032204-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023032504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023032504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023032505-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023032505-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023032701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023032701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023032801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023032801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023033002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023033002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023040102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023040102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023040302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023040302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023040504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023040504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023040702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023040702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023040902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023040902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023040903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023040903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023041201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023041201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023041402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023041402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023041602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023041602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023041702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023041702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023042201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023042201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023042302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023042302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023042501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023042501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023042701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023042701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023043001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023043001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023050201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023050201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023050402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023050402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023050602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023050602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023050805-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023050805-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023051102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023051102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023051103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023051103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023051202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023051202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023051402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023051402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023051601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023051601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023051901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023051901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023052101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023052101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023052201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023052201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023052401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023052401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023052601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023052601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023052801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023052801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023053001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023053001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023060101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023060101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023060301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023060301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023060502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023060502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023060801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023060801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023060901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023060901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023061101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023061101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023061301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023061301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023061501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023061501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023061802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023061802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023061901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023061901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023062102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023062102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023062403-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023062403-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023062603-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023062603-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023062802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023062802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023063003-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023063003-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023070203-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023070203-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023070403-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023070403-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023070603-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023070603-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023070803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023070803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023071203-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023071203-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023071403-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023071403-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023071603-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023071603-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023071803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023071803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023072203-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023072203-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023072204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023072204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023072205-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023072205-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023072401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023072401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023072601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023072601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023072801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023072801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023072901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023072901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023073101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023073101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023080201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023080201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023080401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023080401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023080601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023080601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023080901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023080901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023081101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023081101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023081302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023081302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023081402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023081402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023081602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023081602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023081702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023081702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023082001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023082001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023082102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023082102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023082301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023082301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023082501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023082501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023082701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023082701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023082901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023082901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023083101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023083101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023090202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023090202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023090402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023090402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023090601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023090601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023090801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023090801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023091101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023091101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023091202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023091202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023091601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023091601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023091901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023091901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023091902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023091902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023092101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023092101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023092202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023092202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023092502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023092502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023092702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023092702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023092902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023092902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023100103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023100103-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023100604-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023100604-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023100601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023100601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023100901-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023100901-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023101003-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023101003-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023101005-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023101005-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023101202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023101202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023101503-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023101503-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023101504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023101504-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023101603-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023101603-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023101802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023101802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023102002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023102002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023102301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023102301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023102402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023102402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023102701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023102701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023102801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023102801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023103002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023103002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023110202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023110202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023110402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023110402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023110801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023110801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023110802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023110802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023111002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023111002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023111202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023111202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023111402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023111402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023111601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023111601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023111701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023111701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023112001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023112001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023112201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023112201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023112501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023112501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023112701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023112701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2023112901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2023112901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023120101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023120101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023120102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023120102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023120402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023120402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023120404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023120404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023120702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023120702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023120902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023120902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023121102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023121102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023121302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023121302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023121502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023121502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023121802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023121802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023121902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023121902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023122102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023122102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023122302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023122302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023122402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023122402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023122702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023122702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023122902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023122902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2023123102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2023123102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024010102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024010102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024010401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024010401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024010601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024010601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024010801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024010801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024010802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024010802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024010803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024010803-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024011001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024011001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024011201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024011201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024011301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024011301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024011601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024011601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024011701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024011701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024011803-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024011803-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024012002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024012002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024012003-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024012003-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024012202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024012202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024012401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024012401-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024012502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024012502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024012702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024012702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024012902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024012902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024012903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024012903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024013102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024013102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024020202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024020202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024020402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024020402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024020602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024020602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024021001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024021001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024021101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024021101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024021301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024021301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024021601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024021601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024021701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024021701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024021901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024021901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024022102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024022102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024022302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024022302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024022501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024022501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024030101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024030101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024022901-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024022901-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024022903-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024022903-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024030102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024030102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024030104-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024030104-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024030202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024030202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024030403-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024030403-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024030602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024030602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024030801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024030801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024031001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024031001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024031202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024031202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024031302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024031302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024031601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024031601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024031702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024031702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024031802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024031802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024032002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024032002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024032202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024032202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024032402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024032402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024032602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024032602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024032901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024032901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024033001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024033001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024033101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024033101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024033102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024033102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024040501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024040501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024040701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024040701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024041001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024041001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024041101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024041101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024041502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024041502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024041601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024041601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024042102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024042102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024042301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024042301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024042502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024042502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024042702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024042702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024042802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024042802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024050101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024050101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024050604-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024050604-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024050601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024050601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024050802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024050802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024051402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024051402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024051802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024051802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024052002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024052002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024052202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024052202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024052402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024052402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024052602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024052602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024052802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024052802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024070101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024070101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024070301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024070301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024070302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024070302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024070501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024070501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024070901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024070901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024071102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024071102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024071302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024071302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024071502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024071502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024071702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024071702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024071902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024071902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024072102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024072102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024072301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024072301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024072501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024072501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024072701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024072701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024072901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024072901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024073102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024073102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024080501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024080501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024080502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024080502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024080801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024080801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024080901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024080901-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024081101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024081101-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024081301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024081301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024081601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024081601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024081701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024081701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024082302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024082302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024082402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024082402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024082602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024082602-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024082802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024082802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024083001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024083001-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024083102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024083102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024090402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024090402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024090701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024090701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024090801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024090801-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024091102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024091102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024091301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024091301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024091501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024091501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024091702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024091702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024091902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024091902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024092202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024092202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024092402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024092402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024092502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024092502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024092802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024092802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024093004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024093004-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024100302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024100302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024100303-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024100303-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024100601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024100601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024100702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024100702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024100902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024100902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024101102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024101102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024101301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024101301-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024101501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024101501-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024101701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024101701-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024102102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024102102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024102402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024102402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024102702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024102702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024102902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024102902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024110102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024110102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024110302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024110302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024110502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024110502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024110702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024110702-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024110902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024110902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024111002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024111002-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024111202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024111202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024111402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024111402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024111502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024111502-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024111902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024111902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024112102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024112102-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024112202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024112202-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024112302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024112302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024112402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024112402-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024112601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024112601-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024112802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024112802-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024112902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024112902-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024120201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024120201-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024120503-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024120503-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024120504-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024120504-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2024120603-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2024120603-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024121001-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024121001-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024121401-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024121401-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024121801-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024121801-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024122101-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024122101-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024122501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024122501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2024122801-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2024122801-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025010101-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025010101-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025010501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025010501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025010801-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025010801-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025010802-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025010802-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025011301-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025011301-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025011501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025011501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025012101-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025012101-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025012501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025012501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025012801-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025012801-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025020101-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025020101-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025020102-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025020102-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025020501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025020501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025020901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025020901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025021301-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025021301-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025021701-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025021701-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025022001-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025022001-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025022301-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025022301-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025022802-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025022802-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025030402-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025030402-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025030902-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025030902-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025031302-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025031302-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025031702-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025031702-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025032102-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025032102-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025032601-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025032601-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025033001-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025033001-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025033002-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025033002-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025040201-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025040201-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025040401-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025040401-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025040901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025040901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025041401-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025041401-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025041601-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025041601-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025042002-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025042002-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025042402-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025042402-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025042702-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025042702-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025050102-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025050102-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025050601-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025050601-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025051201-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025051201-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025051401-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025051401-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025051802-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025051802-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025052202-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025052202-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025052602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025052602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025053102-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025053102-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025060703-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025060703-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025060901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025060901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025061206-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025061206-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025061501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025061501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025062001-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025062001-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025062501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025062501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025062901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025062901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025070202-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025070202-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025070203-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025070203-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025070501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025070501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025071002-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025071002-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025071402-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025071402-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025071802-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025071802-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025072202-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025072202-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025072502-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025072502-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025072902-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025072902-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025080302-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025080302-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025080602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025080602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025081201-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025081201-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025081501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025081501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025081901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025081901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025082201-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025082201-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025082501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025082501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025082901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025082901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025090301-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025090301-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025090901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025090901-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025091102-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025091102-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025091602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025091602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025091702-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025091702-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025092302-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025092302-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025092601-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025092601-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025093002-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025093002-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/O2025100501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/O2025100501-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025100902-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025100902-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025101202-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025101202-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025101602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025101602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025101902-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025101902-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025102302-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025102302-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2025102602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2025102602-NRCA1_FP6-1.fits ...
[Done]
Trending Plots#
stpsf.trending.wavefront_time_series_plot(opdtable)
WARNING: TimeDeltaMissingUnitWarning: Numerical value without unit or explicit format passed to TimeDelta, assuming days [astropy.time.core]
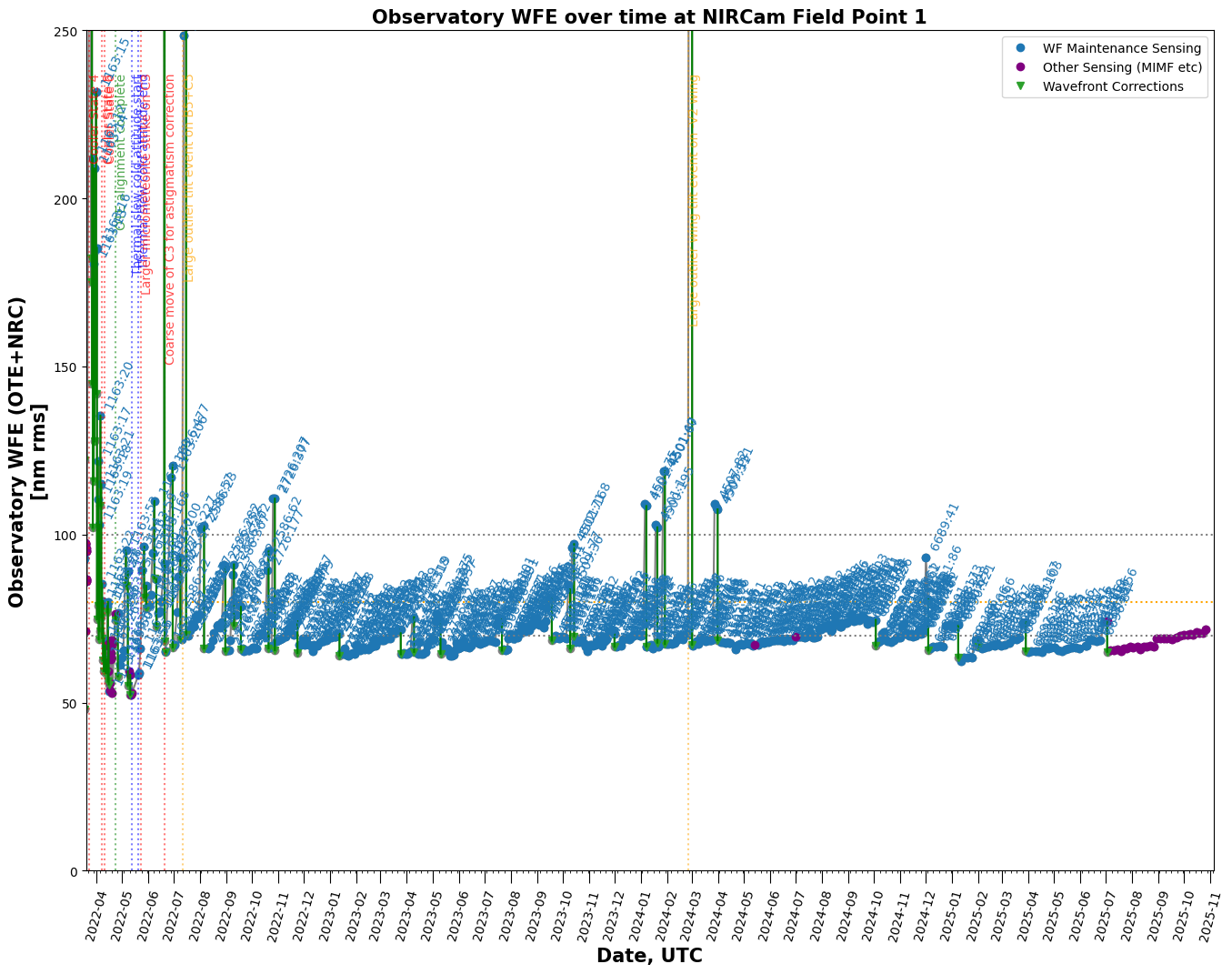
Plot over a time range#
start_date = datetime.datetime.fromisoformat('2022-11-22')
end_date = datetime.datetime.fromisoformat('2022-12-01')
stpsf.trending.wavefront_time_series_plot(opdtable, start_date=start_date,
end_date=end_date, ymax=85, ymin=60,
label_visits=True, label_events=True)
WARNING: TimeDeltaMissingUnitWarning: Numerical value without unit or explicit format passed to TimeDelta, assuming days [astropy.time.core]
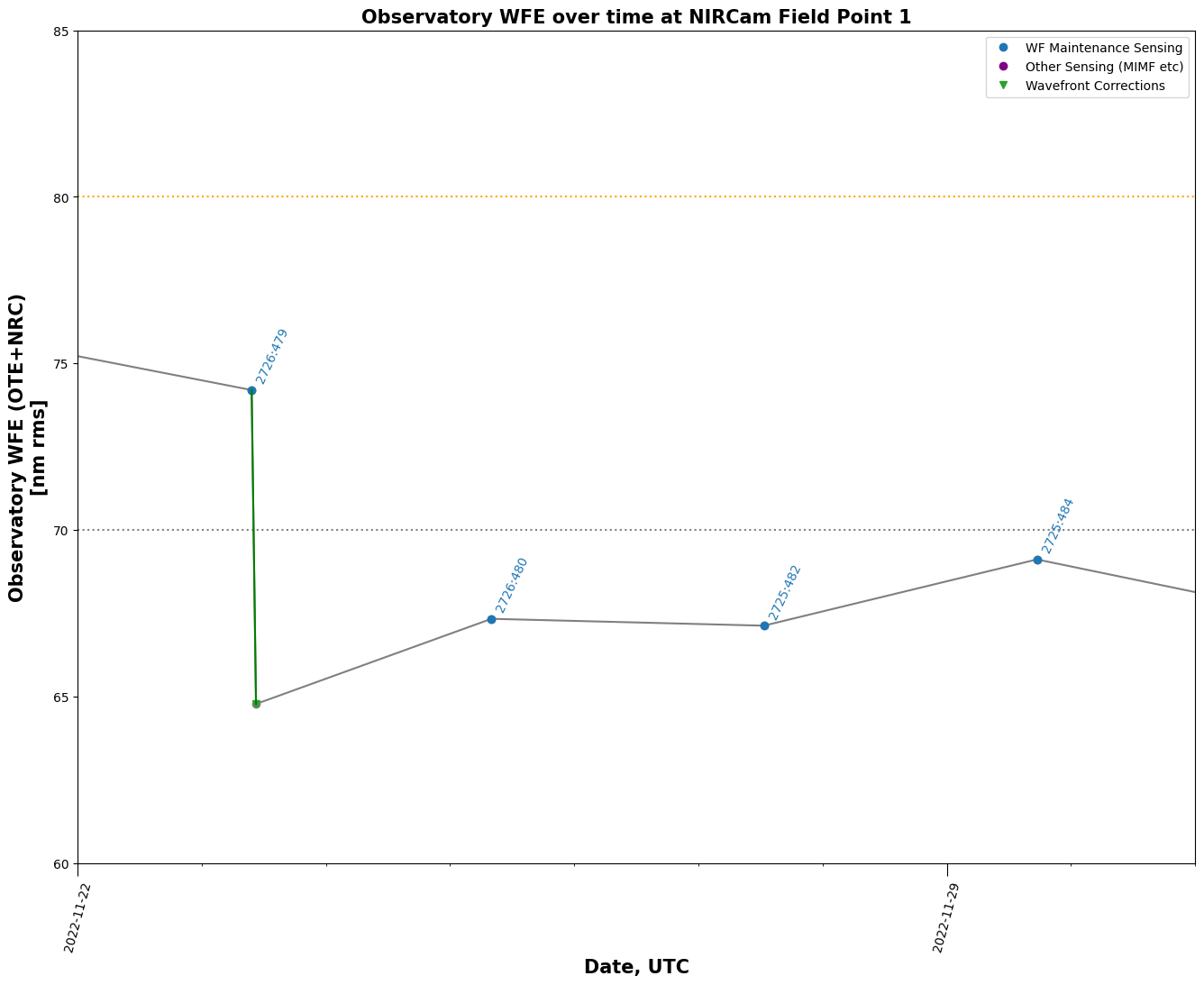
# We can also plot all measured wavefront drifts over specified time periods
start_time = astropy.time.Time('2024-01-01T00:00:00')
end_time = astropy.time.Time.now()
stpsf.trending.wavefront_drift_plots(opdtable, start_time=start_time, end_time=end_time, n_per_row=10)
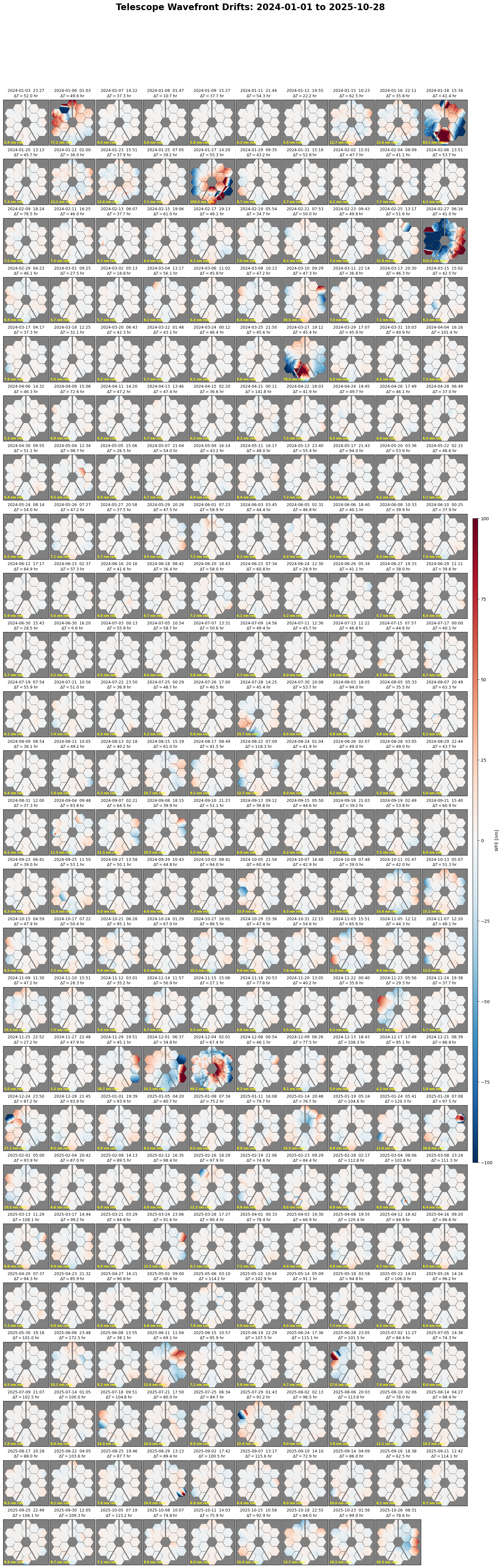
# We can plot histograms of wavefront error levels over time
stpsf.trending.wfe_histogram_plot(opdtable, thresh=70, ote_only=True)
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
Locator attempting to generate 1317 ticks ([19131.0, ..., 20447.0]), which exceeds Locator.MAXTICKS (1000).
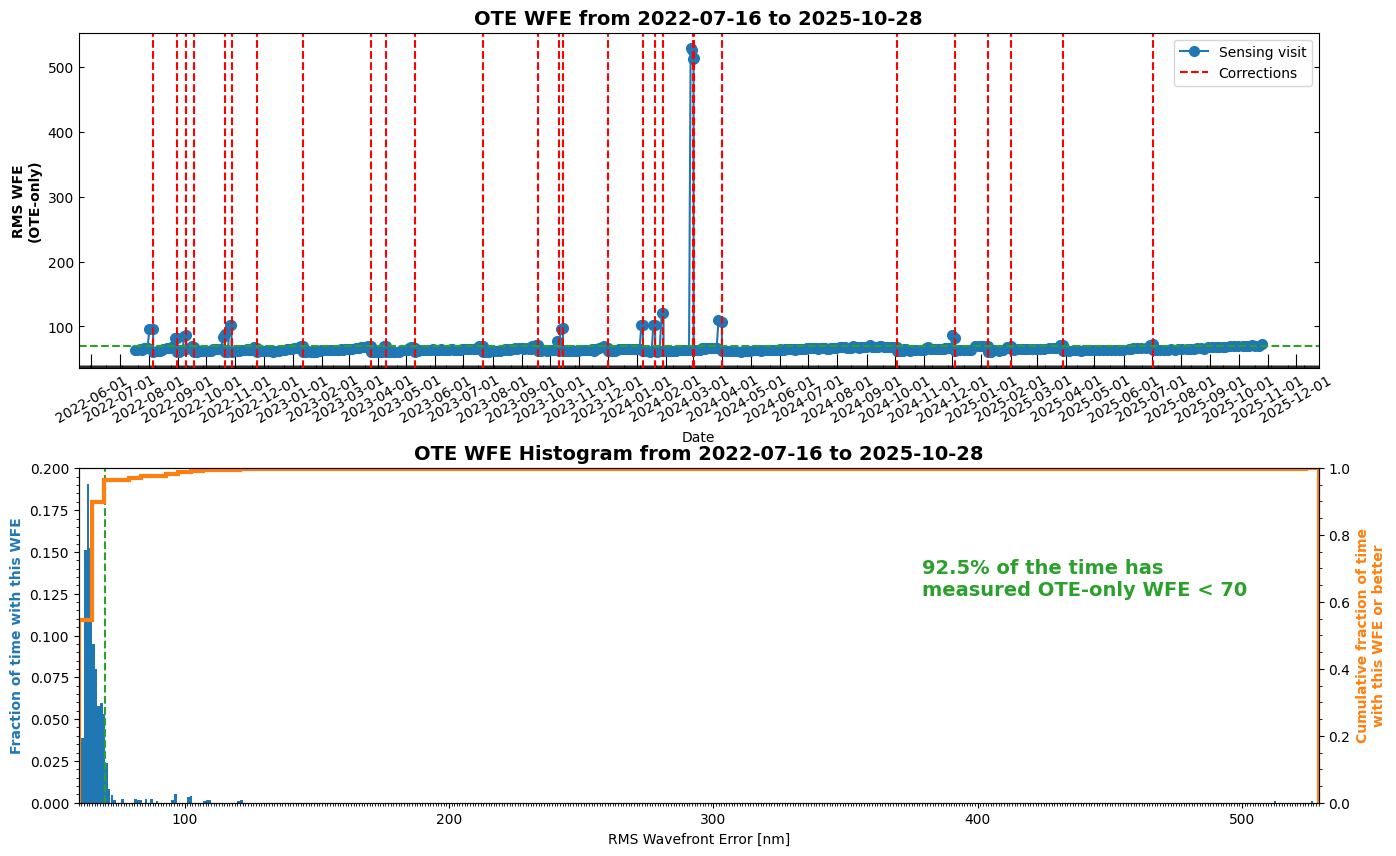
# Or select a particular time period
start_date = astropy.time.Time('2024-04-01')
end_date = astropy.time.Time.now()
stpsf.trending.wfe_histogram_plot(opdtable, start_date=start_date, thresh=70, ote_only=True)
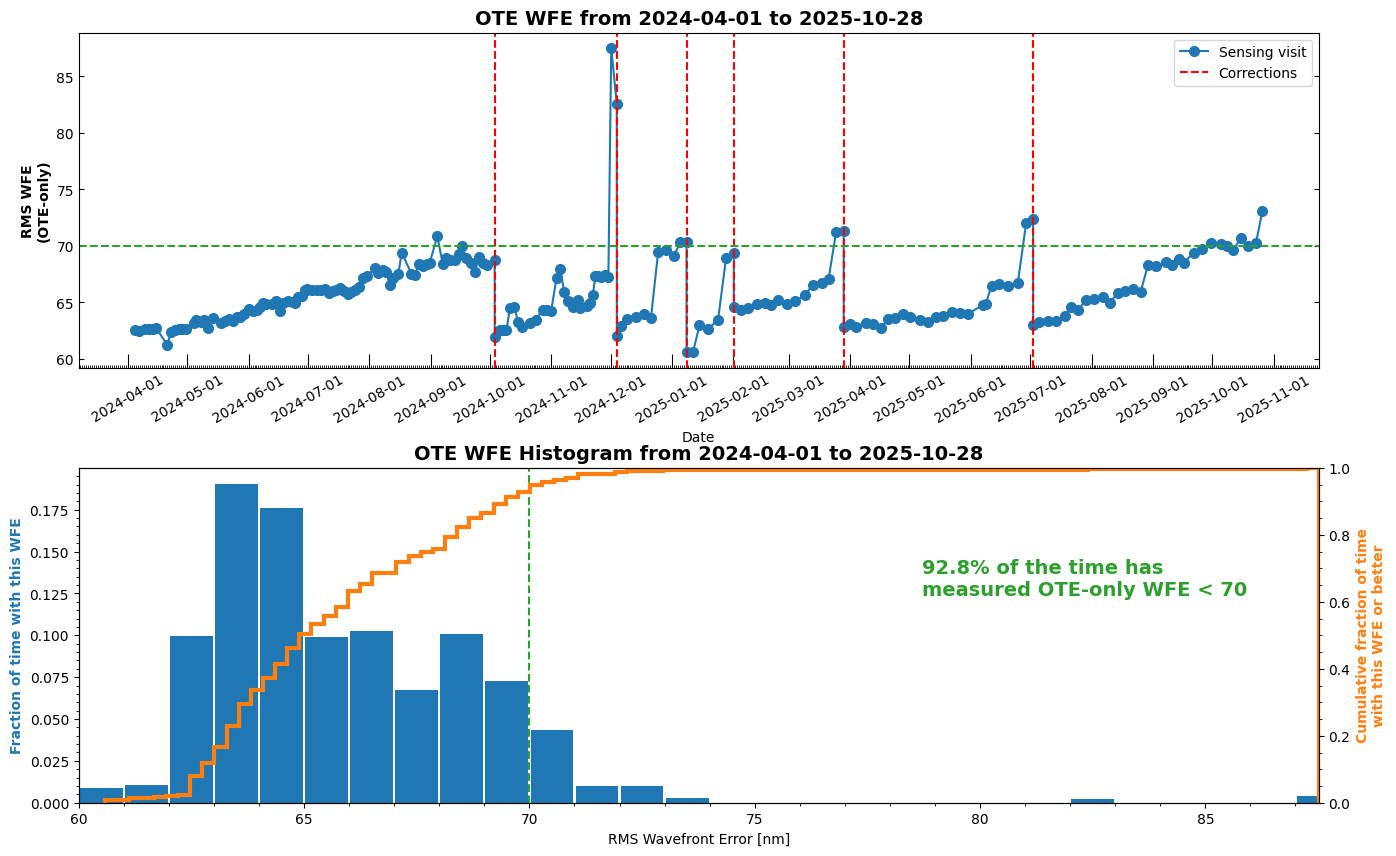
Load and plot a Single OPD#
Inspect the OPD table above for an OPD around your observation
nrc = stpsf.NIRCam()
nrc.filter = 'F212N'
opd_fn = 'R2022120204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits'
nrc.load_wss_opd(opd_fn, output_path=output_path)
fov_pixels = 511
psf = nrc.calc_psf(oversample=4, fov_pixels=fov_pixels)
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022120204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to /home/runner/work/jdat_notebooks/jdat_notebooks/notebooks/cross_instrument/stpsf_examples/R2022120204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Importing and format-converting OPD from /home/runner/work/jdat_notebooks/jdat_notebooks/notebooks/cross_instrument/stpsf_examples/R2022120204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Backing out SI WFE and OTE field dependence at the WF sensing field point (NRCA3_FP1)
psf.info()
Filename: (No file associated with this HDUList)
No. Name Ver Type Cards Dimensions Format
0 OVERSAMP 1 PrimaryHDU 104 (2044, 2044) float64
1 DET_SAMP 1 ImageHDU 106 (511, 511) float64
2 OVERDIST 1 ImageHDU 158 (2044, 2044) float64
3 DET_DIST 1 ImageHDU 159 (511, 511) float64
# display the PSF and plot the encircled energy
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
stpsf.display_psf(psf, colorbar_orientation='horizontal')
axis2 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
stpsf.display_ee(psf, ext=1, ax=axis2)
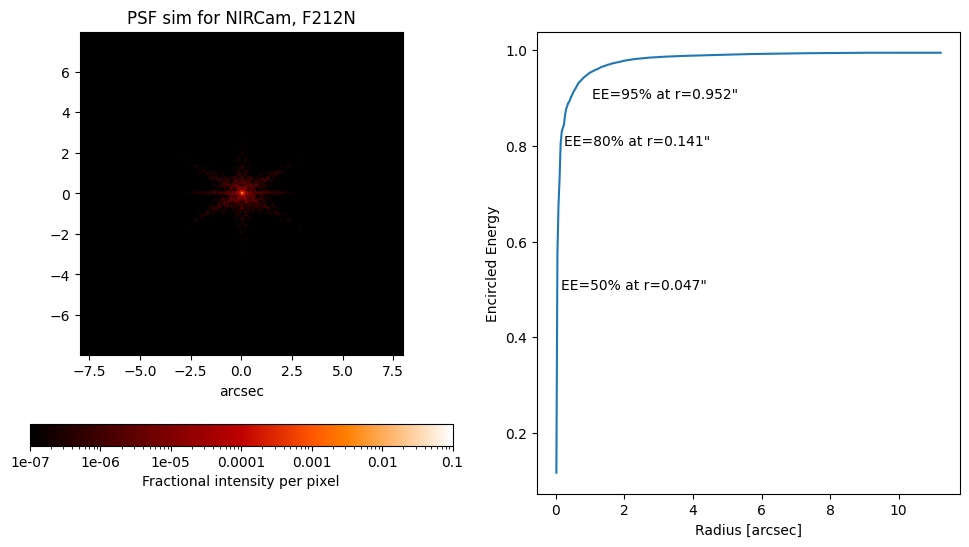
JWST Simulated PSF Subtraction from in-flight data#
https://stpsf.readthedocs.io/en/latest/jwst_psf_subtraction.html
file = 'jw02725-o484_t097_nircam_clear-f356w-nrcalong_wfscmb-04.fits'
mast_retrieve_files(file)
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/jw02725-o484_t097_nircam_clear-f356w-nrcalong_wfscmb-04.fits to ./jw02725-o484_t097_nircam_clear-f356w-nrcalong_wfscmb-04.fits ...
[Done]
'./jw02725-o484_t097_nircam_clear-f356w-nrcalong_wfscmb-04.fits'
# Open and inspect observation
psf = fits.open(file)
data = psf['SCI'].data
mask = (psf['DQ'].data % 2).astype('bool')
sigma_clip = SigmaClip(sigma=3.0)
bkg_estimator = MedianBackground()
# norm = simple_norm(data1, 'log',min_cut = min_cut, max_cut = max_cut)
bkg = Background2D(data, (50, 50), filter_size=(3, 3),
sigma_clip=sigma_clip, bkg_estimator=bkg_estimator, mask=mask)
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
norm = simple_norm(data - bkg.background, 'asinh', min_percent=20, max_percent=98.99)
plt.imshow(data - bkg.background, norm=norm, origin='lower', cmap='viridis')
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f7447fecc10>
Extract a subarray around source of interest, and measure source location#
position = (550, 1950) # approximate location. This will be improved below.
size_pixels = 200
data_source = Cutout2D(data - bkg.background, position, size_pixels).data
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
norm = simple_norm(data_source, 'asinh', min_percent=20, max_percent=99.6)
plt.imshow(data_source, norm=norm, origin='lower', cmap='viridis')
plt.title("Cutout around a galaxy merger and a star")
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Cutout around a galaxy merger and a star')
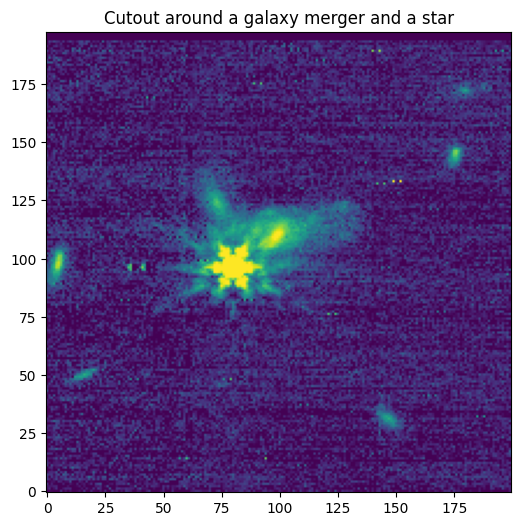
Find the source#
starfind = IRAFStarFinder(fwhm=3.0, threshold=100. * bkg.background_median)
sources = starfind(data_source)
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
plt.imshow(data_source, norm=norm, origin='lower', cmap='viridis')
plt.title("Cutout around a galaxy merger and a star")
plt.scatter(sources['xcentroid'], sources['ycentroid'], color='red', marker='x')
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x7f744cb56250>
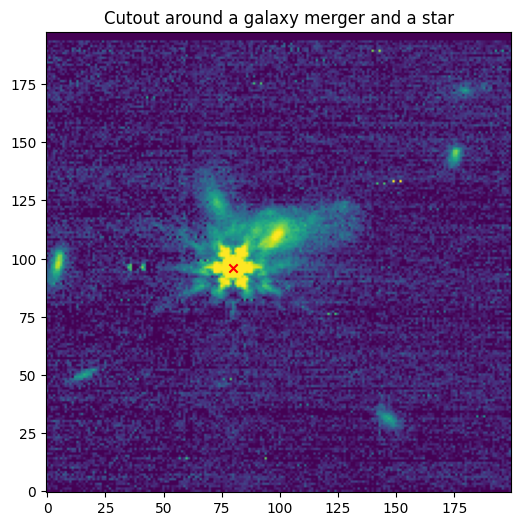
# Let's re-center the image
positions_original = Cutout2D(data - bkg.background, position, size_pixels).to_original_position((sources['xcentroid'], sources['ycentroid']))
position = (positions_original[0].value[0], positions_original[1].value[0])
size = 200
data_source = Cutout2D(data - bkg.background, position, size_pixels).data
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
norm = simple_norm(data_source, 'asinh', min_percent=20, max_percent=99.6)
plt.imshow(data_source, norm=norm, origin='lower', cmap='viridis')
plt.title("Cutout centered on the star")
print(position)
(np.float64(530.0226717404875), np.float64(1946.0707943817745))
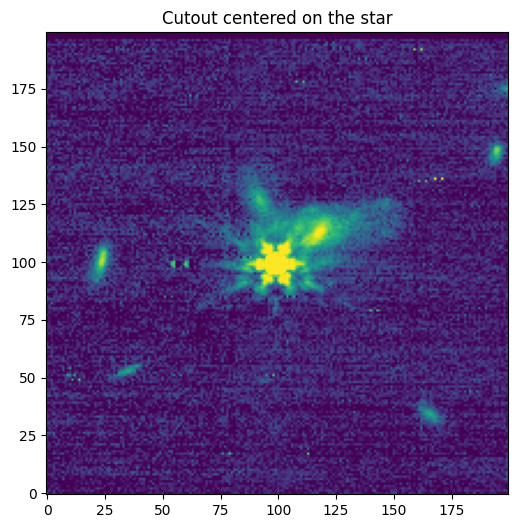
Use previous function to set up our simulation#
inst = stpsf.setup_sim_to_match_file(file)
inst.detector_position = position
single_stpsf_nrc = inst.calc_psf(fov_pixels=size_pixels)
Setting up sim to match jw02725-o484_t097_nircam_clear-f356w-nrcalong_wfscmb-04.fits
iterating query, tdelta=3.0
MAST OPD query around UTC: 2022-11-29T17:26:17.630
MJD: 59912.72659293981
OPD immediately preceding the given datetime:
URI: mast:JWST/product/R2022112903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Date (MJD): 59912.7265
Delta time: -0.0001 days
OPD immediately following the given datetime:
URI: mast:JWST/product/R2022120203-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Date (MJD): 59915.1683
Delta time: 2.4417 days
User requested choosing OPD time closest in time to 2022-11-29T17:26:17.630, which is R2022112903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits, delta time -0.000 days
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022112903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022112903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Importing and format-converting OPD from data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022112903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Backing out SI WFE and OTE field dependence at the WF sensing field point (NRCA3_FP1)
Configured simulation instrument for:
Instrument: NIRCam
Filter: F356W
Detector: NRCA5
Apername: NRCA5_FULL
Det. Pos.: (1024, 1024)
Image plane mask: None
Pupil plane mask: None
single_stpsf_nrc[3].header
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
XTENSION= 'IMAGE ' / Image extension
BITPIX = -64 / array data type
NAXIS = 2 / number of array dimensions
NAXIS1 = 200
NAXIS2 = 200
PCOUNT = 0 / number of parameters
GCOUNT = 1 / number of groups
PLANE1 = 'Wavefront Intensity'
WAVELEN = 3.52998044562017E-06 / Weighted mean wavelength in meters
DIFFLMT = 0.0976844608559387 / Diffraction limit lambda/D in arcsec
OVERSAMP= 1 / These data are rebinned to detector pixels
DET_SAMP= 4 / Oversampling factor for MFT to detector plane
PIXELSCL= 0.06290713 / Scale in arcsec/pix (after oversampling)
FOV = 12.581426 / Field of view in arcsec (full array)
NWAVES = 21 / Number of wavelengths used in calculation
WAVE0 = 3.12731886916690E-06 / Wavelength 0
WGHT0 = 0.029010311119741023 / Wavelength weight 0
WAVE1 = 3.17097412253077E-06 / Wavelength 1
WGHT1 = 0.05689236899019836 / Wavelength weight 1
WAVE2 = 3.21462937589464E-06 / Wavelength 2
WGHT2 = 0.05750257615337047 / Wavelength weight 2
WAVE3 = 3.25828462925851E-06 / Wavelength 3
WGHT3 = 0.05665770867940551 / Wavelength weight 3
WAVE4 = 3.30193988262238E-06 / Wavelength 4
WGHT4 = 0.05599172516198777 / Wavelength weight 4
WAVE5 = 3.34559513598625E-06 / Wavelength 5
WGHT5 = 0.055850313012947225 / Wavelength weight 5
WAVE6 = 3.38925038935012E-06 / Wavelength 6
WGHT6 = 0.05544478069113173 / Wavelength weight 6
WAVE7 = 3.43290564271399E-06 / Wavelength 7
WGHT7 = 0.05465666724163407 / Wavelength weight 7
WAVE8 = 3.47656089607787E-06 / Wavelength 8
WGHT8 = 0.0536889406582253 / Wavelength weight 8
WAVE9 = 3.52021614944174E-06 / Wavelength 9
WGHT9 = 0.052769619836572045 / Wavelength weight 9
WAVE10 = 3.56387140280561E-06 / Wavelength 10
WGHT10 = 0.05174556293270933 / Wavelength weight 10
WAVE11 = 3.60752665616948E-06 / Wavelength 11
WGHT11 = 0.050926124841304 / Wavelength weight 11
WAVE12 = 3.65118190953335E-06 / Wavelength 12
WGHT12 = 0.05008430229370746 / Wavelength weight 12
WAVE13 = 3.69483716289722E-06 / Wavelength 13
WGHT13 = 0.04911627277824833 / Wavelength weight 13
WAVE14 = 3.73849241626109E-06 / Wavelength 14
WGHT14 = 0.048066127719162625 / Wavelength weight 14
WAVE15 = 3.78214766962496E-06 / Wavelength 15
WGHT15 = 0.04674715249735926 / Wavelength weight 15
WAVE16 = 3.82580292298883E-06 / Wavelength 16
WGHT16 = 0.0454832673914629 / Wavelength weight 16
WAVE17 = 3.86945817635270E-06 / Wavelength 17
WGHT17 = 0.044181453325114764 / Wavelength weight 17
WAVE18 = 3.91311342971657E-06 / Wavelength 18
WGHT18 = 0.0413649282857484 / Wavelength weight 18
WAVE19 = 3.95676868308044E-06 / Wavelength 19
WGHT19 = 0.03220514808749848 / Wavelength weight 19
WAVE20 = 4.00042393644431E-06 / Wavelength 20
WGHT20 = 0.011614648302470809 / Wavelength weight 20
FFTTYPE = 'numpy.fft' / Algorithm for FFTs: numpy or fftw
NORMALIZ= 'first ' / PSF normalization method
JITRTYPE= 'Gaussian convolution' / Type of jitter applied
JITRSIGM= 0.0008 / Gaussian sigma for jitter, per axis [arcsec]
JITRSTRL= 1.0 / Strehl reduction from jitter
PUPILINT= 'jwst_pupil_RevW_npix1024.fits.gz' / Pupil aperture intensity source
PUPILOPD= 'OPD from supplied FITS HDUlist object' / Pupil OPD source
OPD_FILE= 'R2022112903-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits' / Pupil OPD file name
OPDSLICE= 0 / Pupil OPD slice number, if file is a datacube
INSTRUME= 'NIRCam ' / Instrument
FILTER = 'F356W ' / Filter name
EXTNAME = 'DET_DIST' / This extension is oversampled.
DATE = '2025-10-28T17:03:27' / Date of calculation
AUTHOR = 'runner@runnervmwhb2z' / username@host for calculation
VERSION = '2.1.0 ' / STPSF software version
DATAVERS= '2.1.0 ' / STPSF reference data files version
DET_NAME= 'NRCA5 ' / Name of detector on this instrument
DET_X = 530.5 / Detector X pixel position of array center
DET_Y = 1946.5 / Detector Y pixel position of array center
DET_V2 = 1.9445793009682408 / [arcmin] Det. pos. in telescope V2,V3 coord sys
DET_V3 = -7.259916804742389 / [arcmin] Det. pos. in telescope V2,V3 coord sys
TEL_WFE = 64.31211781548207 / [nm] Telescope pupil RMS wavefront error
OTETHMDL= 'BOL ' / OTE Thermal slew model case
OTETHSTA= 0.0 / OTE Starting pitch angle for thermal slew model
OTETHEND= 0.0 / OTE Ending pitch angle for thermal slew model
OTETHRDT= 0.0 / OTE Thermal slew model delta time after slew
OTETHRWF= 0.0 / OTE WFE amplitude from 'thermal slew' term
OTEFRLWF= 0.0 / OTE WFE amplitude from 'frill tension' term
OTEIECWF= 0.0 / OTE WFE amplitude from 'IEC thermal cycling' te
SI_WFE = 71.92925624358796 / [nm] instrument pupil RMS wavefront error
SIWFETYP= 'Extrapolated' / SI WFE was extrapolated outside available meas.
SIWFEFPT= 'ISIM42 ' / Closest ISIM CV3 WFE meas. field point
SIZERN1 = -1.0697917988307E-08 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 1
SIZERN2 = 3.08048159443971E-10 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 2
SIZERN3 = -1.9196041984348E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 3
SIZERN4 = -8.1173126758238E-08 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 4
SIZERN5 = 1.51797969643943E-08 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 5
SIZERN6 = 4.32636655822125E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 6
SIZERN7 = -8.0281498018401E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 7
SIZERN8 = -1.5951952117892E-10 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 8
SIZERN9 = -1.9417997569617E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 9
SIZERN10= 1.16285054335882E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 10
SIZERN11= -1.1748250980632E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 11
SIZERN12= -1.4078671907797E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 12
SIZERN13= -6.6810299931733E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 13
SIZERN14= 3.7853868843729E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 14
SIZERN15= -1.4415140518215E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 15
SIZERN16= -3.9703513237096E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 16
SIZERN17= 1.31563560122644E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 17
SIZERN18= 3.77897113698746E-10 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 18
SIZERN19= -1.8404320671331E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 19
SIZERN20= -3.1559659796023E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 20
SIZERN21= 9.70396713584626E-11 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 21
SIZERN22= -4.1669897552317E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 22
SIZERN23= 1.75844652958335E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 23
SIZERN24= 1.56437696827783E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 24
SIZERN25= 1.98457418229480E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 25
SIZERN26= 3.41706025271797E-10 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 26
SIZERN27= 1.00589037061746E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 27
SIZERN28= 8.04885292119649E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 28
SIZERN29= 2.44073543618285E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 29
SIZERN30= -1.1286841969615E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 30
SIZERN31= -2.3313034957157E-10 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 31
SIZERN32= 3.80384668407082E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 32
SIZERN33= 2.87255591936445E-11 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 33
SIZERN34= 1.39286599091967E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 34
SIZERN35= 1.22687031149893E-09 / [m] SI WFE coeff for Zernike term 35
APERNAME= 'NRCA5_FULL' / SIAF aperture name
MODULE = 'A ' / NIRCam module: A or B
CHANNEL = 'Long ' / NIRCam channel: long or short
PILIN = 'False ' / Pupil imaging lens in optical path: T/F
ROTATION= -0.06338311 / PSF rotated to match detector rotation
DISTORT = 'True ' / SIAF distortion coefficients applied
SIAF_VER= 'PRDOPSSOC-068' / SIAF PRD version used
COEF_X00= 0.0 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX00
COEF_X10= 15.935064289 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX10
COEF_X11= 0.00062662311666 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX11
COEF_X20= -0.0004866509075 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX20
COEF_X21= 0.0029284279113 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX21
COEF_X22= 0.00038194617433 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX22
COEF_X30= -6.765142999E-06 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX30
COEF_X31= -2.5133479064E-08 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX31
COEF_X32= -5.9888336301E-06 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX32
COEF_X33= 9.6468885579E-08 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX33
COEF_X40= 4.7744230522E-09 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX40
COEF_X41= -2.0517544492E-09 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX41
COEF_X42= 1.3815714874E-09 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX42
COEF_X43= -2.426584853E-09 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX43
COEF_X44= 1.2928805585E-09 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX44
COEF_X50= 1.3344738859E-11 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX50
COEF_X51= -5.3342857046E-11 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX51
COEF_X52= -1.0440706849E-10 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX52
COEF_X53= -1.7536898874E-11 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX53
COEF_X54= -3.4500183346E-11 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX54
COEF_X55= 1.5806704408E-11 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciX55
COEF_Y00= 0.0 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY00
COEF_Y10= 0.023739771631 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY10
COEF_Y11= 15.858052334 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY11
COEF_Y20= -0.0012404007583 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY20
COEF_Y21= -0.00089790574444 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY21
COEF_Y22= 0.0017034211874 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY22
COEF_Y30= 2.0629748211E-07 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY30
COEF_Y31= -7.0626833341E-06 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY31
COEF_Y32= -3.4856432882E-07 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY32
COEF_Y33= -6.1165886835E-06 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY33
COEF_Y40= -3.6220865015E-09 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY40
COEF_Y41= 1.4877764101E-09 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY41
COEF_Y42= -3.5926010043E-09 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY42
COEF_Y43= 5.2665557003E-10 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY43
COEF_Y44= -3.8007690059E-09 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY44
COEF_Y50= -1.8738092393E-11 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY50
COEF_Y51= -2.7459579135E-11 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY51
COEF_Y52= 1.7468257099E-11 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY52
COEF_Y53= -8.7857813876E-11 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY53
COEF_Y54= -1.6157416544E-12 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY54
COEF_Y55= -5.0913836989E-11 / SIAF distortion coefficient for Idl2SciY55
CHDFTYPE= 'gaussian' / Type of detector charge diffusion model
CHDFSIGM= 0.018 / [arcsec] Gaussian sigma for charge diff model
CALCSAMP= 4 / This much oversampling used in calculation
IPCINST = 'NIRCam ' / Interpixel capacitance (IPC)
IPCTYPA = '485 ' / NRC SCA num used for IPC and PPC model
IPCFILE = 'KERNEL_IPC_CUBE.fits' / IPC model source file
PPCFILE = 'KERNEL_PPC_CUBE.fits' / PPC model source file
HISTORY Created wavefront: wavelength=3.127e-06 m, diam=6.603 m
HISTORY using array size (1024, 1024)
HISTORY Multiplied WF by phasor for Pupil plane: JWST Entrance Pupil
HISTORY Propagating wavefront to Coordinate Inversion in y axis.
HISTORY Inverted axis direction for Y axes
HISTORY Multiplied WF by phasor for Pupil plane: NIRCamLWA internal WFE at V2V
HISTORY 3=(1.94,-7.26)', near ISIM42
HISTORY Propagating wavefront to Detector plane: NIRCam detector (200x200 pixe
HISTORY ls, 0.063 arcsec / pix).
HISTORY Propagating w/ MFT: 0.0157 arcsec / pix fov=128.797 lam/D npi
HISTORY x=800
HISTORY Calculation completed in 5.156 seconds
HISTORY Created by POPPY version
HISTORY Applied detector charge diffusion model.
HISTORY Applied detector interpixel capacitance (IPC) model
Use photutils to create our model PSF#
We’ll use photutils to fit and subtract the PSF from the data. First, we take the output simulated PSF and convert it into a photutils fittable model:
stpsf_model = photutils.psf.FittableImageModel(single_stpsf_nrc['DET_DIST'].data, normalize=True, oversampling=1)
WARNING: AstropyDeprecationWarning: The FittableImageModel class is deprecated and may be removed in a future version.
Use `ImagePSF` instead. [warnings]
fit_shape = (5, 5)
psfphot = PSFPhotometry(stpsf_model, fit_shape,
finder=starfind, aperture_radius=4)
# fit model PSF to background subtracted data
phot = psfphot(data_source)
Check the location of the source to be subtracted#
print(phot) # single source
id group_id group_size local_bkg ... cfit reduced_chi2 flags
--- -------- ---------- --------- ... --------------------- ------------ -----
1 1 1 0.0 ... -0.011884677868931921 nan 0
Subtract PSF and create residual image#
residual = psfphot.make_residual_image(data_source, psf_shape=(size_pixels, size_pixels))
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 16))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(data_source, norm=norm, origin='lower', cmap='viridis')
plt.title('Original - zoom')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(residual, norm=norm, origin='lower', cmap='viridis')
plt.title('Clean - PSFPhotometry zoom')
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Clean - PSFPhotometry zoom')
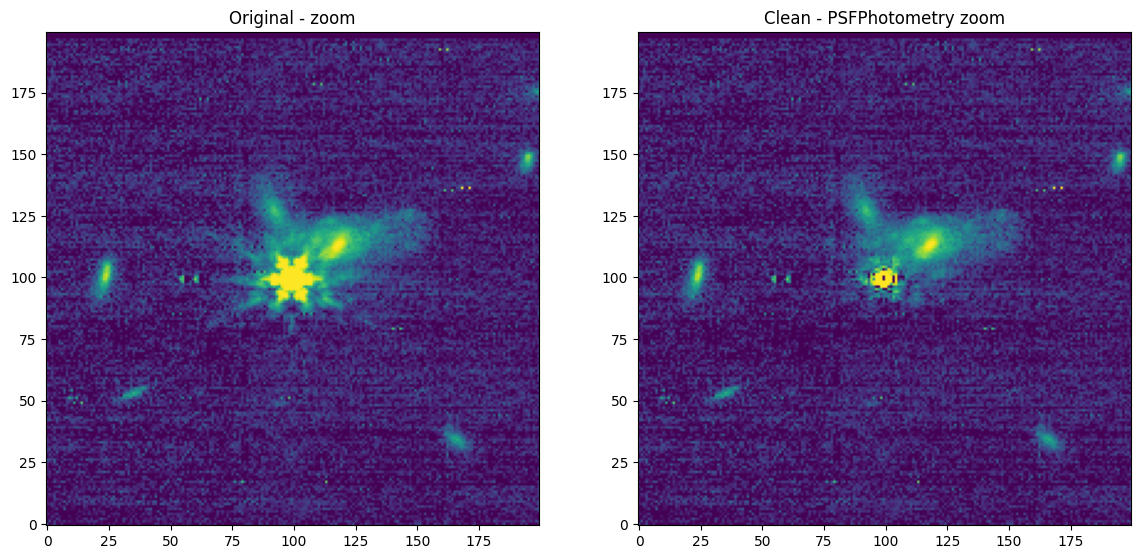
PSF properties and differences#
pixelscale = nrc.pixelscale
ee_pixel_radius = 2.5
ee_arcsec_radius = ee_pixel_radius * pixelscale
ee_psf = poppy.measure_ee(single_stpsf_nrc, ext=3, normalize='total')
ee_val = ee_psf(ee_arcsec_radius)
print("ee ({}px, {:.3f}arsec) = {:.4f}".format(ee_pixel_radius, ee_arcsec_radius, ee_val.item(0)))
ee (2.5px, 0.078arsec) = 0.5124
def measure_fwhm(array):
"""Fit a Gaussian2D model to a PSF and return the fitted PSF
the FWHM is x and y can be found with fitted_psf.x_fwhm, fitted_psf.y_fwhm
Parameters
----------
array : numpy.ndarray
Array containing PSF
Returns
-------
x_fwhm : float
FWHM in x direction in units of pixels
y_fwhm : float
FWHM in y direction in units of pixels
x_mean : float
x centroid position in units of pixels
y_mean : float
y centroid position in units of pixels
"""
yp, xp = array.shape
y, x = np.mgrid[:yp, :xp]
p_init = models.Gaussian2D(amplitude=array.max(), x_mean=xp * 0.5, y_mean=yp * 0.5)
fit_p = fitting.LevMarLSQFitter()
fitted_psf = fit_p(p_init, x, y, array)
return fitted_psf
fitted_psf = measure_fwhm(single_stpsf_nrc["DET_SAMP"].data)
print("FWHM X-direction: {:.3f}, FWHM y-direction: {:.2f}".format(fitted_psf.x_fwhm, fitted_psf.y_fwhm))
FWHM X-direction: 1.835, FWHM y-direction: 1.88
# Note that the OPD is loaded in STPSF instrument object
# norm = ImageNormalize(stretch=LinearStretch(), vmin = 1e-9 , vmax = 1e-7)
plt.figure(figsize=[10, 10])
plt.imshow(nrc.pupilopd[0].data, origin='lower')
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f744c338710>
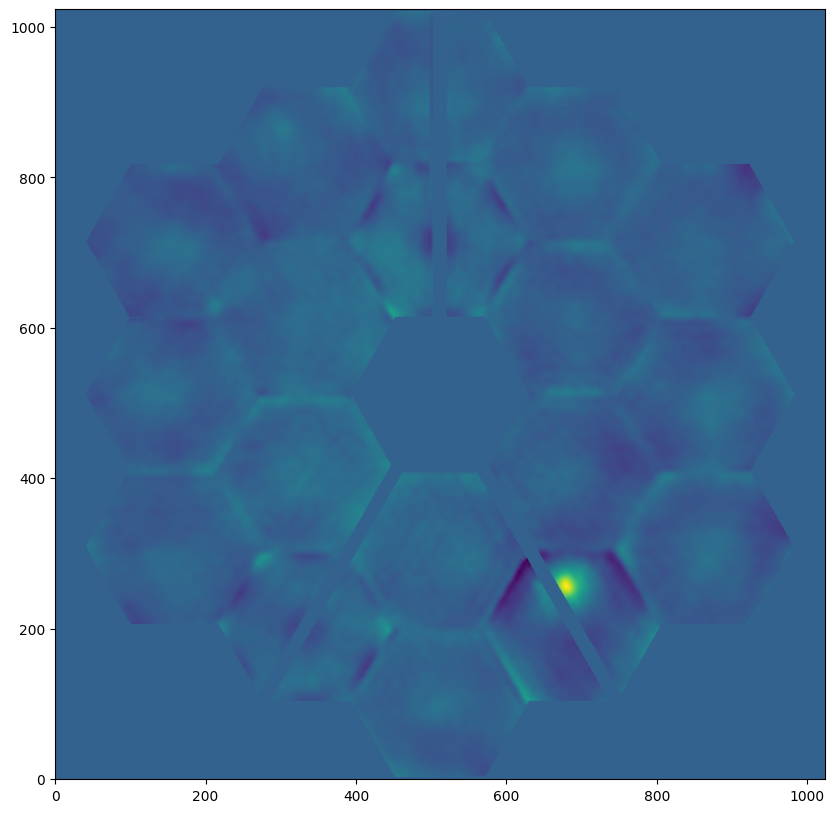
# check OPD header information
nrc.pupilopd[0].header
SIMPLE = T / Written by IDL: Fri Dec 2 22:39:16 2022
BITPIX = -64 / Number of bits per data pixel
NAXIS = 2 / Number of data axes
NAXIS1 = 1024
NAXIS2 = 1024
EXTEND = T / FITS data may contain extensions
DATE = '2022-12-02' / Creation UTC (CCCC-MM-DD) date of FITS header
COMMENT FITS (Flexible Image Transport System) format is defined in 'Astronomy
COMMENT and Astrophysics', volume 376, page 359; bibcode 2001A&A...376..359H
FILECONT= 'Analysis output products' /
TSTAMP = '2022-12-02T22:39:16' /
DATE-OBS= '2022-12-02' /
TIME-OBS= '04:02:21.595' /
OBS_ID = 'V02724347001P0000000003104' /
OP_TYPE = 'WAVEFRONT_MAINTENANCE' /
MODE = 'AUTOMATIC' /
OPER = 'TRUE ' /
CORR_ID = 'R2022120204' /
GROUP_ID= 1 /
GRP_CNT = 2 /
INSTRUME= 'NIRCam-A' /
DETECTOR= 'NRCA3 ' /
APERNAME= 'NRCA3_FP1' /
FPX = -1.16891 /
FPY = -0.767005 /
BUNIT = 'm '
PUPLDIAM= 6.603464
PUPLSCAL= 0.0064486953125
CONTENTS= 'Estimated OTE WFE from Wavefront Sensing Measurements'
HISTORY OPD file retrieved from MAST for use by STPSF.
HISTORY Converting input for use with STPSF:
HISTORY Input file is: /home/runner/work/jdat_notebooks/jdat_notebooks/noteboo
HISTORY ks/cross_instrument/stpsf_examples/R2022120204-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
HISTORY Need to rescale from 256x256 to 1024x1024 pixels.
HISTORY Dilated OPD values to fill adjacent invalid pixels (i.e. fill in gaps)
HISTORY Interpolated array to 1024x1024 pixels across
HISTORY Converted units from microns to meters
HISTORY Estimating SI WFE at sensing field point NRCA3_FP1.
HISTORY See FITS extension SENSING_SI_WFE for the SI WFE model used.
HISTORY Subtracted SI WFE to estimate OTE-only global WFE.
HISTORY Estimating OTE field dependence term at NRCA3_FP1.
HISTORY Selected instrument field point is at V2,V3 = [ 1.1595149 -8.59714411
HISTORY ] arcmin.
HISTORY See FITS extension SENSING_OTE_FD_WFE for the WFE model used.
HISTORY Subtracted OTE field dependence to estimate OTE global WFE.
# Let's calculate the difference between two different times
# We can use the same instrument setup from before
opd_fn = 'R2022120404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits'
inst.load_wss_opd(opd_fn)
psf2 = inst.calc_psf(fov_pixels=size_pixels)
Found OPD file previously downloaded: R2022120404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Importing and format-converting OPD from data/stpsf-data/MAST_JWST_WSS_OPDs/R2022120404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Backing out SI WFE and OTE field dependence at the WF sensing field point (NRCA3_FP1)
pixelscale = nrc.pixelscale
ee_pixel_radius = 2.5
ee_arcsec_radius = ee_pixel_radius * pixelscale
ee_psf = poppy.measure_ee(psf2, ext=1, normalize='total')
ee_val = ee_psf(ee_arcsec_radius)
print("ee ({}px, {:.3f}arsec) = {:.4f}".format(ee_pixel_radius, ee_arcsec_radius, ee_val.item(0)))
ee (2.5px, 0.078arsec) = 0.5545
stpsf.display_psf_difference(single_stpsf_nrc, psf2, imagecrop=2, title='Difference between two OPDs', cmap='gist_heat')
def miri_psfs_for_ee():
miri = stpsf.MIRI()
# opd_fn = 'R2022120404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits'
# miri.load_wss_opd(opd_fn, output_path = output_path)
miri.load_wss_opd_by_date('2022-07-12T00:00:00', plot=True, output_path=output_path)
for wave in [5.0, 7.5, 10, 14]:
fov = 18
outname = "PSF_MIRI_%.1fum_wfed.fits" % (wave)
psf = miri.calc_psf(outname, monochromatic=wave * 1e-6,
oversample=4, fov_arcsec=fov, display=True)
return psf
def plot_ee_curves():
plt.clf()
for iw, wave in enumerate([5.0, 7.5, 10, 14]):
ees60 = []
ees51 = []
ax = plt.subplot(2, 2, iw+1)
name = "PSF_MIRI_%.1fum_wfed.fits" % (wave)
stpsf.display_ee(name, ax=ax, mark_levels=False)
eefn = stpsf.measure_ee(name)
ees60.append(eefn(0.60))
ees51.append(eefn(0.51))
ax.text(1, 0.6, 'Mean EE inside 0.60": %.3f' % np.asarray(ees60).mean())
ax.text(1, 0.5, 'Mean EE inside 0.51": %.3f' % np.asarray(ees51).mean())
ax.set_title(f"Wavelength = {wave:.1f} $\\mu$m")
ax.axvline(0.6, ls=":", color='k')
ax.axvline(0.51, ls=":", color='k')
plt.tight_layout()
miri_psfs_for_ee()
iterating query, tdelta=3.0
MAST OPD query around UTC: 2022-07-12T00:00:00.000
MJD: 59772.0
OPD immediately preceding the given datetime:
URI: mast:JWST/product/O2022071001-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits
Date (MJD): 59770.4830
Delta time: -1.5170 days
OPD immediately following the given datetime:
URI: mast:JWST/product/R2022071302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Date (MJD): 59772.6632
Delta time: 0.6632 days
User requested choosing OPD time closest in time to 2022-07-12T00:00:00.000, which is R2022071302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits, delta time 0.663 days
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022071302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to /home/runner/work/jdat_notebooks/jdat_notebooks/notebooks/cross_instrument/stpsf_examples/R2022071302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Importing and format-converting OPD from /home/runner/work/jdat_notebooks/jdat_notebooks/notebooks/cross_instrument/stpsf_examples/R2022071302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Backing out SI WFE and OTE field dependence at the WF sensing field point (NRCA3_FP1)
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
[<astropy.io.fits.hdu.image.PrimaryHDU object at 0x7f7446b2e650>, <astropy.io.fits.hdu.image.ImageHDU object at 0x7f74aa446210>, <astropy.io.fits.hdu.image.ImageHDU object at 0x7f7454257e10>, <astropy.io.fits.hdu.image.ImageHDU object at 0x7f745503eb10>]
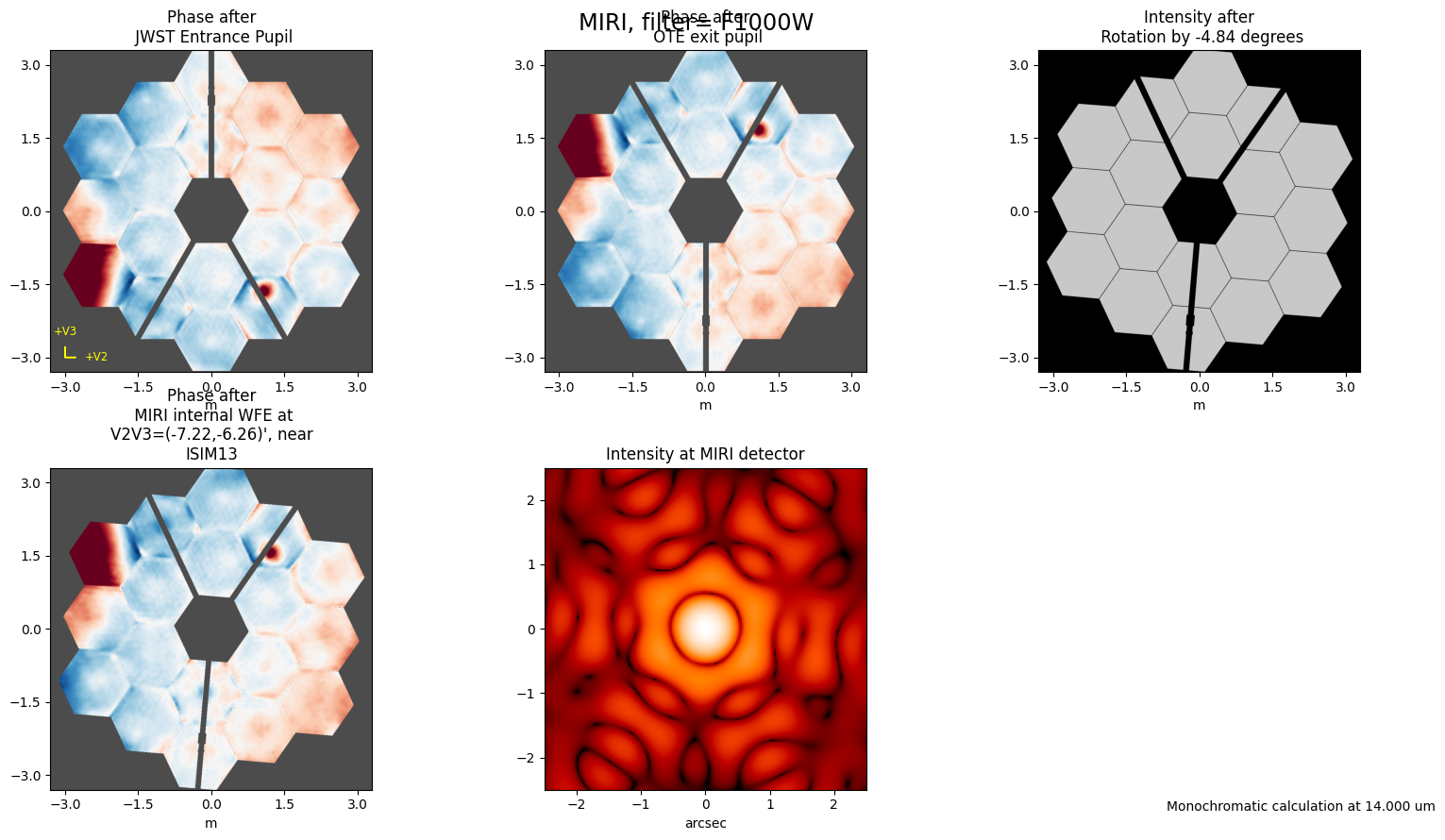
plot_ee_curves()
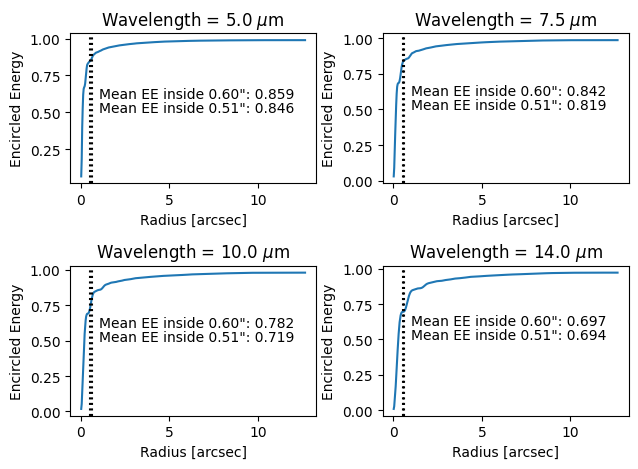
nsp = stpsf.NIRSpec()
# or you can specify a full path name.
# please make an output PSF with its center
# aligned to the center of a single pixel
nsp.options['parity'] = 'odd'
opd_fn = 'R2022120404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits'
nsp.load_wss_opd(opd_fn, output_path=output_path)
waves = np.linspace(0.8, 5, 50) * 1e-6 # iterate over wavelengths in meters
for iw, wavelength in enumerate(waves):
psffile = 'psf_NIRSPec_mono_%.1fum_opd1.fits' % (wavelength * 1e6)
psf = nsp.calc_psf(fov_arcsec=3, oversample=4,
monochromatic=wavelength, display=False,
outfile=psffile)
ax = plt.subplot(8, 8, iw + 1)
stpsf.display_psf(psffile, ext='DET_SAMP', colorbar=False, imagecrop=8)
ax.set_title('')
ax.xaxis.set_visible(False)
ax.yaxis.set_visible(False)
ax.text(-3.5, 0, '{0:.1f}'.format(wavelength * 1e6))
Downloading URL https://mast.stsci.edu/api/v0.1/Download/file?uri=mast:JWST/product/R2022120404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits to /home/runner/work/jdat_notebooks/jdat_notebooks/notebooks/cross_instrument/stpsf_examples/R2022120404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits ...
[Done]
Importing and format-converting OPD from /home/runner/work/jdat_notebooks/jdat_notebooks/notebooks/cross_instrument/stpsf_examples/R2022120404-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Backing out SI WFE and OTE field dependence at the WF sensing field point (NRCA3_FP1)
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
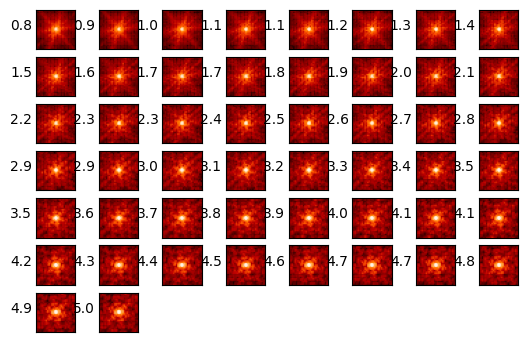
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 12))
nsp.image_mask = 'MSA all open'
nsp.display()
msapsf = nsp.calc_psf(monochromatic=2e-6, oversample=8)
stpsf.display_psf(msapsf, ext='DET_SAMP')
miri_psfs_for_ee()
iterating query, tdelta=3.0
MAST OPD query around UTC: 2022-07-12T00:00:00.000
MJD: 59772.0
OPD immediately preceding the given datetime:
URI: mast:JWST/product/O2022071001-NRCA3_FP1-0.fits
Date (MJD): 59770.4830
Delta time: -1.5170 days
OPD immediately following the given datetime:
URI: mast:JWST/product/R2022071302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Date (MJD): 59772.6632
Delta time: 0.6632 days
User requested choosing OPD time closest in time to 2022-07-12T00:00:00.000, which is R2022071302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits, delta time 0.663 days
Importing and format-converting OPD from /home/runner/work/jdat_notebooks/jdat_notebooks/notebooks/cross_instrument/stpsf_examples/R2022071302-NRCA3_FP1-1.fits
Backing out SI WFE and OTE field dependence at the WF sensing field point (NRCA3_FP1)
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
WARNING: VerifyWarning: Card is too long, comment will be truncated. [astropy.io.fits.card]
[<astropy.io.fits.hdu.image.PrimaryHDU object at 0x7f74a7d0e310>, <astropy.io.fits.hdu.image.ImageHDU object at 0x7f74474a3010>, <astropy.io.fits.hdu.image.ImageHDU object at 0x7f74aa345f50>, <astropy.io.fits.hdu.image.ImageHDU object at 0x7f74475ee910>]

plot_ee_curves()

Improved IFU sims#
miri = stpsf.MIRI()
miri.mode = 'IFU'
miri.band = '2A'
waves = miri.get_IFU_wavelengths()
cube = miri.calc_datacube_fast(waves)
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.11.13/x64/lib/python3.11/site-packages/stpsf/opds.py:1759: UserWarning: For (V2,V3) = [-8.39108833 -5.32144667] arcmin, Field point -8.254199999999999 arcmin, -2.478553333333333 arcmin not within valid region for field dependence model of OTE WFE for MIRI: -8.254199999999999 arcmin--6.21738 arcmin, -2.557224 arcmin--0.5632056 arcmin. Clipping to closest available valid location, 0.13688833333333505 arcmin away from the requested coordinates.
warnings.warn(warning_message)
cube.info()
Filename: (No file associated with this HDUList)
No. Name Ver Type Cards Dimensions Format
0 OVERSAMP 1 PrimaryHDU 1075 (284, 284, 970) float64
nrs = stpsf.NIRSpec()
nrs.mode = 'IFU'
nrs.disperser = 'PRISM'
nrs.filter = 'CLEAR'
waves = nrs.get_IFU_wavelengths()
cube = nrs.calc_datacube_fast(waves)
cube.info()
Filename: (No file associated with this HDUList)
No. Name Ver Type Cards Dimensions Format
0 OVERSAMP 1 PrimaryHDU 1049 (192, 192, 940) float64
