Galaxy Morphology with SDSS and Astrocut#
Learning Goals#
By the end of this tutorial, you will:
Understand how to use
astroquery.mastto download the SDSS Legacy Imaging Survey Data from the MAST archive.Utilize
astrocutto create colorized cropped images from 12 different galaxies.Construct a Hubble Tuning Fork Diagram from the cropped images to learn about galaxy morphology.
Table of Contents#
Introduction#

In the early 1900s, most astronomers believed objects such as the Andromeda galaxy were nebulous clouds within our galaxy. In 1923, Edwin Hubble proved Andromeda was outside the Milky Way using the period-luminosity relationship with Cepheid variables [2]. Once Hubble discovered most “nebulae” visible in the sky were actually galaxies, he created a classification scheme known as the Hubble Tuning Fork, or the Hubble Sequence. Hubble initially separated galaxies into two main groups: elliptical galaxies and spiral galaxies. Elliptical galaxies lack spiral arms, but are ellipses in shape. Hubble classified them by their ellipticity; the more elongated the galaxy, the higher its classification number (i.e. E0 to E7).
Spiral galaxies, which have prominent spiral arms, were further divided into two types based on the presence of a central bar: barred spirals (with a bar) and normal spirals (without). Both types were then categorized as early, intermediate, or late, depending on how tightly wound their arms were. Galaxies that lacked both a central nucleus and spiral structure were classified as “irregular” [3].
Hubble initially proposed that galaxies evolved from left to right on his tuning fork diagram, starting at E0 ellipticals and ending at late-type spiral/barred spiral galaxies. However, we now know this to be incorrect! Despite this, the Hubble Sequence remains a widely used tool for galaxy morphological classification [1].
In this notebook, we’ll construct our own Hubble Tuning Fork Diagram based on this classification scheme using imaging data from the SDSS Legacy Imaging Survey. We can utilize the Astrocut package to crop selected fields and generate color cutouts of various galaxies for our diagram.
Imports#
The main packages and their use-cases in this tutorial are as follows:
numpy to handle array functions
matplotlib.pyplot for plotting data
matplotlib.image to handle .png images
astroquery.mast.Observations to access SDSS data from MAST
astrocut.FITSCutout to mosaic images
astropy for handling FITS files
astropy.table.vstack for combining Astropy tables
warnings to suppress FITS warnings
bz2 to decompress the data files
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
from astroquery.mast import Observations
from astrocut import FITSCutout
import astropy
from astropy.table import vstack
import warnings
import bz2
If you’re not sure if you have the required versions of packages installed on your device, you can run the following cell:
with open("requirements.txt") as f:
print(f"Required packages for this notebook:\n{f.read()}")
Required packages for this notebook:
numpy >= 1.26.4
matplotlib >= 3.9.1
astroquery >= 0.4.9
astropy >= 5.3
astrocut >= 1.0.1
To ensure these requirements are installed, you can run the following command in the terminal:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Accessing SDSS Legacy Imaging Survey Data from MAST#
The Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes (MAST) hosts a large array of data from several telescope missions. In this tutorial, we will be specifically focusing on data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey’s (SDSS) Imaging Survey.
The SDSS Legacy Imaging Survey was the first SDSS survey completed! Beginning in 1998, the SDSS Legacy Imaging Survey captured around 35,000 square degrees of images until 2009, which covers about one-third of the whole sky. To do this, the survey took millions of 10 by 13 arcminute pictures (called “fields”). Not only does the SDSS Legacy Imaging Survey data at MAST provide users with preview images in .jpg format, but it also has photometric data in all five broad band SDSS filters (u, g, r, i, and z). For more information about the data and products from the SDSS Legacy Imaging Survey, you can check out the SDSS Imaging Archive Manual.
Querying SDSS Legacy Imaging Survey#
You can query data from MAST using the website portal. You can also query MAST data in Python using the module astroquery.mast!
We can query all of the SDSS Legacy Imaging data using the Observations.query_criteria() function with the parameter provenance_name = "SDSS Legacy Imaging". Since there is a large amount of data in the SDSS Legacy Imaging archive, we can display the first 10 results using the pagesize parameter as well as the page parameter.
# Querying SDSS Legacy Imaging
imaging_data = Observations.query_criteria(
provenance_name="SDSS Legacy Imaging", pagesize=10, page=1
)
# Display first 10 entries
imaging_data
| intentType | obs_collection | provenance_name | instrument_name | project | filters | wavelength_region | target_name | target_classification | obs_id | s_ra | s_dec | dataproduct_type | proposal_pi | calib_level | t_min | t_max | t_exptime | em_min | em_max | obs_title | t_obs_release | proposal_id | proposal_type | sequence_number | s_region | jpegURL | dataURL | dataRights | mtFlag | srcDen | obsid | objID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str7 | str4 | str19 | str11 | str4 | str9 | str7 | str13 | str5 | str24 | float64 | float64 | str5 | str18 | int64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | str51 | float64 | str3 | str1 | int64 | str197 | str61 | str61 | str6 | bool | float64 | str9 | str9 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 003631-3-0173 | FIELD | sdss_image_003631-3-0173 | 142.34760173 | 10.8280313892 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 52667.378010532404 | 52667.38195135944 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 142.2856830207712 10.702818790899348 142.24546270637723 10.92441207248235 142.4095918267478 10.953123368763942 142.44969461492158 10.731508866734153 142.2856830207712 10.702818790899348 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3631/3/173/frame-irg-003631-3-0173.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3631/3/173/photoObj-003631-3-0173.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298416061 | 886141297 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 004646-3-0116 | FIELD | sdss_image_004646-3-0116 | 211.294213232 | 27.2583034313 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 53147.31616226852 | 53147.320103558515 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 211.1764556994774 27.16659279972585 211.2323929615006 27.386090674530603 211.41213750068607 27.34980817472196 211.35586413930838 27.1303818939345 211.1764556994774 27.16659279972585 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/4646/3/116/frame-irg-004646-3-0116.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/4646/3/116/photoObj-004646-3-0116.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298416062 | 886141318 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 005061-1-0362 | FIELD | sdss_image_005061-1-0362 | 170.167453826 | 28.0032830563 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 53352.48167337963 | 53352.485614206664 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 170.09200395243514 27.881125247088647 170.05904279875978 28.104322534202637 170.24309090602264 28.125290528454187 170.27567751239198 27.902049642763988 170.09200395243514 27.881125247088647 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/5061/1/362/frame-irg-005061-1-0362.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/5061/1/362/photoObj-005061-1-0362.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298416063 | 886141326 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 005598-1-0179 | FIELD | sdss_image_005598-1-0179 | 9.60169528537 | 6.32144682181 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 53625.34287800926 | 53625.34681906778 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 9.518238822737876 6.209713675281979 9.520509691921863 6.434776115517112 9.68518666754958 6.433056712424404 9.68284416208174 6.207994997573957 9.518238822737876 6.209713675281979 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/5598/1/179/frame-irg-005598-1-0179.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/5598/1/179/photoObj-005598-1-0179.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298416064 | 886141336 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 000273-5-0348 | FIELD | sdss_image_000273-5-0348 | 62.0225361347 | 0.530895732365 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 51136.303583333334 | 51136.30752439185 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 61.94071034991705 0.4183101048489016 61.9407245311594 0.6433986484087005 62.104364889435445 0.6433703171896982 62.10434475139734 0.4182817740841008 61.94071034991705 0.4183101048489016 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/273/5/348/frame-irg-000273-5-0348.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/273/5/348/photoObj-000273-5-0348.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298416065 | 886141343 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 008117-3-0067 | FIELD | sdss_image_008117-3-0067 | 351.466998663 | 29.200383354 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 55122.34369270833 | 55122.34763388259 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 351.38904270769706 29.07897780082915 351.3587284481966 29.302461855993133 351.5451540865375 29.321634435258055 351.57506796825066 29.098108697003447 351.38904270769706 29.07897780082915 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/8117/3/67/frame-irg-008117-3-0067.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/8117/3/67/photoObj-008117-3-0067.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298416066 | 886141350 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 007754-5-0365 | FIELD | sdss_image_007754-5-0365 | 7.62505051253 | 5.72849634356 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 54764.214852777775 | 54764.2187938363 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 7.5423905603197285 5.616195810190497 7.543251877538096 5.841293187693011 7.7077425220348195 5.84067506445307 7.706816391301905 5.615577941725014 7.5423905603197285 5.616195810190497 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/7754/5/365/frame-irg-007754-5-0365.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/7754/5/365/photoObj-007754-5-0365.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298416067 | 886141361 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 002385-6-0029 | FIELD | sdss_image_002385-6-0029 | 310.159014364 | 1.1553004002 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 52075.32131099537 | 52075.3252512437 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 310.0771400762918 1.0426926277507749 310.07717786821064 1.2678058591633476 310.240895117248 1.2677958420277167 310.24084435391956 1.0426826131653033 310.0771400762918 1.0426926277507749 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/2385/6/29/frame-irg-002385-6-0029.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/2385/6/29/photoObj-002385-6-0029.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298416068 | 886141369 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 004836-6-0127 | FIELD | sdss_image_004836-6-0127 | 321.662301971 | 19.7217045531 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 53265.14422476852 | 53265.148165827035 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 321.61382955617984 19.59021600255788 321.54439190128875 19.80559625018339 321.7108880697989 19.853074813762714 321.78012204808095 19.637630602481746 321.61382955617984 19.59021600255788 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/4836/6/127/frame-irg-004836-6-0127.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/4836/6/127/photoObj-004836-6-0127.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298416069 | 886141373 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 001345-2-0285 | FIELD | sdss_image_001345-2-0285 | 159.668563964 | 62.1421936525 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 51639.230040625 | 51639.23398145204 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 159.60071687634849 62.00660386219628 159.41334875101535 62.21394439955758 159.73711254674646 62.27764851222691 159.92265873936543 62.069873919552435 159.60071687634849 62.00660386219628 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/1345/2/285/frame-irg-001345-2-0285.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/1345/2/285/photoObj-001345-2-0285.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298416070 | 886141382 |
The table above provides some basic information for each object:
instrument_name:SDSS Cameraindicates that the imaging data were collected using the SDSS camera.filters: Indicates the SDSS filters used in the survey (u, g, r, i, and z).wavelength_region: Indicates the region of the electromagnetic spectrum observed. This should beOPTICAL, since the SDSS Legacy Imaging Survey observed in the optical wavelength range.target_classification:FIELDindicates the survey captured images of the sky.obs_id: Observation ID associated with the image.s_raands_dec: Right ascension and declination.dataproduct_type: This should beimagesince we’re focusing on an imaging survey.t_minandt_max: The modified Julian dates indicating the start and end times of the exposures.em_minandem_max: The minimum and maximum wavelengths observed by the survey. For the SDSS Legacy Imaging survey, this range is approximately 304.8 - 1083.3 nanometers (optical).
Gathering Galaxies from the SDSS Legacy Imaging Survey#
In this tutorial, we’ll be gathering a variety of galaxies to make a Hubble Tuning Fork Diagram. We’ll select the following galaxies:
Elliptical:
M89 (E0)
NGC 5982 (E3)
NGC 4697 (E6)
Lenticular:
NGC 3384 (S0)
Spiral:
NGC 488 (Sa)
M88 (Sb)
M99 (Sc)
Barred Spiral:
NGC 109 (SBa)
M91 (SBb)
NGC 5068 (SBc)
Irregular:
IC 3583
NGC 7292
These galaxies were selected based on their NED classification as well as how they fit in an SDSS field using the MAST Portal Astroview.
We can query MAST using the target name directly! We’ll use M89 as an example:
# Querying MAST for M89 using search radius of 0
m89 = Observations.query_criteria(
objectname="M89", radius=0, provenance_name="SDSS Legacy Imaging"
)
# Displaying the results
m89
| intentType | obs_collection | provenance_name | instrument_name | project | filters | wavelength_region | target_name | target_classification | obs_id | s_ra | s_dec | dataproduct_type | proposal_pi | calib_level | t_min | t_max | t_exptime | em_min | em_max | obs_title | t_obs_release | proposal_id | proposal_type | sequence_number | s_region | jpegURL | dataURL | dataRights | mtFlag | srcDen | obsid | objID | objID1 | distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str7 | str4 | str19 | str11 | str4 | str9 | str7 | str13 | str5 | str24 | float64 | float64 | str5 | str18 | int64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | str51 | float64 | str3 | str1 | int64 | str194 | str61 | str61 | str6 | bool | float64 | str9 | str9 | str9 | float64 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 003805-4-0012 | FIELD | sdss_image_003805-4-0012 | 188.898701441 | 12.5764587394 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 52721.22948229167 | 52721.23342288722 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 188.8132288137322 12.46506119358693 188.81649298124918 12.690134070168584 188.98424657174562 12.687719213107714 188.9808354852855 12.462648412357575 188.8132288137322 12.46506119358693 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3805/4/12/frame-irg-003805-4-0012.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3805/4/12/photoObj-003805-4-0012.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 297084970 | 877110806 | 877110806 | 0.0 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 003064-4-0048 | FIELD | sdss_image_003064-4-0048 | 188.888058594 | 12.5775588961 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 52356.43429236111 | 52356.43823341963 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 188.80250968110988 12.46618524586542 188.80590815690954 12.69122285024466 188.97368000165366 12.688795440850217 188.97013460213253 12.463759996247843 188.80250968110988 12.46618524586542 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3064/4/48/frame-irg-003064-4-0048.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3064/4/48/photoObj-003064-4-0048.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 297485968 | 878009148 | 878009148 | 0.0 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 003804-4-0207 | FIELD | sdss_image_003804-4-0207 | 188.89762961 | 12.5766093494 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 52721.21609756944 | 52721.220038743704 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 188.81217294825396 12.46522271055066 188.81545014737785 12.690283256904873 188.98315874867606 12.687858932000672 188.97973467649607 12.46280046903323 188.81217294825396 12.46522271055066 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3804/4/207/frame-irg-003804-4-0207.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3804/4/207/photoObj-003804-4-0207.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 297868245 | 880840069 | 880840069 | 0.0 |
There are three fields available for M89, but we’ll be using the field with target_name=003804-4-0207 since it completely captures the galaxy. For the rest of the tutorial, we’ll be querying by target name (field) as we preselected these from the MAST Portal depending on how the galaxy fit into each field.
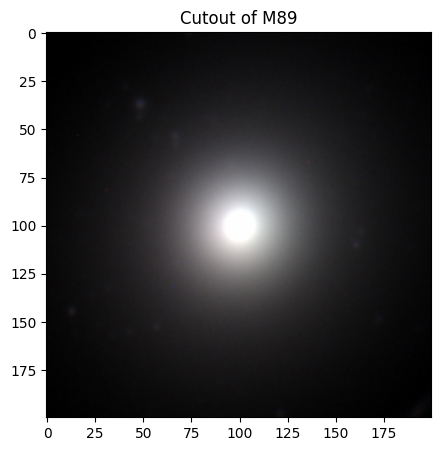
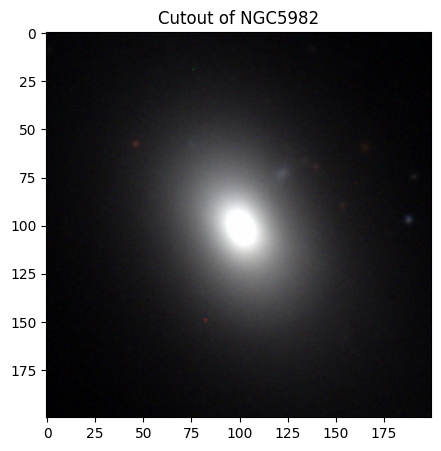
Elliptical Galaxies#
Elliptical galaxies have a distinct nucleus, but do not have a disk or spiral arms. Due to the minimal dust and gas present, these galaxies are mostly made up of population II stars. Elliptical galaxies are categorized by number, with E0 being the most round in shape, and E7 being the most elliptical in shape. The elliptical galaxy classification numbers are derived from the equation:
where \(n\) is the classification number, \(b\) is the projected length of the semi-minor axis on the sky, and \(a\) is the projected length of the semi-major axis on the sky [4]. However, this system is sensitive to the angle at which we observe the galaxy. A galaxy that appears highly elliptical when viewed edge-on may be more circular when viewed face-on. Although this classification scheme remains in use, it’s important to remember the limitations imposed by our viewing perspective.
We’ll use the following fields for each galaxy:
M89 field:
003804-4-0207NGC 5982 field:
004679-1-0034NGC 4697 field:
006121-1-0124
# Elliptical Galaxies
ellipticals = Observations.query_criteria(
provenance_name="SDSS Legacy Imaging",
target_name=[
"003804-4-0207", # M89
"004679-1-0034", # NGC 5982
"006121-1-0124", # NGC 4697
],
)
ellipticals
| intentType | obs_collection | provenance_name | instrument_name | project | filters | wavelength_region | target_name | target_classification | obs_id | s_ra | s_dec | dataproduct_type | proposal_pi | calib_level | t_min | t_max | t_exptime | em_min | em_max | obs_title | t_obs_release | proposal_id | proposal_type | sequence_number | s_region | jpegURL | dataURL | dataRights | mtFlag | srcDen | obsid | objID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str7 | str4 | str19 | str11 | str4 | str9 | str7 | str13 | str5 | str24 | float64 | float64 | str5 | str18 | int64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | str51 | float64 | str3 | str1 | int64 | str196 | str61 | str61 | str6 | bool | float64 | str9 | str9 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 003804-4-0207 | FIELD | sdss_image_003804-4-0207 | 188.89762961 | 12.5766093494 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 52721.21609756944 | 52721.220038743704 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 188.81217294825396 12.46522271055066 188.81545014737785 12.690283256904873 188.98315874867606 12.687858932000672 188.97973467649607 12.46280046903323 188.81217294825396 12.46522271055066 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3804/4/207/frame-irg-003804-4-0207.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3804/4/207/photoObj-003804-4-0207.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 297868245 | 880840069 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 004679-1-0034 | FIELD | sdss_image_004679-1-0034 | 234.574548776 | 59.3448234453 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 53170.30600509259 | 53170.309946266854 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 234.3046197895768 59.32444261506588 234.62038966365222 59.481940250855786 234.84464256375884 59.36456934478688 234.52892307987 59.20761382067637 234.3046197895768 59.32444261506588 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/4679/1/34/frame-irg-004679-1-0034.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/4679/1/34/photoObj-004679-1-0034.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298084026 | 883250573 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 006121-1-0124 | FIELD | sdss_image_006121-1-0124 | 192.206354543 | -5.7765959424 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 53856.28209305555 | 53856.28603411408 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 192.31583595794746 -5.863292886582556 192.08978940731004 -5.853419106917138 192.0970170390151 -5.689882899407467 192.32299845386115 -5.699753837522322 192.31583595794746 -5.863292886582556 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/6121/1/124/frame-irg-006121-1-0124.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/6121/1/124/photoObj-006121-1-0124.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 297963442 | 881902351 |
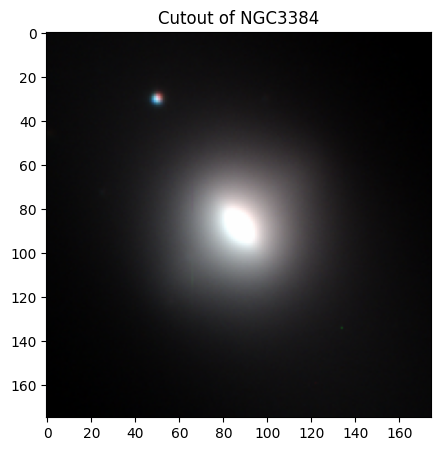
Lenticular Galaxies#
Lenticular galaxies are in-between elliptical and spiral galaxies. They have a central bulge and a disk similar to a spiral galaxy, but lack the spiral arm structure. These galaxies are thought to be former spiral galaxies that lost their interstellar material, likely due to interactions with other galaxies or their environments [5] [6].
We’ll use the field 003631-1-0302 for NGC 3384.
# Lenticular Galaxy
lenticular = Observations.query_criteria(
provenance_name="SDSS Legacy Imaging",
target_name="003631-1-0302", # NGC 3384
)
lenticular
| intentType | obs_collection | provenance_name | instrument_name | project | filters | wavelength_region | target_name | target_classification | obs_id | s_ra | s_dec | dataproduct_type | proposal_pi | calib_level | t_min | t_max | t_exptime | em_min | em_max | obs_title | t_obs_release | proposal_id | proposal_type | sequence_number | s_region | jpegURL | dataURL | dataRights | mtFlag | srcDen | obsid | objID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str7 | str4 | str19 | str11 | str4 | str9 | str7 | str13 | str5 | str24 | float64 | float64 | str5 | str18 | int64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | str51 | float64 | str3 | str1 | int64 | str194 | str61 | str61 | str6 | bool | float64 | str9 | str9 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 003631-1-0302 | FIELD | sdss_image_003631-1-0302 | 162.00495917 | 12.6948375209 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 52667.431497453705 | 52667.43543804926 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 161.9332351533888 12.574530580964552 161.90978380682168 12.798441361659597 162.0767624598467 12.815015802635779 162.10006839174622 12.591090421528067 161.9332351533888 12.574530580964552 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3631/1/302/frame-irg-003631-1-0302.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3631/1/302/photoObj-003631-1-0302.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298398508 | 885964246 |
Spiral Galaxies#
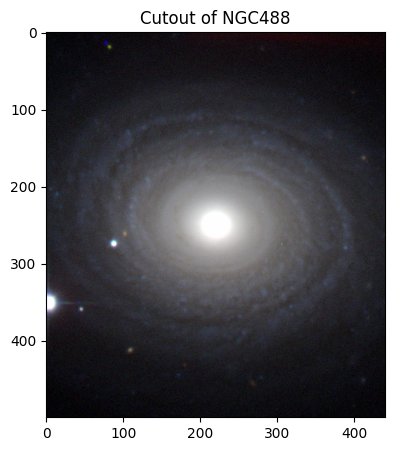
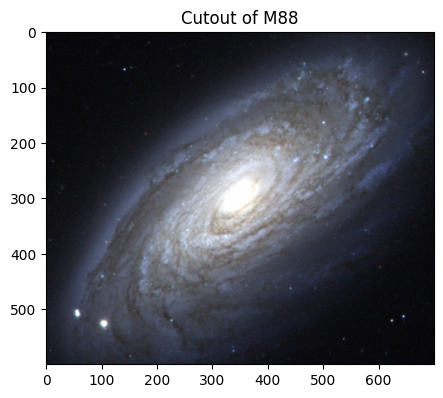
Spiral galaxies have distinct spiral arms that protrude from a central bulge of older stars. Within the spiral arms lie stellar “nurseries” of gas and dust that fuel young star formation. Spiral galaxies are classified into Sa, Sb, or Sc groups based on how tightly wound their spirals are, the thickness of the spiral arms, and the size of the central bulge. Sa spirals have large bulges and faint, small spiral arms whereas Sc spirals have smaller bulges, but larger, loose spiral arms [7].
We’ll use the following fields for each galaxy:
NGC 488 field:
007727-5-0202M88 field:
004381-2-0114M99 field:
004381-2-0093
# Spiral Galaxies
spirals = Observations.query_criteria(
provenance_name="SDSS Legacy Imaging",
target_name=[
"007727-5-0202", # NGC 488
"004381-2-0114", # M88
"004381-2-0093", # M99
],
)
spirals
| intentType | obs_collection | provenance_name | instrument_name | project | filters | wavelength_region | target_name | target_classification | obs_id | s_ra | s_dec | dataproduct_type | proposal_pi | calib_level | t_min | t_max | t_exptime | em_min | em_max | obs_title | t_obs_release | proposal_id | proposal_type | sequence_number | s_region | jpegURL | dataURL | dataRights | mtFlag | srcDen | obsid | objID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str7 | str4 | str19 | str11 | str4 | str9 | str7 | str13 | str5 | str24 | float64 | float64 | str5 | str18 | int64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | str51 | float64 | str3 | str1 | int64 | str195 | str61 | str61 | str6 | bool | float64 | str9 | str9 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 004381-2-0093 | FIELD | sdss_image_004381-2-0093 | 184.719136049 | 14.4769892626 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 53032.39776828704 | 53032.401709229816 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 184.63484872415157 14.364236748218197 184.6343524567763 14.58938512819659 184.80350921612668 14.589601743912382 184.80383394846027 14.364453070729992 184.63484872415157 14.364236748218197 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/4381/2/93/frame-irg-004381-2-0093.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/4381/2/93/photoObj-004381-2-0093.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298352265 | 885500811 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 004381-2-0114 | FIELD | sdss_image_004381-2-0114 | 187.966141332 | 14.457917178 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 53032.40647534722 | 53032.41041640574 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 187.88016114963244 14.346363232959801 187.8830848748545 14.571503687912221 188.05220635612855 14.569329914111023 188.0491114033052 14.344191605583559 187.88016114963244 14.346363232959801 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/4381/2/114/frame-irg-004381-2-0114.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/4381/2/114/photoObj-004381-2-0114.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298351741 | 885496458 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 007727-5-0202 | FIELD | sdss_image_007727-5-0202 | 20.406804076 | 5.3457659483 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 54747.40886678241 | 54747.41280784093 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 20.321964096341954 5.235060749739203 20.32725877200831 5.460113241855058 20.49167212052815 5.4563495479137645 20.48631705941364 5.231298472919874 20.321964096341954 5.235060749739203 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/7727/5/202/frame-irg-007727-5-0202.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/7727/5/202/photoObj-007727-5-0202.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298036044 | 882777689 |
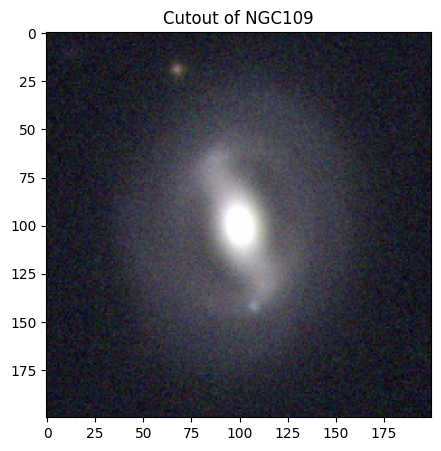
Barred Spiral Galaxies#
Barred spiral galaxies have a distinct, luminous bar/stripe across their center. This bar is thought to form either from internal dynamical instabilities or from gravitational interactions with neighboring galaxies. Like regular spiral galaxies, they are classified into SBa, SBb, and SBc types: SBa galaxies have tightly wound spiral arms and a larger central bulge, while SBc galaxies have loosely wound arms and a smaller bulge. [8].
We’ll use the following fields for each galaxy:
NGC 109 field:
007932-2-0051M91 field:
004381-2-0120NGC 5068 field:
001449-5-0093
# Barred Spirals
barred_spirals = Observations.query_criteria(
provenance_name="SDSS Legacy Imaging",
target_name=[
"007932-2-0051", # NGC 109
"004381-2-0120", # M91
"001449-5-0093", # NGC 5068
],
)
barred_spirals
| intentType | obs_collection | provenance_name | instrument_name | project | filters | wavelength_region | target_name | target_classification | obs_id | s_ra | s_dec | dataproduct_type | proposal_pi | calib_level | t_min | t_max | t_exptime | em_min | em_max | obs_title | t_obs_release | proposal_id | proposal_type | sequence_number | s_region | jpegURL | dataURL | dataRights | mtFlag | srcDen | obsid | objID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str7 | str4 | str19 | str11 | str4 | str9 | str7 | str13 | str5 | str24 | float64 | float64 | str5 | str18 | int64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | str51 | float64 | str3 | str1 | int64 | str198 | str61 | str61 | str6 | bool | float64 | str9 | str9 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 001449-5-0093 | FIELD | sdss_image_001449-5-0093 | 199.759449788 | -21.0895968268 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 51667.208523726855 | 51667.21246478537 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 199.68382220371453 -21.209641458700236 199.6605346260022 -20.98555578244084 199.83496672259864 -20.969628194410113 199.8585150712067 -21.19368991756911 199.68382220371453 -21.209641458700236 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/1449/5/93/frame-irg-001449-5-0093.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/1449/5/93/photoObj-001449-5-0093.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298381053 | 885786836 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 004381-2-0120 | FIELD | sdss_image_004381-2-0120 | 188.893660009 | 14.4440133289 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 53032.408963194444 | 53032.412904368706 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 188.8072050207449 14.332814743629992 188.81110366536907 14.557938939364815 188.98019947543165 14.55507039558893 188.97612983550505 14.329949038635592 188.8072050207449 14.332814743629992 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/4381/2/120/frame-irg-004381-2-0120.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/4381/2/120/photoObj-004381-2-0120.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298353167 | 885509568 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 007932-2-0051 | FIELD | sdss_image_007932-2-0051 | 6.52840089436 | 21.7582967467 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 54857.14674201389 | 54857.15068307241 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 6.439077306737359 21.646492711571536 6.441505431337264 21.87164565721037 6.617862374334172 21.869942774151156 6.615157893982057 21.644792545902753 6.439077306737359 21.646492711571536 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/7932/2/51/frame-irg-007932-2-0051.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/7932/2/51/photoObj-007932-2-0051.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 298320511 | 885204258 |
Irregular Galaxies#
Irregular galaxies are galaxies that do not fit into the elliptical or spiral/barred spiral categories. They typically have chaotic or asymmetric structures, often resulting from violent interactions with other galaxies, collisions, or internal processes. Well-known examples include the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds [9].
We’ll use the following fields for each galaxy:
IC 3583 field:
003836-5-0268NGC 7292 field:
008115-6-0118
# Irregular galaxies
irregulars = Observations.query_criteria(
provenance_name="SDSS Legacy Imaging",
target_name=[
"003836-5-0268", # IC 3583
"008115-6-0118", # NGC 7292
],
)
irregulars
| intentType | obs_collection | provenance_name | instrument_name | project | filters | wavelength_region | target_name | target_classification | obs_id | s_ra | s_dec | dataproduct_type | proposal_pi | calib_level | t_min | t_max | t_exptime | em_min | em_max | obs_title | t_obs_release | proposal_id | proposal_type | sequence_number | s_region | jpegURL | dataURL | dataRights | mtFlag | srcDen | obsid | objID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str7 | str4 | str19 | str11 | str4 | str9 | str7 | str13 | str5 | str24 | float64 | float64 | str5 | str18 | int64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | float64 | str51 | float64 | str3 | str1 | int64 | str197 | str61 | str61 | str6 | bool | float64 | str9 | str9 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 003836-5-0268 | FIELD | sdss_image_003836-5-0268 | 189.175059735 | 13.1998869096 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 52729.241773726855 | 52729.24571490111 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 189.08925682499807 13.088602004029513 189.09279407361726 13.313649665325844 189.26093904132443 13.311033284196608 189.25724699913016 13.085987980105468 189.08925682499807 13.088602004029513 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3836/5/268/frame-irg-003836-5-0268.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/3836/5/268/photoObj-003836-5-0268.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 297915282 | 881405426 |
| science | SDSS | SDSS Legacy Imaging | SDSS Camera | SDSS | u;g;r;i;z | OPTICAL | 008115-6-0118 | FIELD | sdss_image_008115-6-0118 | 337.063165401 | 30.3475793355 | image | SDSS Collaboration | 3 | 55122.10941539352 | 55122.1133563363 | 53.907456 | 304.79999999999995 | 1083.3000000000002 | Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) Legacy Imaging Data | 55571.0 | N/A | -- | -- | POLYGON 337.0043270910967 30.21800053821113 336.9384683229479 30.435781036316044 337.12219177360197 30.47702529132038 337.18766967475585 30.259153076577768 337.0043270910967 30.21800053821113 | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/8115/6/118/frame-irg-008115-6-0118.jpg | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/8115/6/118/photoObj-008115-6-0118.fits | PUBLIC | False | nan | 297726821 | 879149237 |
Downloading SDSS Legacy Imaging Survey Data Products#
For each image, there are 7 available products: The preview .jpg image, the FITS files in each respective SDSS filter (u, g, r, i, and z), and a catalog file containing photometric measurements from all five filters combined. The catalog file is listed as SDSS Imaging Catalogs for the productSubGroupDescription parameter.
For more information about products available at MAST, you can check out the SDSS Legacy Imaging Survey Documentation.
# Combining the Astropy tables for all galaxies
all_galaxies = vstack(
[ellipticals, lenticular, spirals, barred_spirals, irregulars]
)
# Viewing available products (first 7)
galaxy_products = Observations.get_product_list(all_galaxies)
galaxy_products[:7]
| obsID | obs_collection | dataproduct_type | obs_id | description | type | dataURI | productType | productGroupDescription | productSubGroupDescription | productDocumentationURL | project | prvversion | proposal_id | productFilename | size | parent_obsid | dataRights | calib_level | filters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| str9 | str4 | str12 | str28 | str246 | str1 | str64 | str7 | str28 | str21 | str70 | str19 | str3 | str3 | str30 | int64 | str9 | str6 | int64 | str9 |
| 297726821 | SDSS | image | sdss_image_008115-6-0118 | Preview-Full | S | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/8115/6/118/frame-irg-008115-6-0118.jpg | PREVIEW | -- | -- | -- | SDSS Legacy Imaging | DR8 | N/A | frame-irg-008115-6-0118.jpg | 1041251 | 297726821 | PUBLIC | 3 | u;g;r;i;z |
| 297726821 | SDSS | image | sdss_image_008115-6-0118 | SDSS calibrated, sky-subtracted corrected photometry frame and associated calibration metadata for each run number, camera column, and field name within SDSS. | S | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/8115/6/118/frame-g-008115-6-0118.fits.bz2 | SCIENCE | Minimum Recommended Products | IMAGE | https://outerspace.stsci.edu/display/SDSS/Legacy+Imaging+Data+Products | SDSS Legacy Imaging | DR8 | N/A | frame-g-008115-6-0118.fits.bz2 | 3077536 | 297726821 | PUBLIC | 2 | g |
| 297726821 | SDSS | image | sdss_image_008115-6-0118 | SDSS calibrated, sky-subtracted corrected photometry frame and associated calibration metadata for each run number, camera column, and field name within SDSS. | S | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/8115/6/118/frame-i-008115-6-0118.fits.bz2 | SCIENCE | Minimum Recommended Products | IMAGE | https://outerspace.stsci.edu/display/SDSS/Legacy+Imaging+Data+Products | SDSS Legacy Imaging | DR8 | N/A | frame-i-008115-6-0118.fits.bz2 | 3876498 | 297726821 | PUBLIC | 2 | i |
| 297726821 | SDSS | image | sdss_image_008115-6-0118 | SDSS calibrated, sky-subtracted corrected photometry frame and associated calibration metadata for each run number, camera column, and field name within SDSS. | S | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/8115/6/118/frame-r-008115-6-0118.fits.bz2 | SCIENCE | Minimum Recommended Products | IMAGE | https://outerspace.stsci.edu/display/SDSS/Legacy+Imaging+Data+Products | SDSS Legacy Imaging | DR8 | N/A | frame-r-008115-6-0118.fits.bz2 | 3661286 | 297726821 | PUBLIC | 2 | r |
| 297726821 | SDSS | image | sdss_image_008115-6-0118 | SDSS calibrated, sky-subtracted corrected photometry frame and associated calibration metadata for each run number, camera column, and field name within SDSS. | S | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/8115/6/118/frame-u-008115-6-0118.fits.bz2 | SCIENCE | Minimum Recommended Products | IMAGE | https://outerspace.stsci.edu/display/SDSS/Legacy+Imaging+Data+Products | SDSS Legacy Imaging | DR8 | N/A | frame-u-008115-6-0118.fits.bz2 | 3537982 | 297726821 | PUBLIC | 2 | u |
| 297726821 | SDSS | image | sdss_image_008115-6-0118 | SDSS calibrated, sky-subtracted corrected photometry frame and associated calibration metadata for each run number, camera column, and field name within SDSS. | S | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/8115/6/118/frame-z-008115-6-0118.fits.bz2 | SCIENCE | Minimum Recommended Products | IMAGE | https://outerspace.stsci.edu/display/SDSS/Legacy+Imaging+Data+Products | SDSS Legacy Imaging | DR8 | N/A | frame-z-008115-6-0118.fits.bz2 | 3897222 | 297726821 | PUBLIC | 2 | z |
| 297726821 | SDSS | image | sdss_image_008115-6-0118 | SDSS Legacy Imaging photoObj catalog. This contains the full, calibrated outputs of the SDSS Imaging Pipeline including source detection, classification, magnitude measurements, and quality flags for each field and all five filters in that field. | S | mast:SDSS/sdss/imaging/8115/6/118/photoObj-008115-6-0118.fits | SCIENCE | Minimum Recommended Products | SDSS Imaging Catalogs | https://outerspace.stsci.edu/display/SDSS/Legacy+Imaging+Data+Products | SDSS Legacy Imaging | DR8 | N/A | photoObj-008115-6-0118.fits | 5705280 | 297726821 | PUBLIC | 3 | u;g;r;i;z |
We’ll now download all FITS files, specifically focusing on the files in specific ugriz filters. For this tutorial, we’ll be using the g, r, and i filters only, so we can filter those out using the filters parameter.
# Downloading products
manifest = Observations.download_products(
galaxy_products, mrp_only=True, verbose=False, filters=["g", "r", "i"]
)
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_008115-6-0118/frame-g-008115-6-0118.fits.bz2 with expected size 3077536. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_008115-6-0118/frame-i-008115-6-0118.fits.bz2 with expected size 3876498. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_008115-6-0118/frame-r-008115-6-0118.fits.bz2 with expected size 3661286. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_003804-4-0207/frame-g-003804-4-0207.fits.bz2 with expected size 2986179. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_003804-4-0207/frame-i-003804-4-0207.fits.bz2 with expected size 3571359. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_003804-4-0207/frame-r-003804-4-0207.fits.bz2 with expected size 3083697. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_003836-5-0268/frame-g-003836-5-0268.fits.bz2 with expected size 3128869. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_003836-5-0268/frame-i-003836-5-0268.fits.bz2 with expected size 3119980. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_003836-5-0268/frame-r-003836-5-0268.fits.bz2 with expected size 3147869. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_006121-1-0124/frame-g-006121-1-0124.fits.bz2 with expected size 3036601. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_006121-1-0124/frame-i-006121-1-0124.fits.bz2 with expected size 3513999. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_006121-1-0124/frame-r-006121-1-0124.fits.bz2 with expected size 3212269. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_007727-5-0202/frame-g-007727-5-0202.fits.bz2 with expected size 3026470. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_007727-5-0202/frame-i-007727-5-0202.fits.bz2 with expected size 3862314. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_007727-5-0202/frame-r-007727-5-0202.fits.bz2 with expected size 3034328. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_004679-1-0034/frame-g-004679-1-0034.fits.bz2 with expected size 3405007. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_004679-1-0034/frame-i-004679-1-0034.fits.bz2 with expected size 3606430. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_004679-1-0034/frame-r-004679-1-0034.fits.bz2 with expected size 3190817. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_007932-2-0051/frame-g-007932-2-0051.fits.bz2 with expected size 2892867. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_007932-2-0051/frame-i-007932-2-0051.fits.bz2 with expected size 3578789. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_007932-2-0051/frame-r-007932-2-0051.fits.bz2 with expected size 3196035. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_004381-2-0114/frame-g-004381-2-0114.fits.bz2 with expected size 3125179. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_004381-2-0114/frame-i-004381-2-0114.fits.bz2 with expected size 3742961. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_004381-2-0114/frame-r-004381-2-0114.fits.bz2 with expected size 3243122. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_004381-2-0093/frame-g-004381-2-0093.fits.bz2 with expected size 2957590. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_004381-2-0093/frame-i-004381-2-0093.fits.bz2 with expected size 3540737. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_004381-2-0093/frame-r-004381-2-0093.fits.bz2 with expected size 3125591. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_004381-2-0120/frame-g-004381-2-0120.fits.bz2 with expected size 3037577. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_004381-2-0120/frame-i-004381-2-0120.fits.bz2 with expected size 3674742. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_004381-2-0120/frame-r-004381-2-0120.fits.bz2 with expected size 3118318. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_001449-5-0093/frame-g-001449-5-0093.fits.bz2 with expected size 3249674. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_001449-5-0093/frame-i-001449-5-0093.fits.bz2 with expected size 3704885. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_001449-5-0093/frame-r-001449-5-0093.fits.bz2 with expected size 3440363. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_003631-1-0302/frame-g-003631-1-0302.fits.bz2 with expected size 3226342. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_003631-1-0302/frame-i-003631-1-0302.fits.bz2 with expected size 3423721. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/SDSS/sdss_image_003631-1-0302/frame-r-003631-1-0302.fits.bz2 with expected size 3234965. [astroquery.query]
Each FITS file follows the following naming scheme: frame-{filter}-{RUN}-{CAMCOL}-{FIELD} where RUN is the zero-padded, six-digit identification number for that photometric run, CAMCOL is the camera column identifying the scanline within the run, and FIELD is field number for that observation.
While we won’t be using the photoObj files in this tutorial, these contain the fully calibrated outputs from the SDSS Imaging Pipeline and other respective measurements such as photometry in all five SDSS filters (u, g, r, i, and z), source classification, and quality flags. There is one photoObj file for each run-camcol-field combination.
Creating the Cutout Images Using Astrocut#
Now that we downloaded the FITS files for each galaxy, we can use Astrocut to trim the images and create cutouts!
Astrocut uses FITS files and specified center coordinates to create a trimmed image. We’ll create a dictionary of galaxy names, their target names, and center coordinates. For more information about Astrocut, you can view the documentation.
We’ll use warnings.filterwarnings to suppress FITS warnings due to the change in keyword names since SDSS data was created.
Each Astrocut image cell takes a few seconds to run!
# Suppressing FITS warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=astropy.wcs.FITSFixedWarning)
In order to center the galaxy in our cutout, we need to know the center coordinates! We can use astroquery to resolve the coordinates for each galaxy using Observations.resolve_object. We’ll now make a dictionary to code in the field ID and coordinates per galaxy.
# Making a dictionary for galaxy names with MAST target names and coordinates
galaxies = {
"m89": {
"id": "003804-4-0207",
"coord": Observations.resolve_object("m89"),
},
"ngc5982": {
"id": "004679-1-0034",
"coord": Observations.resolve_object("ngc5982"),
},
"ngc4697": {
"id": "006121-1-0124",
"coord": Observations.resolve_object("ngc4697"),
},
"ngc3384": {
"id": "003631-1-0302",
"coord": Observations.resolve_object("ngc3384"),
},
"ngc488": {
"id": "007727-5-0202",
"coord": Observations.resolve_object("ngc488"),
},
"m88": {
"id": "004381-2-0114",
"coord": Observations.resolve_object("m88"),
},
"m99": {
"id": "004381-2-0093",
"coord": Observations.resolve_object("m99"),
},
"ngc109": {
"id": "007932-2-0051",
"coord": Observations.resolve_object("ngc109"),
},
"m91": {
"id": "004381-2-0120",
"coord": Observations.resolve_object("m91"),
},
"ngc5068": {
"id": "001449-5-0093",
"coord": Observations.resolve_object("ngc5068"),
},
"ic3583": {
"id": "003836-5-0268",
"coord": Observations.resolve_object("ic3583"),
},
"ngc7292": {
"id": "008115-6-0118",
"coord": Observations.resolve_object("ngc7292"),
},
}
# Creating a function to locate files from download, find the r, g, and i files
def get_files_for_galaxy(galaxy_name):
"""
Finds the files based on galaxy name and returns their r, g, and i FITS files
"""
# Finding the file by galaxy name
galaxy_mask = (
np.char.find(
manifest["Local Path"].astype(str), galaxies[galaxy_name]["id"]
)
>= 0
)
files = np.array(manifest["Local Path"][galaxy_mask], dtype=str)
# Decompressing the files
fits_files = np.array([], dtype=str)
for file in files:
fits_filename = file.replace('.bz2', '')
fits_files = np.append(fits_files, fits_filename)
with bz2.open(file, 'rb') as compressed_file:
with open(fits_filename, 'wb') as decompressed_file:
decompressed_file.write(compressed_file.read())
# Finding the r, g, and i files
rmask = np.char.find(fits_files, "frame-r") >= 0
gmask = np.char.find(fits_files, "frame-g") >= 0
imask = np.char.find(fits_files, "frame-i") >= 0
r_file = fits_files[rmask]
g_file = fits_files[gmask]
i_file = fits_files[imask]
return i_file[0], r_file[0], g_file[0]
# Helper function for creating cutout images
def create_cutouts(galaxy_name, cutout_size):
"""
This function takes the name of the galaxy and size of the cutout,
creates cutout using Astrocut, then plots the image using matplotlib
"""
# Using previous function to get the r, g, and i files
galaxy_input = get_files_for_galaxy(galaxy_name)
# Creating the cutouts
galaxy_colorimage = FITSCutout(
galaxy_input, galaxies[galaxy_name]["coord"], cutout_size
).get_image_cutouts(colorize=True)[0]
galaxy_colorimage.save(f"{galaxy_name}_cutout.png")
# Capitalizing the title
title_name = np.char.upper(galaxy_name)
# Displaying the cutouts
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.imshow(galaxy_colorimage)
plt.title(f"Cutout of {title_name}")
plt.show()
# M89
# Creating and displaying the cutout image of M89!
m89_img = create_cutouts("m89", [200, 200])

# NGC 5982
# Creating and displaying the cutout image of NGC 5982!
ngc5982_img = create_cutouts("ngc5982", [200, 200])

# NGC 4697
# Creating and displaying the cutout image of NGC 4697!
ngc4697_img = create_cutouts("ngc4697", [300, 200])
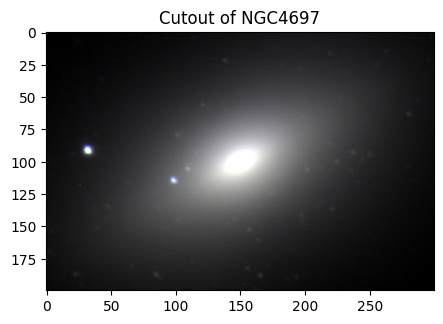
# NGC 3384
# Creating and displaying the cutout image of NGC 3384!
ngc3384_img = create_cutouts("ngc3384", [175, 175])
# NGC 488
# Creating and displaying the cutout image of NGC 488!
ngc488_img = create_cutouts("ngc488", [440, 500])
# M88
# Creating and displaying the cutout image of M88!
m88_img = create_cutouts("m88", [700, 600])
# M99
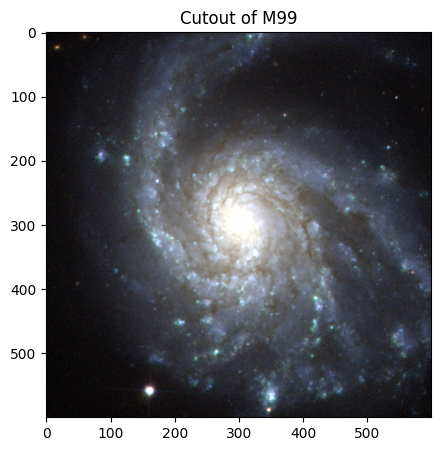
# Creating and displaying the cutout image of M99!
m99_img = create_cutouts("m99", [600, 600])
# NGC 109
# Creating and displaying the cutout image of NGC 109!
ngc109_img = create_cutouts("ngc109", [200, 200])

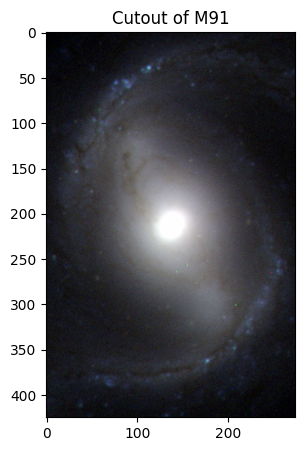
# M91
# Creating and displaying the cutout image of M91!
m91_img = create_cutouts("m91", [275, 425])
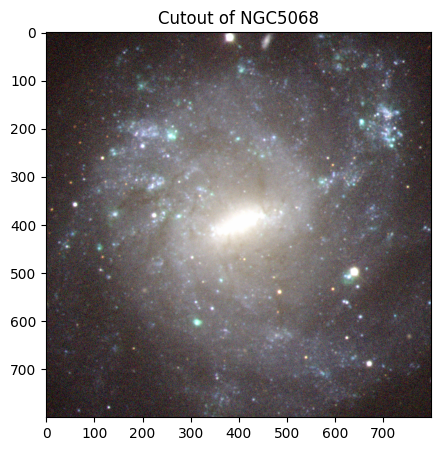
# NGC 5068
# Creating and displaying the cutout image of NGC 5068!
ngc5068_img = create_cutouts("ngc5068", [800, 800])
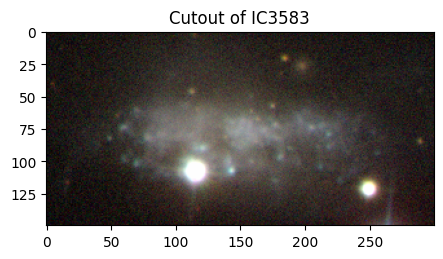
# IC 3583
# Creating and displaying the cutout image of IC 3583!
ic3583_img = create_cutouts("ic3583", [300, 150])
# NGC 7292
# Creating and displaying the cutout image of NGC 7292!
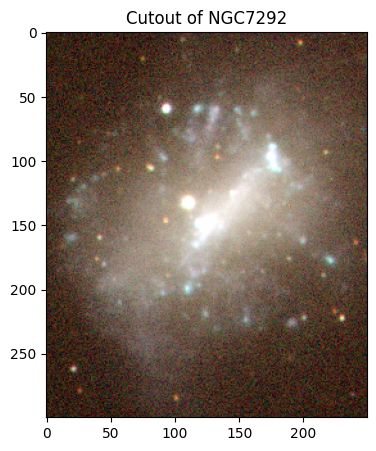
ngc7292_img = create_cutouts("ngc7292", [250, 300])
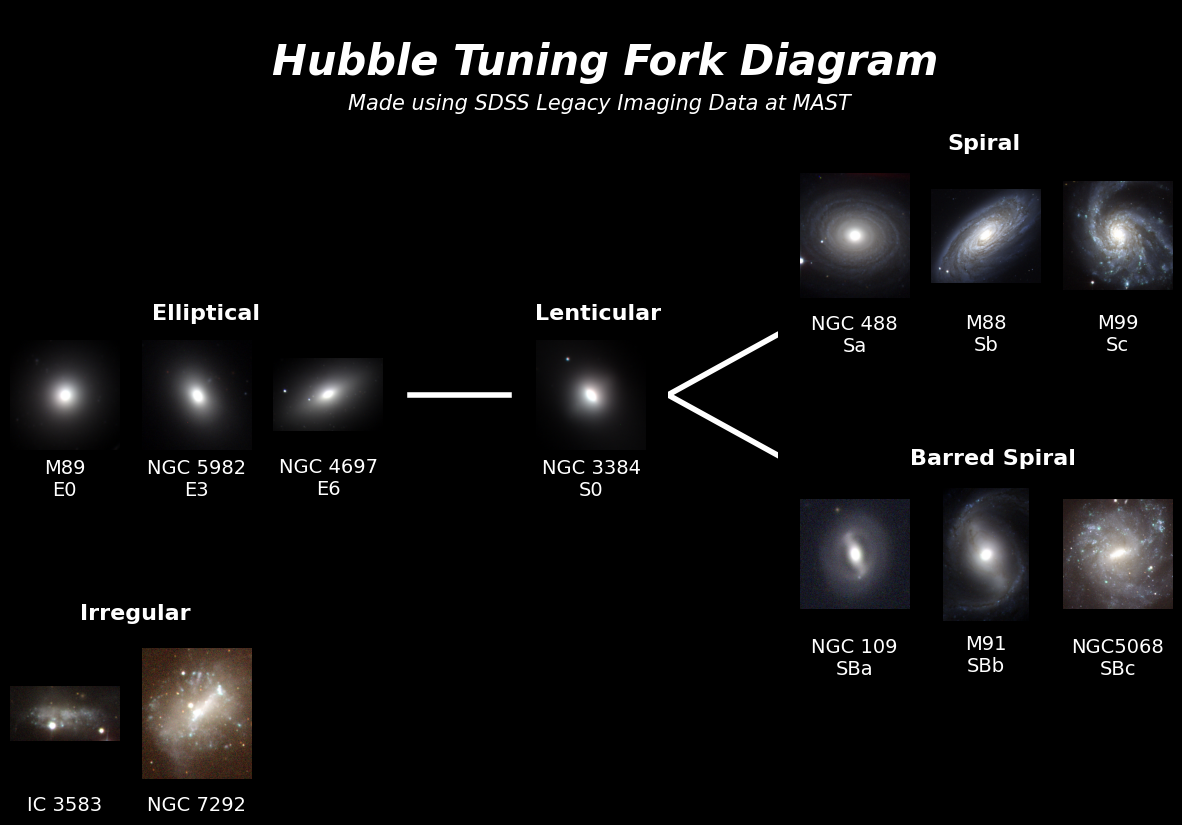
Making the Hubble Tuning Fork Diagram#
Now that we have our cutouts saved as .png files, we can create our Hubble Tuning Fork Diagram using matplotlib.image and a series of subplots!
# Creating subplots
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=5, ncols=9, figsize=(15, 10), facecolor="black")
for row in ax:
for a in row:
a.axis("off")
# Reading the cutout images
images = {}
for galaxy in galaxies.keys():
images[galaxy] = mpimg.imread(f"{galaxy}_cutout.png")
# Ading connecting lines
# Straight line
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 11)
y1 = 5 * np.ones(11)
# Plotting the images and lines
# Plotting the elliptical galaxies in the center left
ax[2, 0].imshow(images["m89"])
ax[2, 0].set_title("M89\nE0", y=-0.5, color="white", fontsize=14)
ax[2, 1].imshow(images["ngc5982"])
ax[2, 1].set_title("NGC 5982\nE3", y=-0.5, color="white", fontsize=14)
ax[2, 2].imshow(images["ngc4697"])
ax[2, 2].set_title("NGC 4697\nE6", y=-0.98, color="white", fontsize=14)
# Plotting the connecting straight line
ax[2, 3].plot(x, y1, color="white", lw=4)
# Plotting the lenticular galaxy between the ellipticals and spirals
ax[2, 4].imshow(images["ngc3384"])
ax[2, 4].set_title("NGC 3384\nS0", y=-0.5, color="white", fontsize=14)
# Plotting the connecting v line
ax[2, 5].plot((lambda x: np.abs(x - 5))(x), x, color="white", lw=4)
ax[2, 5].set_xlim(0, 5)
# Plotting the spiral galaxies in the top right
ax[1, 6].imshow(images["ngc488"])
ax[1, 6].set_title("NGC 488\nSa", y=-0.5, color="white", fontsize=14)
ax[1, 7].imshow(images["m88"])
ax[1, 7].set_title("M88\nSb", y=-0.82, color="white", fontsize=14)
ax[1, 8].imshow(images["m99"])
ax[1, 8].set_title("M99\nSc", y=-0.63, color="white", fontsize=14)
# Plotting the barred spirals in the bottom right
ax[3, 6].imshow(images["ngc109"])
ax[3, 6].set_title("NGC 109\nSBa", y=-0.68, color="white", fontsize=14)
ax[3, 7].imshow(images["m91"])
ax[3, 7].set_title("M91\nSBb", y=-0.45, color="white", fontsize=14)
ax[3, 8].imshow(images["ngc5068"])
ax[3, 8].set_title("NGC5068\nSBc", y=-0.68, color="white", fontsize=14)
# Plotting the irregular galaxies in the bottom left
ax[4, 0].imshow(images["ic3583"])
ax[4, 0].set_title("IC 3583", y=-1.43, color="white", fontsize=14)
ax[4, 1].imshow(images["ngc7292"])
ax[4, 1].set_title("NGC 7292", y=-0.3, color="white", fontsize=14)
# Adding labels
fig.text(
0.3,
0.815,
"Hubble Tuning Fork Diagram",
fontsize=30,
fontstyle="oblique",
fontweight="bold",
color="white",
)
fig.text(
0.35,
0.78,
"Made using SDSS Legacy Imaging Data at MAST",
fontsize=15,
fontstyle="oblique",
# fontweight="bold",
color="white",
)
fig.text(
0.22, 0.57, "Elliptical", color="white", fontsize=16, fontweight="bold"
)
fig.text(
0.475, 0.57, "Lenticular", color="white", fontsize=16, fontweight="bold"
)
fig.text(0.75, 0.74, "Spiral", color="white", fontsize=16, fontweight="bold")
fig.text(
0.725,
0.425,
"Barred Spiral",
color="white",
fontsize=16,
fontweight="bold",
)
fig.text(
0.172, 0.27, "Irregular", color="white", fontsize=16, fontweight="bold"
)
plt.show()
End of Tutorial#
Congratulations, you’ve reached the end of this notebook! You’ve learned how to use astroquery.mast and astrocut to create a Hubble Tuning Fork Diagram!
Exercise#
Can you classify these three galaxies referencing the Hubble Tuning Fork Diagram you constructed above?:
M95
NGC 4125
M74
To choose the right field, you can look at the AstroView on the MAST Portal.
(Hint: You can download just the preview image by using Observations.filter_products and adding the argument productType="PREVIEW")
# Query and download data from MAST
# View preview images
Exercise Solution#
# Query and download data from MAST
# Querying MAST
exercise_galaxies = Observations.query_criteria(
provenance_name="SDSS Legacy Imaging",
target_name=["003836-4-0084", "006118-3-0168", "007845-2-0104"],
)
# Get product list for query
exercise_products = Observations.get_product_list(exercise_galaxies)
# Filter products to get preview jpgs only
filtered_products = Observations.filter_products(
exercise_products,
# Selecting preview jpgs
productType="PREVIEW",
)
# Download products
Observations.download_products(filtered_products, flat=True, verbose=False)
INFO: Found cached file ./frame-irg-006118-3-0168.jpg with expected size 988026. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./frame-irg-003836-4-0084.jpg with expected size 1047832. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./frame-irg-007845-2-0104.jpg with expected size 1177388. [astroquery.query]
| Local Path | Status | Message | URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| str29 | str8 | object | object |
| ./frame-irg-006118-3-0168.jpg | COMPLETE | None | None |
| ./frame-irg-003836-4-0084.jpg | COMPLETE | None | None |
| ./frame-irg-007845-2-0104.jpg | COMPLETE | None | None |
# Viewing the previews side-by-side
fig2, ax2 = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=3, figsize=(15, 10), facecolor="black")
for a in ax2:
a.axis("off")
# Reading images
img1 = mpimg.imread("frame-irg-003836-4-0084.jpg")
img2 = mpimg.imread("frame-irg-006118-3-0168.jpg")
img3 = mpimg.imread("frame-irg-007845-2-0104.jpg")
# Plotting images
ax2[0].imshow(img1)
ax2[0].set_title("M95", color="white", y=-0.2, fontsize=14, fontweight="bold")
ax2[1].imshow(img2)
ax2[1].set_title(
"NGC 4125", color="white", y=-0.2, fontsize=14, fontweight="bold"
)
ax2[2].imshow(img3)
ax2[2].set_title("M74", color="white", y=-0.2, fontsize=14, fontweight="bold")
plt.show()

Assumptions:
It appears that M95 is fairly similar to NGC 109 and M91; this must be a barred spiral galaxy! While the spiral arms are somewhat tight, M95 is most likely between an SBa and an SBb.
NGC 4125 does not have spiral arms or dust lanes, so it must be elliptical. Since elliptical galaxies are classified by their ellipticity, NGC 4125 is likely between an E3 and an E6.
M74 has distinct spiral arms, but no visible bar. The spiral arms are fairly loose, but not as loose as M99. M74 is likely between an Sb and an Sc galaxy.
Results from NED:
M95: SBb
NGC 4125: E6
M74: Sc
Additional Resources#
Additional resources are linked below:
Citations#
If you use data from MAST for published research, please see the following links for information on which citations to include in your paper:
About this Notebook#
Author(s): Natalie Haugen (nhaugen@terpmail.umd.edu) and Julie Imig (jimig@stsci.edu)
Keyword(s): Tutorial, SDSS, SDSS Legacy Imaging Survey, galaxies, galaxy morphology
First published: July 2025
Last updated: July 2025

