
Correcting for Scattered Light in WFC3/IR Exposures: Using calwf3 to Mask Bad Reads#
Learning Goals#
This notebook shows one of two available methods to correct for time-variable background
(TVB) due to scattered light from observing close to the Earth’s limb. This method illustrates how to mask bad reads in the RAW image and then reprocess with calwf3, and it may be used for rejecting anomalous reads occurring either at the beginning or at the end of an exposure.
By the end of this tutorial, you will:
Compute and plot the difference between IMA reads to identify the reads affected by TVB.
Reprocess a single exposure with
calwf3by excluding the first few reads which are affected by scattered light.Compare the original FLT to the reprocessed FLT image.
Compare the original DRZ to the reprocessed DRZ image.
A second method (manually subtracting bad reads from the final IMA read) can be found in the notebook Correcting for Scattered Light in WFC3/IR Exposures: Manually Subtracting Bad Reads (O’Connor 2023). This provides a method for removing anomalies such as satellite trails which appear in the middle of an IMA exposure. One caveat of the second method is that it does not perform the ‘ramp fitting’ step and therefore the calibrated FLT products will still contain cosmic rays.
Please note that this method may leave large sky residuals in regions corresponding to WFC3/IR ‘blobs’, flagged in the FLT data quality (DQ) array as a value of 512. This method is therefore recommended for observations acquired using an WFC3-IR-DITHER-BLOB dither (or POSTARG equivalent) to step over blob regions. Software such as AstroDrizzle may then be used to combine the FLT exposures, while excluding pixels with 512 flags (or any bit-wise combination of 512 and another flag e.g. 576 = 512 + 64).
Table of Contents#
Introduction
1. Imports
2. Downloading Data
3. Identifying Reads with Time Variable Background
4. Querying CRDS for the Reference File
5. Reprocessing the Observation
6. Drizzling Nominal and Reprocessed FLT Products
7. Conclusions
Additional Resources
About this Notebook
Citations
Introduction #
Observations with strong time variability in the sky background during a MULTIACCUM ramp can corrupt the WFC3 calwf3 ‘linear ramp fit’ and cosmic-ray identification algorithm (CRCORR, Section 3.3.10 of the Data Handbook). The CRCORR
algorithm assumes that a given pixel sees a constant count rate throughout the read from a
combination of sources and diffuse background (i.e., the integrated signal “ramps” are linear). A background
varying strongly with time (i.e. where the “ramps” are non-linear) can trigger the cosmic-ray
(CR) flagging thresholds in calwf3, causing the algorithm to identify most or all of the pixels as a CR at any given read.
In this notebook we will examine an observation affected by strong TVB,
specifically due to Earth limb scattered light (Section 7.10 of the WFC3 Data Handbook) affecting the first few reads and producing a spatially variable background. We will run calwf3 while rejecting the affected reads to create an improved FLT product with a flat background and an improved ramp fit. One caveat is that the new FLT will
have a reduced total exposure time, given the rejection of some number of reads, and
therefore a lower signal-to-noise ratio.
Please see the notebook WFC3/IR IMA Visualization with An Example of Time Variable Background (O’Connor 2023) for a walkthrough of how to identify a TVB in due to scattered light.
1. Imports #
This notebook assumes you have created the virtual environment in WFC3 Library’s installation instructions.
We import:
os for setting environment variables
glob for finding lists of files
shutil for managing directories
numpy for handling array functions
matplotlib.pyplot for plotting data
astropy.io fits for accessing FITS files
astroquery.mast Observations for downloading data
wfc3tools
calwf3for calibrating WFC3 dataginga for finding min/max outlier pixels
stwcs for updating World Coordinate System images
drizzlepac for combining images with AstroDrizzle
We import the following modules:
ima_visualization_and_differencing to take the difference between reads, plot the ramp, and visualize the difference in images
import os
import glob
import shutil
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from astropy.io import fits
from astroquery.mast import Observations
from wfc3tools import calwf3
from ginga.util.zscale import zscale
from stwcs import updatewcs
from drizzlepac import astrodrizzle
import ima_visualization_and_differencing as diff
%matplotlib inline
2. Downloading Data#
The following commands query MAST for the necessary data products and download them to the current directory. Here we obtain WFC3/IR observations from HST Frontier Fields program 14037, Visit BB. We specifically want the observation icqtbbbxq, as it is strongly affected by Earth limb scattered light. The data products requested are the RAW, IMA, and FLT files. For an example of TVB at the end of an exposure, we include an alternate dataset (OBS_ID = ICXT27020, file_id = icxt27hkq) in which the Earth limb affects the reads at the end of the MULTIACCUM sequence (SCI,1 through SCI,5).
Warning: this cell may take a few minutes to complete.
OBS_ID = 'ICQTBB020' # Earth-limb at the start
# OBS_ID = 'ICXT27020' # Earth-limb at the end
data_list = Observations.query_criteria(obs_id=OBS_ID)
file_id = "icqtbbbxq"
# file_id = 'icxt27hkq'
Observations.download_products(data_list['obsid'], project='CALWF3',
obs_id=file_id, mrp_only=False,
productSubGroupDescription=['RAW', 'IMA', 'FLT'])
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbbxq/icqtbbbxq_ima.fits with expected size 168261120. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbbxq/icqtbbbxq_flt.fits with expected size 16583040. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbbxq/icqtbbbxq_raw.fits with expected size 34027200. [astroquery.query]
| Local Path | Status | Message | URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| str47 | str8 | object | object |
| ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbbxq/icqtbbbxq_ima.fits | COMPLETE | None | None |
| ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbbxq/icqtbbbxq_flt.fits | COMPLETE | None | None |
| ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbbxq/icqtbbbxq_raw.fits | COMPLETE | None | None |
Now, we will move our IMA and FLT files to a separate directory called “orig/” so they are not overwritten when we run calwf3. We leave our RAW file in the working directory for later use.
if not os.path.exists('orig/'):
os.mkdir('orig/')
shutil.copy(f'mastDownload/HST/{file_id}/{file_id}_ima.fits', f'orig/{file_id}_ima.fits')
shutil.copy(f'mastDownload/HST/{file_id}/{file_id}_flt.fits', f'orig/{file_id}_flt.fits')
raw_file = f'mastDownload/HST/{file_id}/{file_id}_raw.fits'
remove_files_list = glob.glob(f'./{file_id}_*.fits')
for rm_file in remove_files_list:
os.remove(rm_file)
shutil.copy(raw_file, f'{file_id}_raw.fits')
'icqtbbbxq_raw.fits'
3. Identifying Reads with Time Variable Background#
In this section, we show how to identify the reads impacted by TVB by examining the difference in count rate between reads. This section was taken from the WFC3/IR IMA Visualization with An Example of Time Variable Background (O’Connor 2023) notebook, which includes a more comprehensive walkthrough of identifying time variable background in WFC3/IR images.
Here we implement a technique to examine the count rate difference between consecutive reads. In this case, we first convert from count rate (electrons/second) back to counts (electrons) before taking the difference, as shown in equation 3 from WFC3 ISR 2018-05.
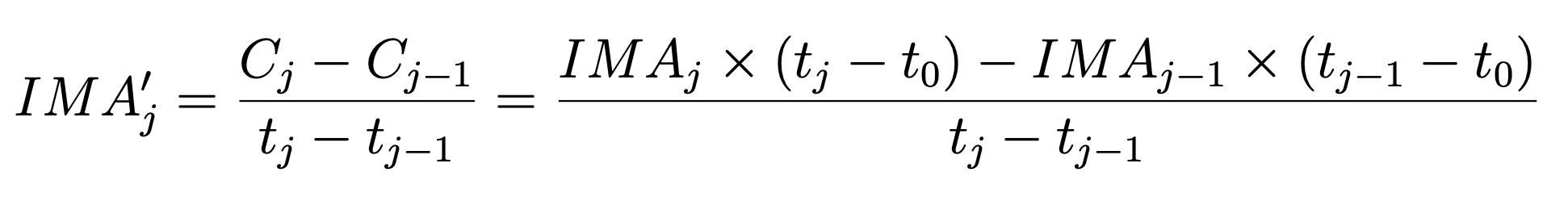
We compare sky values in different regions of the detector (left side, right side, and full frame). If you would like to specify your own regions for the left and right sides of your image, you can change the lhs_region and rhs_region parameters. Each region must be specified as a dictionary including the four “corners” (x0, x1, y0, and y1) of the region you would like to select. You may want to avoid the edges of the detector which have a large number of bad pixels and higher flat field errors.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
ima_filepath = f'orig/{file_id}_ima.fits'
path, filename = os.path.split(ima_filepath)
cube, integ_time = diff.read_wfc3(ima_filepath)
lhs_region = {"x0": 50, "x1": 250, "y0": 100, "y1": 900}
rhs_region = {"x0": 700, "x1": 900, "y0": 100, "y1": 900}
# Please use a limit that makes sense for your own data, when running your images through this notebook.
cube[np.abs(cube) > 3] = np.nan
diff_cube = diff.compute_diff_imas(cube, integ_time, diff_method="instantaneous")
median_diff_fullframe, median_diff_lhs, median_diff_rhs = (
diff.get_median_fullframe_lhs_rhs(
diff_cube,
lhs_region=lhs_region,
rhs_region=rhs_region))
plt.rc('xtick', labelsize=20)
plt.rc('ytick', labelsize=20)
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 30})
plt.rcParams.update({'lines.markersize': 15})
diff.plot_ramp(ima_filepath, integ_time, median_diff_fullframe, median_diff_lhs, median_diff_rhs)
plt.ylim(0.5, 2.5)
_ = plt.title(filename)
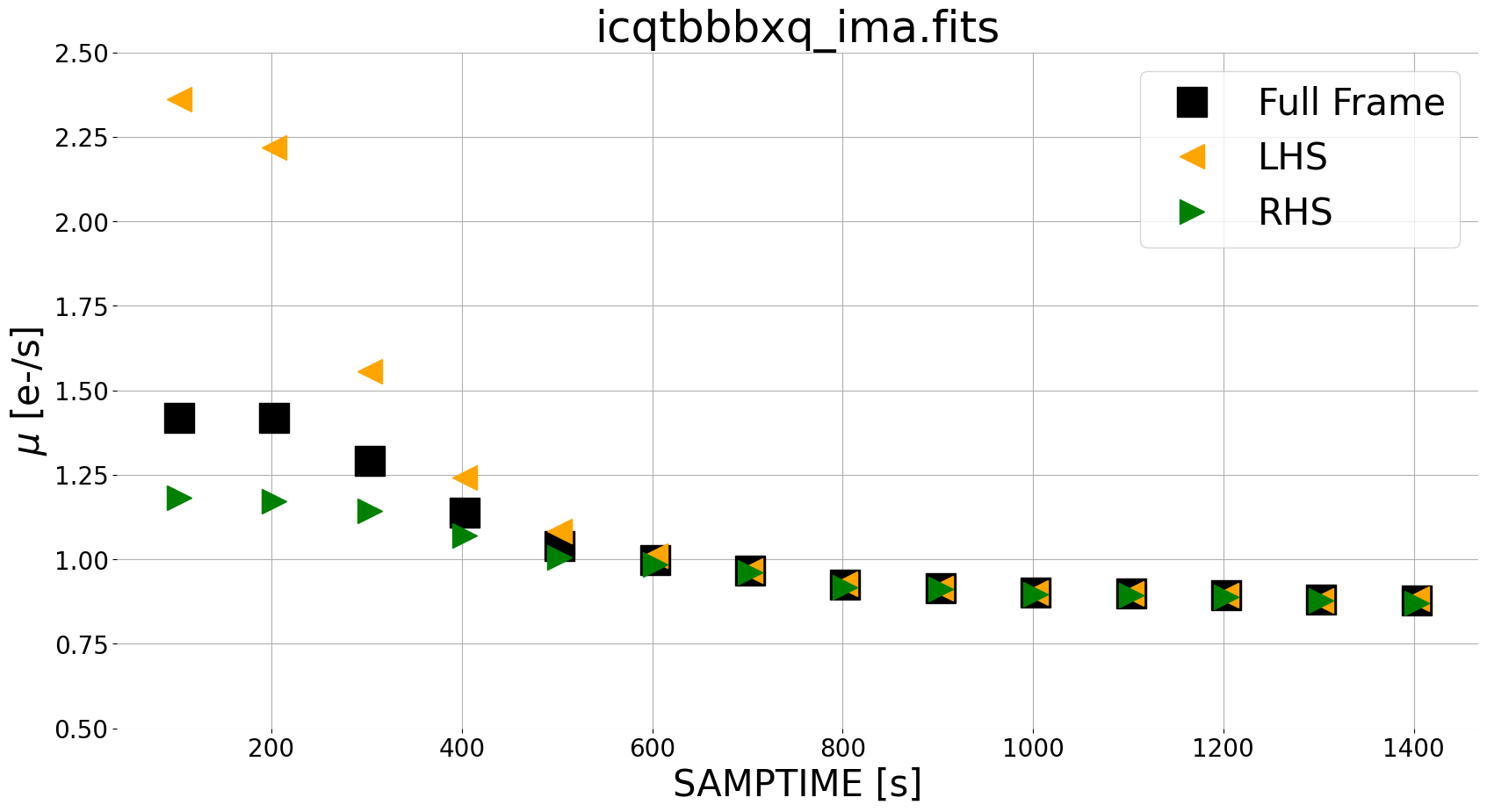
Here, we utilize a few functions from our module ima_visualization_and_differencing. We use read_wfc3 to grab the IMA data from all reads and corresponding integration times. We also implement upper and lower limits on our pixel values to exclude sources when plotting our ramp. We take the instantaneous difference using compute_diff_imas, which computes the difference as described in the equation above. Finally, we use plot_ramp to plot the median count rate from the left side, right side, and full frame image.
For our scattered light exposure, we see zodiacal light at a level of ~0.9e-/s in later reads, with the scattered light component affecting the first several reads where the median count rate for the left side (orange triangles) is larger than the right side (green triangles). We can visualize this in 2 dimensions in the panel plot below, using the plot_ima_difference_subplots.
In the panel plot, we see that sources (small galaxies) are visible in the difference images using this new method. Note that this may complicate the analysis of the spatial background (e.g. left versus right) for images with extended targets, such as large galaxies. In this case, users may wish to adjust the regions of the detector used for the ramp plots. We therefore recommend inspecting both the panel plots as well as the ramp fits for diagnosing any issues with the data.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
ima_filepath = f'orig/{file_id}_ima.fits'
lhs_region = {"x0": 50, "x1": 250, "y0": 100, "y1": 900}
rhs_region = {"x0": 700, "x1": 900, "y0": 100, "y1": 900}
diff.plot_ima_difference_subplots(ima_filepath,
difference_method='instantaneous',
lhs_region=lhs_region,
rhs_region=rhs_region)
<Figure size 2000x1000 with 0 Axes>

In this figure, we see that the ratio of instantaneous rate for the left versus right side of the image is ~1.0 for all but the first few reads (which are affected by scattered light). We choose to exclude reads with a ratio greater than 1.1 from the exposure and reprocess the image with calwf3. While this reduces the total exposure from 1403 to 1000 seconds, it removes the spatial component from the sky background and allows for a more accurate ‘up-the-ramp’ fit with calwf3.
4. Querying CRDS for the Reference File#
Before running calwf3, we need to set some environment variables.
We will point to a subdirectory called crds_cache using the IREF environment variable, which is used for WFC3 reference files. Other instruments use other variables, e.g., JREF for ACS.
os.environ['CRDS_SERVER_URL'] = 'https://hst-crds.stsci.edu'
os.environ['CRDS_SERVER'] = 'https://hst-crds.stsci.edu'
os.environ['CRDS_PATH'] = './crds_cache'
os.environ['iref'] = './crds_cache/references/hst/wfc3/'
The code block below will query CRDS for the best reference files currently available for our dataset and update the header keywords to point to these new files. We will use the Python package os to run terminal commands. In the terminal, the line would be:
…where ‘filename’ is the name of your fits file.
Warning: this cell may take a few minutes to complete.
raw_file = f'{file_id}_raw.fits'
print(f"Querying CRDS for the reference file associated with {raw_file}.")
command_line_input = 'crds bestrefs --files {:} --sync-references=1 --update-bestrefs'.format(raw_file)
os.system(command_line_input)
Querying CRDS for the reference file associated with icqtbbbxq_raw.fits.
CRDS - INFO - No comparison context or source comparison requested.
CRDS - INFO - ===> Processing icqtbbbxq_raw.fits
CRDS - INFO - 0 errors
CRDS - INFO - 0 warnings
CRDS - INFO - 2 infos
0
5. Reprocessing the Observation#
As discussed in the introduction to this notebook, the accuracy of the ramp fit performed during the CRCORR cosmic-ray rejection step of the pipeline determines the quality of the calibrated WFC3/IR FLT data products. Given that a time variable background can compromise the quality of the ramp fit, observations affected by TVB will likely result in poor-quality calibrated FLT images (see the Appendix of WFC3 ISR 2021-01).
To address poorly calibrated FLT images where some reads are affected by scattered light TVB (as in our example observation), we can remove these reads and re-run calwf3 to produce cleaner FLT images. We choose to exclude reads where the ratio of background signal is greater than 1.1 e-/s (see the notebook WFC3/IR IMA Visualization with An Example of Time Variable Background (O’Connor 2023) for a more complete demonstration of how we find this ratio).
The following reprocessing example is replacing section 7.10.1 of the WFC3 Data Handbook.
5.1 Re-running calwf3 #
Below, we select our excluded reads (in this case reads 11-15), which are at the beginning of the exposure. We set the DQ value to 1024 for these reads, prompting calwf3 to flag all pixels in these reads as bad, effectively rejecting the reads.
raw_filepath = f'{file_id}_raw.fits'
# Remove existing products or calwf3 will die
flt_filepath = raw_filepath.replace('raw', 'flt')
ima_filepath = raw_filepath.replace('raw', 'ima')
for filepath in [flt_filepath, ima_filepath]:
if os.path.exists(filepath):
os.remove(filepath)
reads = np.arange(11, 16) # numpy arange creates an array including the start value (11) but excluding the stop value (16), so the array is actually 11-15.
for read in reads:
fits.setval(raw_filepath, extver=read, extname='DQ', keyword='pixvalue', value=1024)
calwf3(raw_filepath)
git tag: 0090c701-dirty
git branch: HEAD
HEAD @: 0090c701d894003cfc690e9f8d5fde81e6939090
CALBEG*** CALWF3 -- Version 3.7.2 (Apr-15-2024) ***
Begin 02-Dec-2025 20:18:42 UTC
Input icqtbbbxq_raw.fits
loading asn
LoadAsn: Processing SINGLE exposure
Trying to open icqtbbbxq_raw.fits...
Read in Primary header from icqtbbbxq_raw.fits...
Revising existing trailer file `icqtbbbxq.tra'.
CALBEG*** WF3IR -- Version 3.7.2 (Apr-15-2024) ***
Begin 02-Dec-2025 20:18:42 UTC
Input icqtbbbxq_raw.fits
Output icqtbbbxq_flt.fits
Trying to open icqtbbbxq_raw.fits...
Read in Primary header from icqtbbbxq_raw.fits...
APERTURE IR-FIX
FILTER F140W
DETECTOR IR
Reading data from icqtbbbxq_raw.fits ...
CCDTAB iref$t2c16200i_ccd.fits
CCDTAB PEDIGREE=Ground
CCDTAB DESCRIP =Reference data based on Thermal-Vac #3, gain=2.5 results for IR-4
CCDTAB DESCRIP =Readnoise,gain,saturation from TV3,MEB2 values. ISRs 2008-25,39,50
readnoise =20.2,19.8,19.9,20.1
gain =2.34,2.37,2.31,2.38
DQICORR PERFORM
DQITAB iref$3562014hi_bpx.fits
DQITAB PEDIGREE=INFLIGHT 03/11/2015 12/09/2016
DQITAB DESCRIP =Bad Pixel Table generated using Cycle 23 Flats and Darks-----------
DQICORR COMPLETE
ZSIGCORR PERFORM
ZSIGCORR detected 1286 saturated pixels in 0th read
ZSIGCORR detected 1346 saturated pixels in 1st read
ZSIGCORR COMPLETE
BLEVCORR PERFORM
OSCNTAB iref$q911321mi_osc.fits
OSCNTAB PEDIGREE=GROUND
OSCNTAB DESCRIP =Initial values for ground test data processing
BLEVCORR COMPLETE
ZOFFCORR PERFORM
ZOFFCORR COMPLETE
NOISCORR PERFORM
Uncertainty array initialized.
NOISCORR COMPLETE
NLINCORR PERFORM
NLINFILE iref$9au15283i_lin.fits
NLINFILE PEDIGREE=INFLIGHT 29/03/2011 25/11/2012
NLINFILE DESCRIP =Non-linearity, pixel-based correction from WFC3 on-orbit frames
NLINCORR detected 1286 saturated pixels in imset 16
NLINCORR detected 1349 saturated pixels in imset 15
NLINCORR detected 1461 saturated pixels in imset 14
NLINCORR detected 1515 saturated pixels in imset 13
NLINCORR detected 1569 saturated pixels in imset 12
NLINCORR detected 1623 saturated pixels in imset 11
NLINCORR detected 1689 saturated pixels in imset 10
NLINCORR detected 1742 saturated pixels in imset 9
NLINCORR detected 1798 saturated pixels in imset 8
NLINCORR detected 1844 saturated pixels in imset 7
NLINCORR detected 1894 saturated pixels in imset 6
NLINCORR detected 1952 saturated pixels in imset 5
NLINCORR detected 2011 saturated pixels in imset 4
NLINCORR detected 2087 saturated pixels in imset 3
NLINCORR detected 2166 saturated pixels in imset 2
NLINCORR detected 2244 saturated pixels in imset 1
NLINCORR COMPLETE
DARKCORR PERFORM
DARKFILE iref$35620125i_drk.fits
DARKFILE PEDIGREE=INFLIGHT 04/09/2009 14/11/2016
DARKFILE DESCRIP =Dark Created from 142 frames spanning cycles 17 to 24--------------
DARKCORR using dark imset 16 for imset 16 with exptime= 0
DARKCORR using dark imset 15 for imset 15 with exptime= 2.93229
DARKCORR using dark imset 14 for imset 14 with exptime= 102.933
DARKCORR using dark imset 13 for imset 13 with exptime= 202.933
DARKCORR using dark imset 12 for imset 12 with exptime= 302.933
DARKCORR using dark imset 11 for imset 11 with exptime= 402.934
DARKCORR using dark imset 10 for imset 10 with exptime= 502.934
DARKCORR using dark imset 9 for imset 9 with exptime= 602.934
DARKCORR using dark imset 8 for imset 8 with exptime= 702.934
DARKCORR using dark imset 7 for imset 7 with exptime= 802.935
DARKCORR using dark imset 6 for imset 6 with exptime= 902.935
DARKCORR using dark imset 5 for imset 5 with exptime= 1002.94
DARKCORR using dark imset 4 for imset 4 with exptime= 1102.94
DARKCORR using dark imset 3 for imset 3 with exptime= 1202.94
DARKCORR using dark imset 2 for imset 2 with exptime= 1302.94
DARKCORR using dark imset 1 for imset 1 with exptime= 1402.94
DARKCORR COMPLETE
PHOTCORR PERFORM
IMPHTTAB iref$8ch15233i_imp.fits
IMPHTTAB PEDIGREE=INFLIGHT 08/05/2009 01/09/2024
IMPHTTAB DESCRIP =Time-dependent image photometry reference table (IMPHTTAB)---------
Found parameterized variable 1.
NUMPAR=1, N=1
Allocated 1 parnames
Adding parameter mjd#57339.3673 as parnames[0]
==> Value of PHOTFLAM = 1.4769486e-20
==> Value of PHOTPLAM = 13922.907
==> Value of PHOTBW = 1132.39
PHOTCORR COMPLETE
UNITCORR PERFORM
UNITCORR COMPLETE
CRCORR PERFORM
CRREJTAB iref$u6a1748ri_crr.fits
CRIDCALC using 4 sigma rejection threshold
256 bad DQ mask
4 max CRs for UNSTABLE
63 pixels detected as unstable
CRCORR COMPLETE
FLATCORR PERFORM
PFLTFILE iref$4ac19224i_pfl.fits
PFLTFILE PEDIGREE=INFLIGHT 31/07/2009 05/12/2019
PFLTFILE DESCRIP =Sky Flat from Combined In-flight observations between 2009 and 2019
DFLTFILE iref$4ac18162i_dfl.fits
DFLTFILE PEDIGREE=INFLIGHT 31/07/2009 05/12/2019
DFLTFILE DESCRIP =Delta-Flat for IR Blobs by Date of Appearance from Sky Flat Dataset
FLATCORR COMPLETE
Warning All output pixels flagged as bad.
Warning All output pixels flagged as bad.
Warning All output pixels flagged as bad.
Warning All output pixels flagged as bad.
Warning All output pixels flagged as bad.
Writing calibrated readouts to icqtbbbxq_ima.fits
Writing final image to icqtbbbxq_flt.fits
with trimx = 5,5, trimy = 5,5
End 02-Dec-2025 20:18:47 UTC
*** WF3IR complete ***
End 02-Dec-2025 20:18:47 UTC
*** CALWF3 complete ***
CALWF3 completion for icqtbbbxq_raw.fits
5.2 Comparing FLT Products #
Please move your reprocessed images to a new directory with a different name each time you run this notebook.
reprocessed_flt = f'{file_id}_flt.fits'
reprocessed_ima = f'{file_id}_ima.fits'
original_flt = f'orig/{file_id}_flt.fits'
original_ima = f'orig/{file_id}_ima.fits'
Now, we can compare our original and reprocessed FLT products.
image_new = fits.getdata(reprocessed_flt)
image_old = fits.getdata(original_flt)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 7))
fig
rows = 1
columns = 2
# add the total exptime in the title
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(rows, columns, 1)
ax1.set_title("Reprocessed FLT image", fontsize=20)
im1 = plt.imshow(image_new, vmin=0.8, vmax=1.3, origin='lower', cmap='Greys_r')
ax1.tick_params(axis='both', labelsize=10)
cbar1 = plt.colorbar(im1, ax=ax1)
cbar1.ax.tick_params(labelsize=10)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(rows, columns, 2)
ax2.set_title("Original FLT image", fontsize=20)
im2 = plt.imshow(image_old, vmin=0.8, vmax=1.3, origin='lower', cmap='Greys_r')
ax2.tick_params(axis='both', labelsize=10)
cbar2 = plt.colorbar(im2, ax=ax2)
cbar2.ax.tick_params(labelsize=10)
plt.rc('xtick', labelsize=10)
plt.rc('ytick', labelsize=10)
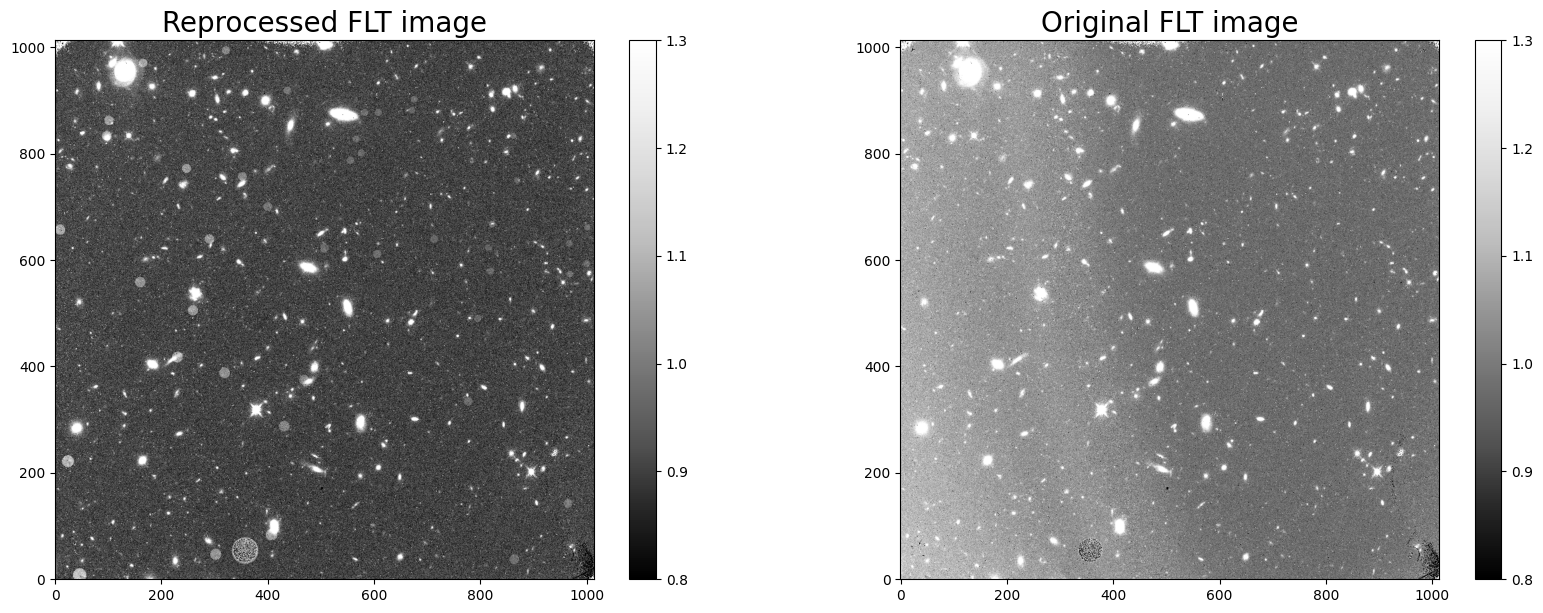
This new image was produced by calwf3 after masking the first 5 reads (not including the zero read) in the RAW file, reducing the effective exposure time from 1403 to 1000 seconds. While the total exposure is reduced from 1403 seconds to 1000 seconds (thus decreasing the overall S/N of the image), the background in the reprocessed image is now uniform over the entire field of view. We can see that the new FLT image is free of the Earth limb scattered light visible in the old FLT image.
Finally, note that the reprocessed FLT product now includes a larger sky background in science pixels corresponding to IR “blobs”, regions of reduced sensitivity due particulate matter on the channel selection mechanism (CSM) mirror (section 7.5 of the WFC3 Data Handbook).
The method for correcting WFC3/IR images described in the notebook Correcting for Scattered Light in WFC3/IR Exposures: Manually Subtracting Bad Reads (O’Connor 2023) provides FLT products without blobs, but that do include cosmic rays.
We update the FLT header keywords “EXPTIME” (in the primary header) and “SAMPTIME” (in the science header) to reflect the new total exposure time.
with fits.open(reprocessed_flt, mode='update') as image_new, fits.open(original_ima) as ima_orig:
hdr = ima_orig[0].header
NSAMP = hdr['NSAMP']
hdr1 = ima_orig[1].header
integ_time = np.zeros(shape=(NSAMP))
for i in range(1, NSAMP+1):
integ_time[i-1] = ima_orig[('TIME', i)].header['PIXVALUE']
integ_time = integ_time[::-1]
dt = np.diff(integ_time)
final_time = integ_time[-1]
if (len(reads) > 0):
for read in reads:
index = len(integ_time)-read-1 # because the reads are stored in reverse order
final_time -= dt[index]
print(f'The final exposure time after reprocessing is {final_time}.')
image_new[0].header['EXPTIME'] = final_time
The final exposure time after reprocessing is 1000.0032699999998.
6. Drizzling Nominal and Reprocessed FLT Products #
In our example we use an exposure (icqtbbbxq) from image association ICQTBB020 acquired in visit BB of program 14037. This visit consists of two orbits of two exposures each, and we now download the three other FLTs in the visit (icqtbbc0q_flt.fits, icqtbbbrq_flt.fits, icqtbbbtq_flt.fits) and the pipeline drizzled DRZ product.
To produce a clean DRZ image (without blob residuals), we can drizzle the four FLTs together (from the nominal exposures and the reprocessed exposure), replacing pixels flagged as blobs with those from the dithered (nominal) image.
data_list = Observations.query_criteria(obs_id=OBS_ID)
Observations.download_products(data_list['obsid'],
project='CALWF3',
mrp_only=False,
productSubGroupDescription=['FLT', 'DRZ'])
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbbrq/icqtbbbrq_flt.fits with expected size 16583040. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbbtq/icqtbbbtq_flt.fits with expected size 16583040. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbbxq/icqtbbbxq_flt.fits with expected size 16583040. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbc0q/icqtbbc0q_flt.fits with expected size 16583040. [astroquery.query]
INFO: Found cached file ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbb020/icqtbb020_drz.fits with expected size 13302720. [astroquery.query]
| Local Path | Status | Message | URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| str47 | str8 | object | object |
| ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbbrq/icqtbbbrq_flt.fits | COMPLETE | None | None |
| ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbbtq/icqtbbbtq_flt.fits | COMPLETE | None | None |
| ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbbxq/icqtbbbxq_flt.fits | COMPLETE | None | None |
| ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbbc0q/icqtbbc0q_flt.fits | COMPLETE | None | None |
| ./mastDownload/HST/icqtbb020/icqtbb020_drz.fits | COMPLETE | None | None |
nominal_file_ids = ["icqtbbc0q", "icqtbbbrq", "icqtbbbtq"]
# nominal_file_ids = ["icxt27hoq"]
nominal_list = []
for nominal_file_id in nominal_file_ids:
shutil.copy(f'mastDownload/HST/{nominal_file_id}/{nominal_file_id}_flt.fits', f'{nominal_file_id}_flt.fits')
nominal_list.append(f'{nominal_file_id}_flt.fits')
print(nominal_list)
['icqtbbc0q_flt.fits', 'icqtbbbrq_flt.fits', 'icqtbbbtq_flt.fits']
Next, we update the image World Coordinate System of the reprocessed image in preparation for drizzling.
updatewcs.updatewcs(reprocessed_flt, use_db=True)
AstrometryDB URL: https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/astrometryDB/availability
AstrometryDB service available...
- IDCTAB: Distortion model from row 4 for chip 1 : F140W
- IDCTAB: Distortion model from row 4 for chip 1 : F140W
Updating astrometry for icqtbbbxq
Accessing AstrometryDB service :
https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/astrometryDB/observation/read/icqtbbbxq
AstrometryDB service call succeeded
Retrieving astrometrically-updated WCS "OPUS" for observation "icqtbbbxq"
Retrieving astrometrically-updated WCS "IDC_w3m18525i" for observation "icqtbbbxq"
Retrieving astrometrically-updated WCS "OPUS-GSC240" for observation "icqtbbbxq"
Retrieving astrometrically-updated WCS "IDC_w3m18525i-GSC240" for observation "icqtbbbxq"
Retrieving astrometrically-updated WCS "OPUS-HSC30" for observation "icqtbbbxq"
Retrieving astrometrically-updated WCS "IDC_w3m18525i-HSC30" for observation "icqtbbbxq"
Updating icqtbbbxq with:
Headerlet with WCSNAME=OPUS
Headerlet with WCSNAME=IDC_w3m18525i
Headerlet with WCSNAME=IDC_w3m18525i-GSC240
Headerlet with WCSNAME=IDC_w3m18525i-HSC30
Initializing new WCSCORR table for icqtbbbxq_flt.fits
INFO:
Inconsistent SIP distortion information is present in the FITS header and the WCS object:
SIP coefficients were detected, but CTYPE is missing a "-SIP" suffix.
astropy.wcs is using the SIP distortion coefficients,
therefore the coordinates calculated here might be incorrect.
If you do not want to apply the SIP distortion coefficients,
please remove the SIP coefficients from the FITS header or the
WCS object. As an example, if the image is already distortion-corrected
(e.g., drizzled) then distortion components should not apply and the SIP
coefficients should be removed.
While the SIP distortion coefficients are being applied here, if that was indeed the intent,
for consistency please append "-SIP" to the CTYPE in the FITS header or the WCS object.
[astropy.wcs.wcs]
Replacing primary WCS with
Headerlet with WCSNAME=IDC_w3m18525i-HSC30
['icqtbbbxq_flt.fits']
Finally, we combine the four FLT images with AstroDrizzle while exluding pixels flagged as blobs and replacing those pixels with those from dithered frames.
astrodrizzle.AstroDrizzle('icqtbb*flt.fits', output='f140w',
mdriztab=True, preserve=False,
build=False, context=False,
skymethod='match', driz_separate=False,
median=False, blot=False,
driz_cr=False, final_bits='16',
clean=True)
# astrodrizzle.AstroDrizzle('icxt27*flt.fits', output='f105w', preserve=False, build=False, context=False, skymethod='match', driz_separate=False, median=False, blot=False, driz_cr=False, final_bits='16')
Setting up logfile : astrodrizzle.log
AstroDrizzle log file: astrodrizzle.log
AstroDrizzle Version 3.10.0 started at: 20:18:50.417 (02/12/2025)
==== Processing Step Initialization started at 20:18:50.419 (02/12/2025)
Reading in MDRIZTAB parameters for 4 files
- MDRIZTAB: AstroDrizzle parameters read from row 3.
WCS Keywords
Number of WCS axes: 2
CTYPE : 'RA---TAN' 'DEC--TAN'
CUNIT : 'deg' 'deg'
CRVAL : 342.32386934251866 -44.54564257214722
CRPIX : 555.5 493.5
CD1_1 CD1_2 : -4.898034677108542e-06 -3.528668216092657e-05
CD2_1 CD2_2 : -3.528668216092657e-05 4.898034677108542e-06
NAXIS : 1111 987
********************************************************************************
*
* Estimated memory usage: up to 20 Mb.
* Output image size: 1111 X 987 pixels.
* Output image file: ~ 12 Mb.
* Cores available: 1
*
********************************************************************************
==== Processing Step Initialization finished at 20:18:50.915 (02/12/2025)
==== Processing Step Static Mask started at 20:18:50.9 (02/12/2025)
==== Processing Step Static Mask finished at 20:18:50.981 (02/12/2025)
==== Processing Step Subtract Sky started at 20:18:50.98 (02/12/2025)
***** skymatch started on 2025-12-02 20:18:51.026609
Version 1.0.11
'skymatch' task will apply computed sky differences to input image file(s).
NOTE: Computed sky values WILL NOT be subtracted from image data ('subtractsky'=False).
'MDRIZSKY' header keyword will represent sky value *computed* from data.
----- User specified keywords: -----
Sky Value Keyword: 'MDRIZSKY'
Data Units Keyword: 'BUNIT'
----- Input file list: -----
** Input image: 'icqtbbbrq_flt.fits'
EXT: 'SCI',1; MASK: icqtbbbrq_skymatch_mask_sci1.fits[0]
** Input image: 'icqtbbbtq_flt.fits'
EXT: 'SCI',1; MASK: icqtbbbtq_skymatch_mask_sci1.fits[0]
** Input image: 'icqtbbbxq_flt.fits'
EXT: 'SCI',1; MASK: icqtbbbxq_skymatch_mask_sci1.fits[0]
** Input image: 'icqtbbc0q_flt.fits'
EXT: 'SCI',1; MASK: icqtbbc0q_skymatch_mask_sci1.fits[0]
----- Sky statistics parameters: -----
statistics function: 'mode'
lower = -100.0
upper = None
nclip = 5
lsigma = 4.0
usigma = 4.0
binwidth = 0.10000000149011612
----- Data->Brightness conversion parameters for input files: -----
* Image: icqtbbbrq_flt.fits
EXT = 'SCI',1
Data units type: COUNT-RATE
Conversion factor (data->brightness): 60.797431635711504
* Image: icqtbbbtq_flt.fits
EXT = 'SCI',1
Data units type: COUNT-RATE
Conversion factor (data->brightness): 60.797431635711504
* Image: icqtbbbxq_flt.fits
EXT = 'SCI',1
Data units type: COUNT-RATE
Conversion factor (data->brightness): 60.797431635711504
* Image: icqtbbc0q_flt.fits
EXT = 'SCI',1
Data units type: COUNT-RATE
Conversion factor (data->brightness): 60.797431635711504
----- Computing differences in sky values in overlapping regions: -----
* Image 'icqtbbbrq_flt.fits['SCI',1]' SKY = 2.02561 [brightness units]
Updating sky of image extension(s) [data units]:
- EXT = 'SCI',1 delta(MDRIZSKY) = 0.0333174
* Image 'icqtbbbtq_flt.fits['SCI',1]' SKY = 0 [brightness units]
Updating sky of image extension(s) [data units]:
- EXT = 'SCI',1 delta(MDRIZSKY) = 0
* Image 'icqtbbbxq_flt.fits['SCI',1]' SKY = None (undetermined)
Sky of image extension(s) [data units]:
- EXT = 'SCI',1 delta(MDRIZSKY) = None NEW MDRIZSKY = OLD MDRIZSKY = 0
* Image 'icqtbbc0q_flt.fits['SCI',1]' SKY = 0.563181 [brightness units]
Updating sky of image extension(s) [data units]:
- EXT = 'SCI',1 delta(MDRIZSKY) = 0.00926324
***** skymatch ended on 2025-12-02 20:18:51.764358
TOTAL RUN TIME: 0:00:00.737749
==== Processing Step Subtract Sky finished at 20:18:51.812 (02/12/2025)
==== Processing Step Separate Drizzle started at 20:18:51.813 (02/12/2025)
==== Processing Step Separate Drizzle finished at 20:18:51.814 (02/12/2025)
==== Processing Step Create Median started at 20:18:51.815 (02/12/2025)
==== Processing Step Blot started at 20:18:51.816 (02/12/2025)
==== Processing Step Blot finished at 20:18:51.817 (02/12/2025)
==== Processing Step Driz_CR started at 20:18:51.81 (02/12/2025)
==== Processing Step Final Drizzle started at 20:18:51.81 (02/12/2025)
WCS Keywords
Number of WCS axes: 2
CTYPE : 'RA---TAN' 'DEC--TAN'
CUNIT : 'deg' 'deg'
CRVAL : 342.32386934251866 -44.54564257214722
CRPIX : 555.5 493.5
CD1_1 CD1_2 : -4.898034677108542e-06 -3.528668216092657e-05
CD2_1 CD2_2 : -3.528668216092657e-05 4.898034677108542e-06
NAXIS : 1111 987
-Generating simple FITS output: f140w_drz_sci.fits
Writing out image to disk: f140w_drz_sci.fits
Writing out image to disk: f140w_drz_wht.fits
==== Processing Step Final Drizzle finished at 20:18:53.126 (02/12/2025)
AstroDrizzle Version 3.10.0 is finished processing at 20:18:53.127 (02/12/2025).
-------------------- --------------------
Step Elapsed time
-------------------- --------------------
Initialization 0.4960 sec.
Static Mask 0.0643 sec.
Subtract Sky 0.8301 sec.
Separate Drizzle 0.0014 sec.
Create Median 0.0000 sec.
Blot 0.0012 sec.
Driz_CR 0.0000 sec.
Final Drizzle 1.3065 sec.
==================== ====================
Total 2.6995 sec.
Trailer file written to: astrodrizzle.log
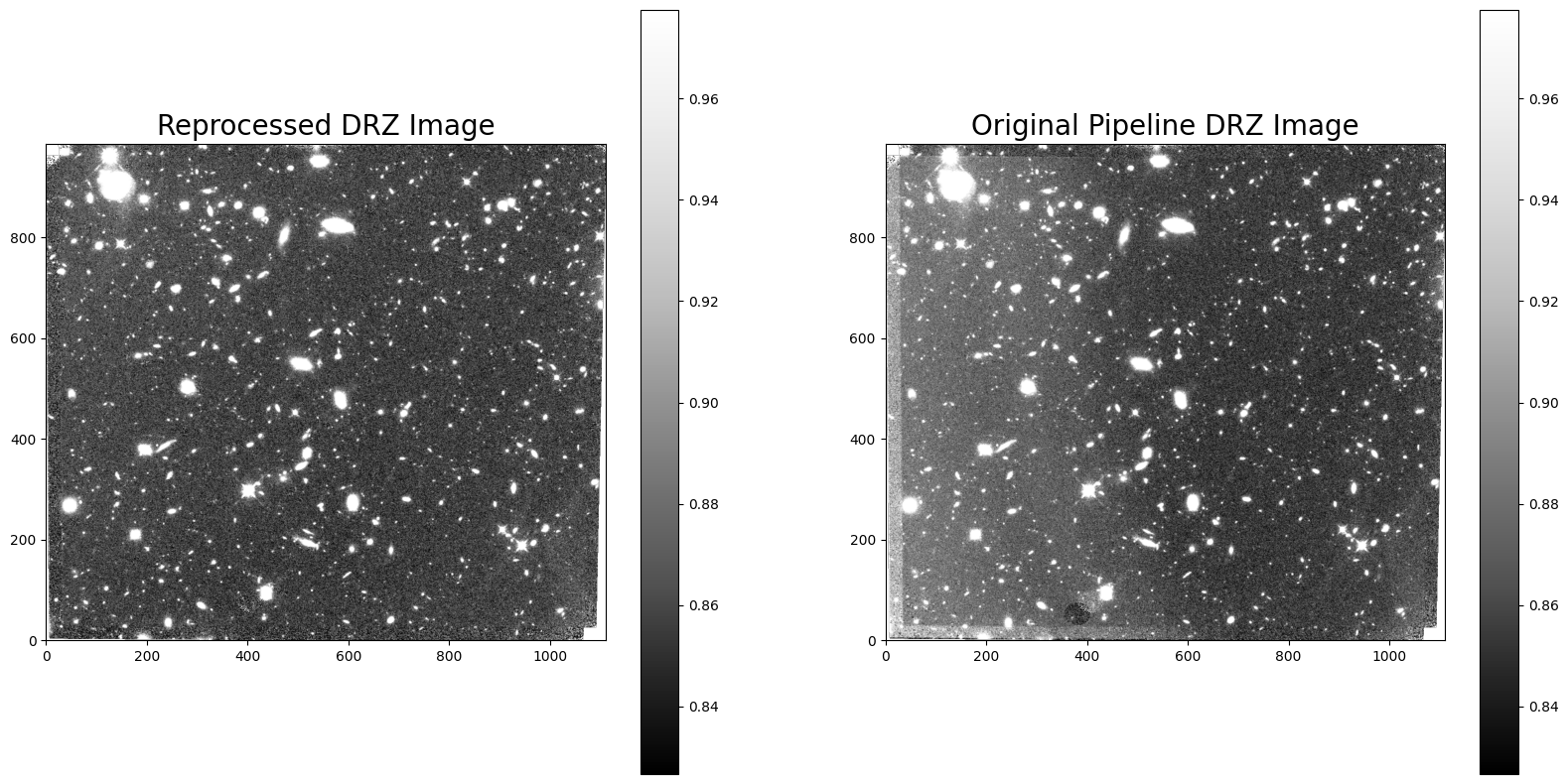
Comparing the new DRZ image made with the reprocessed FLT product against the original pipeline DRZ image, we see that the new DRZ image no longer includes scattered light but has a slightly lower S/N due the reduced total exposure time from 1403 to 1000 seconds.
with fits.open("f140w_drz_sci.fits") as DRZ_image, fits.open('mastDownload/HST/icqtbb020/icqtbb020_drz.fits') as Orig_DRZ:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
rows = 1
columns = 2
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(rows, columns, 1)
ax1.set_title("Reprocessed DRZ Image", fontsize=20)
vmin, vmax = zscale(Orig_DRZ[1].data)
im1 = plt.imshow(DRZ_image[0].data, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax, origin='lower', cmap='Greys_r')
_ = plt.colorbar()
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(rows, columns, 2)
ax2.set_title("Original Pipeline DRZ Image", fontsize=20)
im2 = plt.imshow(Orig_DRZ[1].data, vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax, origin='lower', cmap='Greys_r')
_ = plt.colorbar()
7. Conclusions #
Congratulations, you have completed the notebook.
You should now be familiar with how to reprocess an observation affected by Earth limb scattered light by removing the first few reads and rerunning calwf3.
Thank you for following along!
Additional Resources #
Below are some additional resources that may be helpful. Please send any questions through the HST Help Desk.
About this Notebook #
Author: Anne O’Connor, Jennifer Mack, Annalisa Calamida, Harish Khandrika – WFC3 Instrument
Updated On: 2023-12-26
Citations #
If you use the following tools for published research, please cite the authors. Follow these links for more information about citing the tools:
If you use this notebook, or information from the WFC3 Data Handbook, Instrument Handbook, or WFC3 ISRs for published research, please cite them:
Citing this notebook: Please cite the primary author and year, and hyperlink the notebook or HST/WFC3 Notebooks


